J Korean Diabetes.
2021 Mar;22(1):38-45. 10.4093/jkd.2021.22.1.38.
Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526178
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2021.22.1.38
Abstract
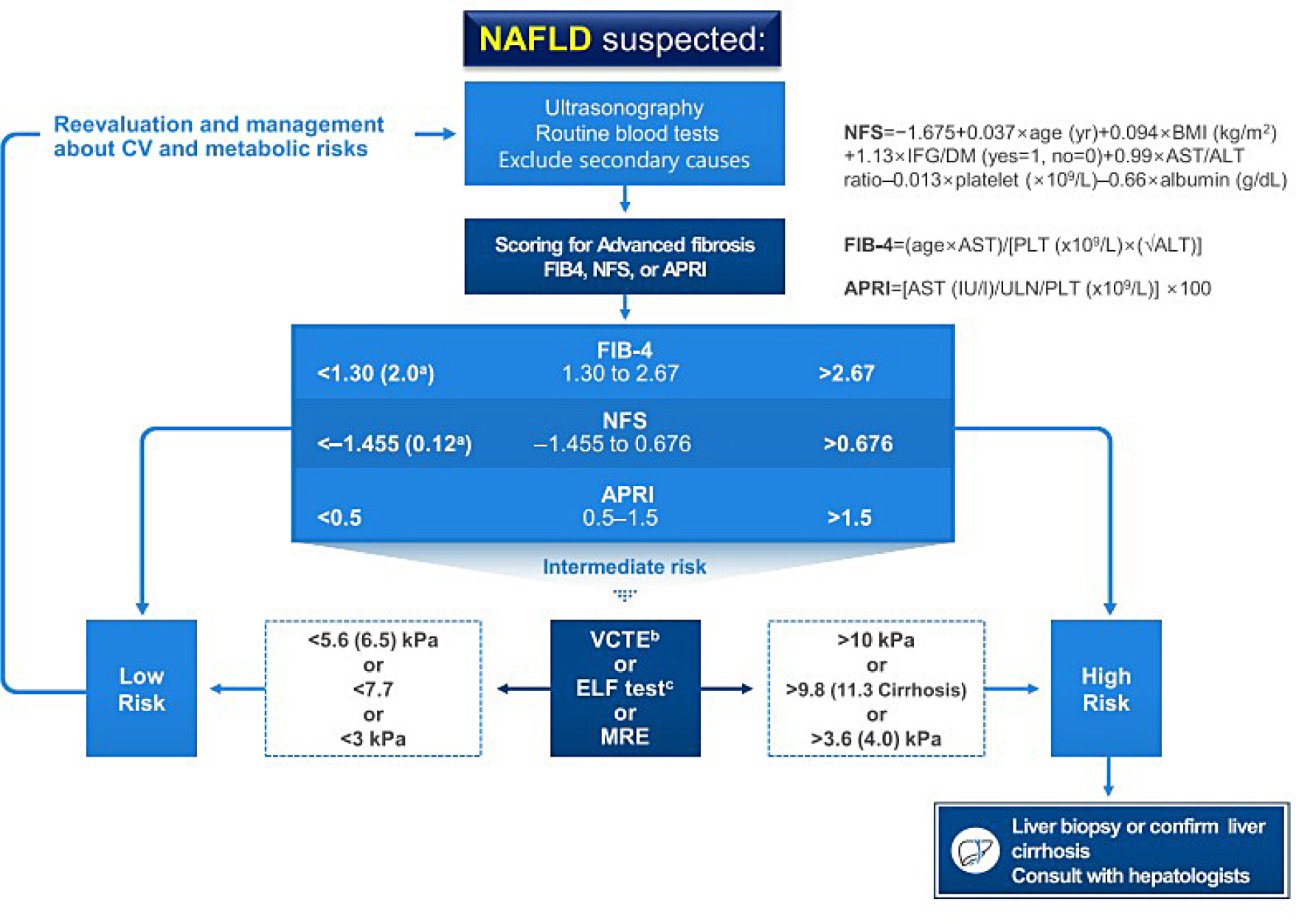
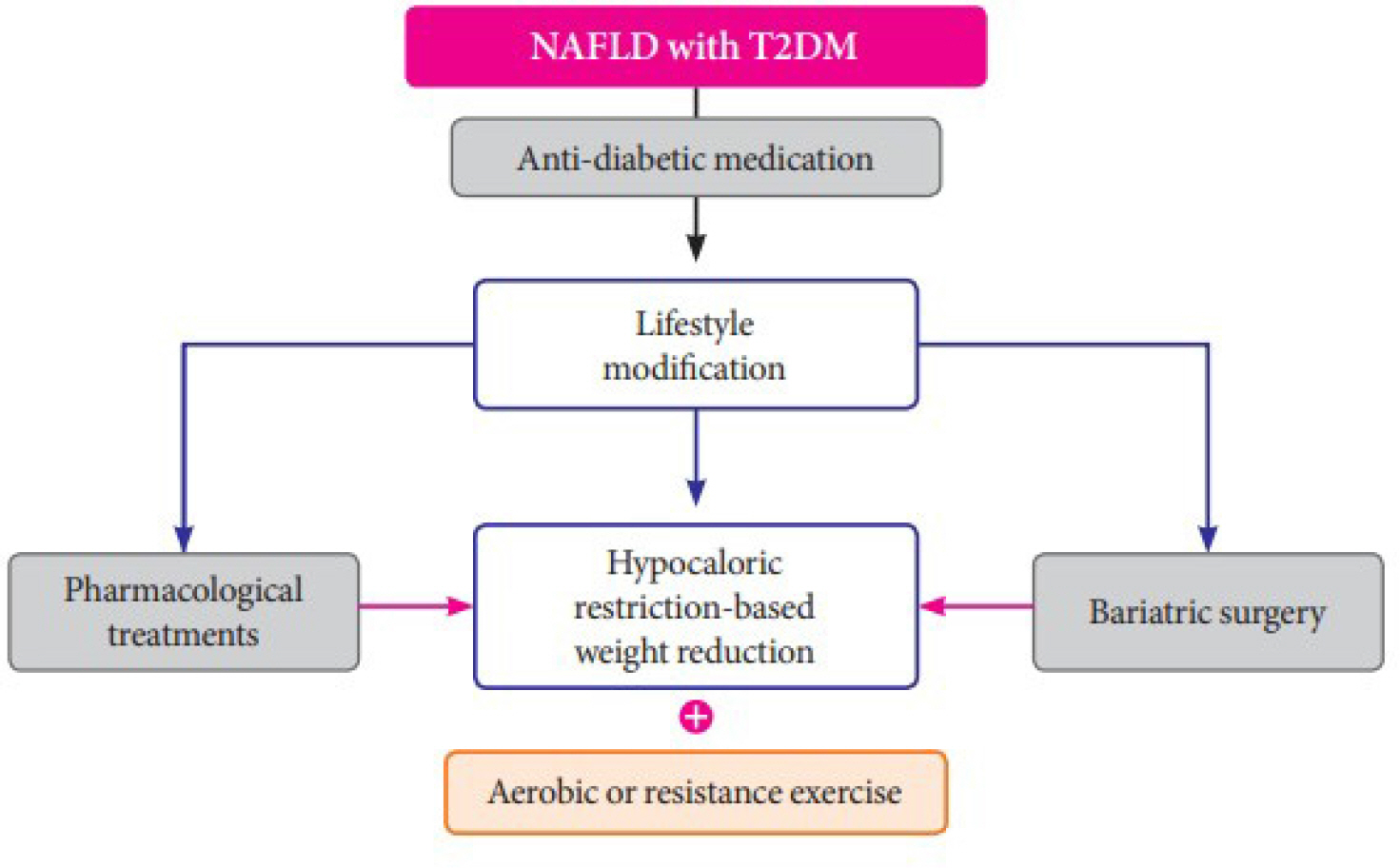
- Stroke is one of the major complications of diabetes and increases morbidity and mortality. Hyperglycemia confers increased risk of stroke occurrence. Furthermore, cardiometabolic risk factors such as hypertension and dyslipidemia frequently coexist in patients with diabetes and increase the risk of stroke. Some recent cardiovascular outcome trials of newer anti-diabetic medications have shown beneficial effects on cardiovascular complications. Prevention and improving outcomes of stroke in patients with diabetes requires proper management of hyperglycemia and additional risk factors. This review is an evidence-based approach to the epidemiology, glycemic control, effects of anti-diabetic medications on stoke, and risk factor management for prevention and improving outcomes of stroke for patients with diabetes.The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome, is rapidly increasing in Korean populations and is estimated to reach 39% among Korean adults. NAFLD is one of the strongest risk factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and the presence of NAFLD in T2DM patients is associated with a worse natural course of diabetic complications. The gold standard for diagnosing NAFLD is liver biopsy, which involves sampling error, high cost, and other disadvantages related to its invasive nature. We summarize non-invasive diagnostic NAFLD algorithms including biomarkers and four major imaging tools (ultrasonography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and liver FibroScanⓇ) for diagnosing NAFLD including hepatic fibrosis. To prevent NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) or liver fibrosis, a combination of lifestyle modification with a low caloric diet and exercise, anti-diabetic agents, and non-anti-diabetic agents should be applied.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee BW., Lee Y., Park CY., Rhee EJ., Lee WY., Kim NH, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. 