J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Feb;37(6):e42. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e42.
Deep Learning Analysis to Automatically Detect the Presence of Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Business Administration, School of Business, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan, Korea
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Information and Communication Engineering, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan, Korea
- 4Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- KMID: 2526031
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e42
Abstract
- Background
Videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) is currently considered the gold standard to precisely diagnose and quantitatively investigate dysphagia. However, VFSS interpretation is complex and requires consideration of several factors. Therefore, considering the expected impact on dysphagia management, this study aimed to apply deep learning to detect the presence of penetration or aspiration in VFSS of patients with dysphagia automatically.
Methods
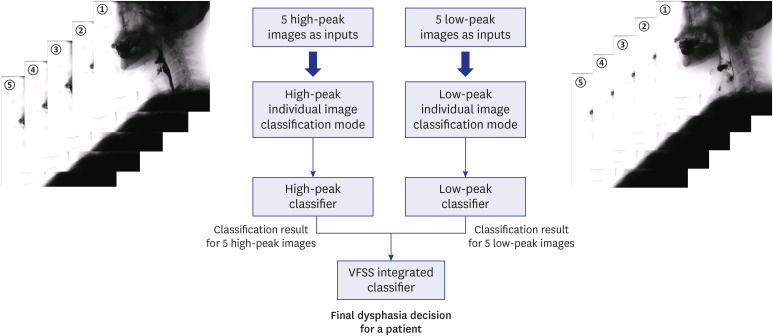
The VFSS data of 190 participants with dysphagia were collected. A total of 10 frame images from one swallowing process were selected (five high-peak images and five low-peak images) for the application of deep learning in a VFSS video of a patient with dysphagia. We applied a convolutional neural network (CNN) for deep learning using the Python programming language. For the classification of VFSS findings (normal swallowing, penetration, and aspiration), the classification was determined in both high-peak and lowpeak images. Thereafter, the two classifications determined through high-peak and low-peak images were integrated into a final classification.
Results
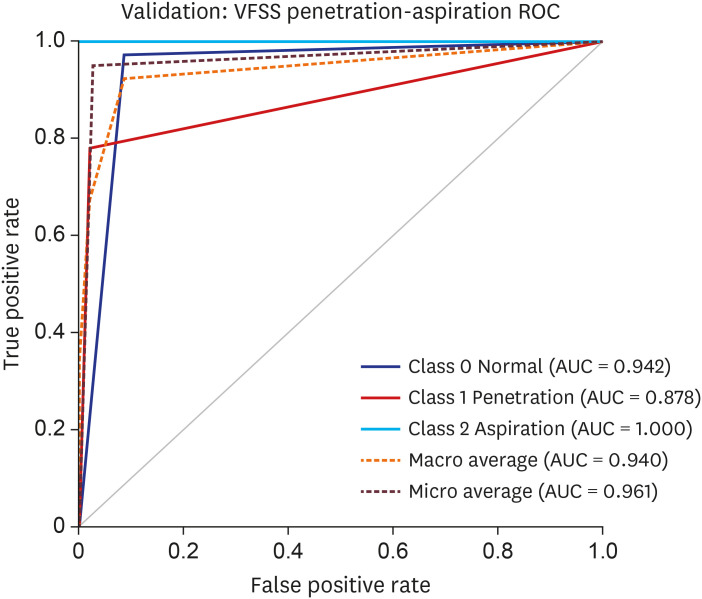
The area under the curve (AUC) for the validation dataset of the VFSS image for the CNN model was 0.942 for normal findings, 0.878 for penetration, and 1.000 for aspiration. The macro average AUC was 0.940 and micro average AUC was 0.961.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that deep learning algorithms, particularly the CNN, could be applied for detecting the presence of penetration and aspiration in VFSS of patients with dysphagia.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Retrospective Clinical Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence Screening Method for Early Detection of STEMI in the Emergency Department
Dongsung Kim, Ji Eun Hwang, Youngjin Cho, Hyoung-Won Cho, Wonjae Lee, Ji Hyun Lee, Il-Young Oh, Sumin Baek, Eunkyoung Lee, Joonghee Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(10):e81. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e81.