44:382–401.2. Lee Y., Cho Y., Lee BW., Park CY., Lee DH., Cha BS, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetes. Part I: epidemiology and diagnosis. Diabetes Metab J. 2019. 43:31–45.3. Rhee EJ. Clinical characteristics of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study. J Korean Diabetes. 2017. 18:81–7.4. Song YM., Lee Y., Kim JW., Ham DS., Kang ES., Cha BS, et al. Metformin alleviates hepatosteatosis by restoring SIRT1-mediated autophagy induction via an AMP-activated protein kinase-independent pathway. Autophagy. 2015. 11:46–59.5. Lee Y. Diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on clinical and laboratory data. J Korean Diabetes. 2017. 18:102–8.6. Kim KJ., Kim SU., Chung YE., Kim CO. Radiologic evaluation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetic patient. J Korean Diabetes. 2017. 18:88–101.7. Lee BW. Management of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with lifestyle modification. J Korean Diabetes. 2018. 19:82–7.8. Yang H., Park CY. Glucose-lowering agents in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Korean Diabetes. 2018. 19:88–96.9. Cusi K., Orsak B., Bril F., Lomonaco R., Hecht J., Ortiz-Lopez C, et al. Long-term pioglitazone treatment for patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2016. 165:305–15.10. Kim KS., Lee BW. Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. 26:430–43.11. Kim KS., Lee BW., Kim YJ., Lee DH., Cha BS., Park CY. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes: part II: treatment. Diabetes Metab J. 2019. 43:127–43.12. Kim SU. Pharmacologic treatment using non-hypoglycemic agents for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Korean Diabetes. 2018. 19:97–100.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is a Stepping Stone in the Path toward Diabetes Mellitus
- Tamoxifen-Induced Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Cirrhosis
- The Effects of Hypoglycemic Agents on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Focused on Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
- Diagnosis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Clinical and Laboratory Data