Reference
-
1. Steele CM, Miller AJ. Sensory input pathways and mechanisms in swallowing: a review. Dysphagia. 2010; 25(4):323–333. PMID: 20814803.2. Ertekin C. Electrophysiological evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson's disease. J Mov Disord. 2014; 7(2):31–56. PMID: 25360228.3. Park S, Cho JY, Lee BJ, Hwang JM, Lee M, Hwang SY, et al. Effect of the submandibular push exercise using visual feedback from pressure sensor: an electromyography study. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):11772. PMID: 32678239.4. Shaker R, Geenen JE. Management of dysphagia in stroke patients. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7(5):308–332. PMID: 21857832.5. Finestone HM, Greene-Finestone LS. Rehabilitation medicine: 2. Diagnosis of dysphagia and its nutritional management for stroke patients. CMAJ. 2003; 169(10):1041–1044. PMID: 14609974.6. Yeom J, Song YS, Lee WK, Oh BM, Han TR, Seo HG. Diagnosis and clinical course of unexplained dysphagia. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016; 40(1):95–101. PMID: 26949675.7. Chang MC, Park JS, Lee BJ, Park D. Effectiveness of pharmacologic treatment for dysphagia in Parkinson's disease: a narrative review. Neurol Sci. 2021; 42(2):513–519. PMID: 33201362.8. Yu KJ, Park D. Clinical characteristics of dysphagic stroke patients with salivary aspiration: a STROBE-compliant retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(12):e14977. PMID: 30896670.9. Lee JT, Park E, Hwang JM, Jung TD, Park D. Machine learning analysis to automatically measure response time of pharyngeal swallowing reflex in videofluoroscopic swallowing study. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):14735. PMID: 32895465.10. Lee JT, Park E, Jung TD. Automatic detection of the pharyngeal phase in raw videos for the videofluoroscopic swallowing study using efficient data collection and 3D convolutional networks † . Sensors (Basel). 2019; 19(18):3873.11. Park D, Lee HH, Lee ST, Oh Y, Lee JC, Nam KW, et al. Normal contractile algorithm of swallowing related muscles revealed by needle EMG and its comparison to videofluoroscopic swallowing study and high resolution manometry studies: a preliminary study. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2017; 36:81–89. PMID: 28763682.12. Park D, Oh Y, Ryu JS. Findings of abnormal videofluoroscopic swallowing study identified by high-resolution manometry parameters. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016; 97(3):421–428. PMID: 26505655.13. Park D, Shin CM, Ryu JS. Effect of different viscosities on pharyngeal pressure during swallowing: a study using high-resolution manometry. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017; 98(3):487–494. PMID: 27523910.14. Lundervold AS, Lundervold A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z Med Phys. 2019; 29(2):102–127. PMID: 30553609.15. Ahmed Z, Mohamed K, Zeeshan S, Dong X. Artificial intelligence with multi-functional machine learning platform development for better healthcare and precision medicine. Database (Oxford). 2020; 2020:baaa010. PMID: 32185396.16. Martin-Harris B, Jones B.. The videofluorographic swallowing study. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2008; 19(4):769–785. PMID: 18940640.17. Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Lazarus C, Boeckxstaens G, Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA. Relationship between manometric and videofluoroscopic measures of swallow function in healthy adults and patients treated for head and neck cancer with various modalities. Dysphagia. 2009; 24(2):196–203. PMID: 18956228.18. Uhm KE, Yi SH, Chang HJ, Cheon HJ, Kwon JY. Videofluoroscopic swallowing study findings in full-term and preterm infants with Dysphagia. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37(2):175–182. PMID: 23705111.19. Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RK, Togashi K. Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging. 2018; 9(4):611–629. PMID: 29934920.20. Tan M, Le QV. EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. Proc Mach Learn Res. 2019; 97:6105–6114.21. Howard AG, Zhu M, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W, Weyand T, et al. Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv. April 17, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861.22. Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In : Proceedings of the 2016 IEEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, NV, USA. Piscataway, NJ, USA: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers;2016. p. 2818–2826.23. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In : Proceedings of the 2016 IEEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, NV, USA. Piscataway, NJ, USA: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers;2016. p. 770–778.24. DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988; 44(3):837–845. PMID: 3203132.25. Mandrekar JN. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5(9):1315–1316. PMID: 20736804.26. Zhang Z, Coyle JL, Sejdić E. Automatic hyoid bone detection in fluoroscopic images using deep learning. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):12310. PMID: 30120314.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between the Type of Laryngeal Penetration and Severity of Tracheal Aspiration in the Brain Injured
- Acoustic Voice Analysis in Patients with Penetration/Aspiration Via Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study
- The Relation Between the Presence of Aspiration or Penetration and the Clinical Indicators of Dysphagia in Poststroke Survivors
- The Functional Dysphagia Scale Using Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study in Stroke Patients
- Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study in Elderly Patients Admitted to a Geriatric Hospital and a Long-Term Care Facility