Korean J Gastroenterol.
2022 Jan;79(1):22-30. 10.4166/kjg.2021.147.
Comparison of Clinical Performance and Safety between Domestic New Pull-type Triple-lumen Sphincterotome and Conventional Sphincterotome: A Prospective Multicenter Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea
- 2Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525519
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.147
Abstract
- Background/Aims
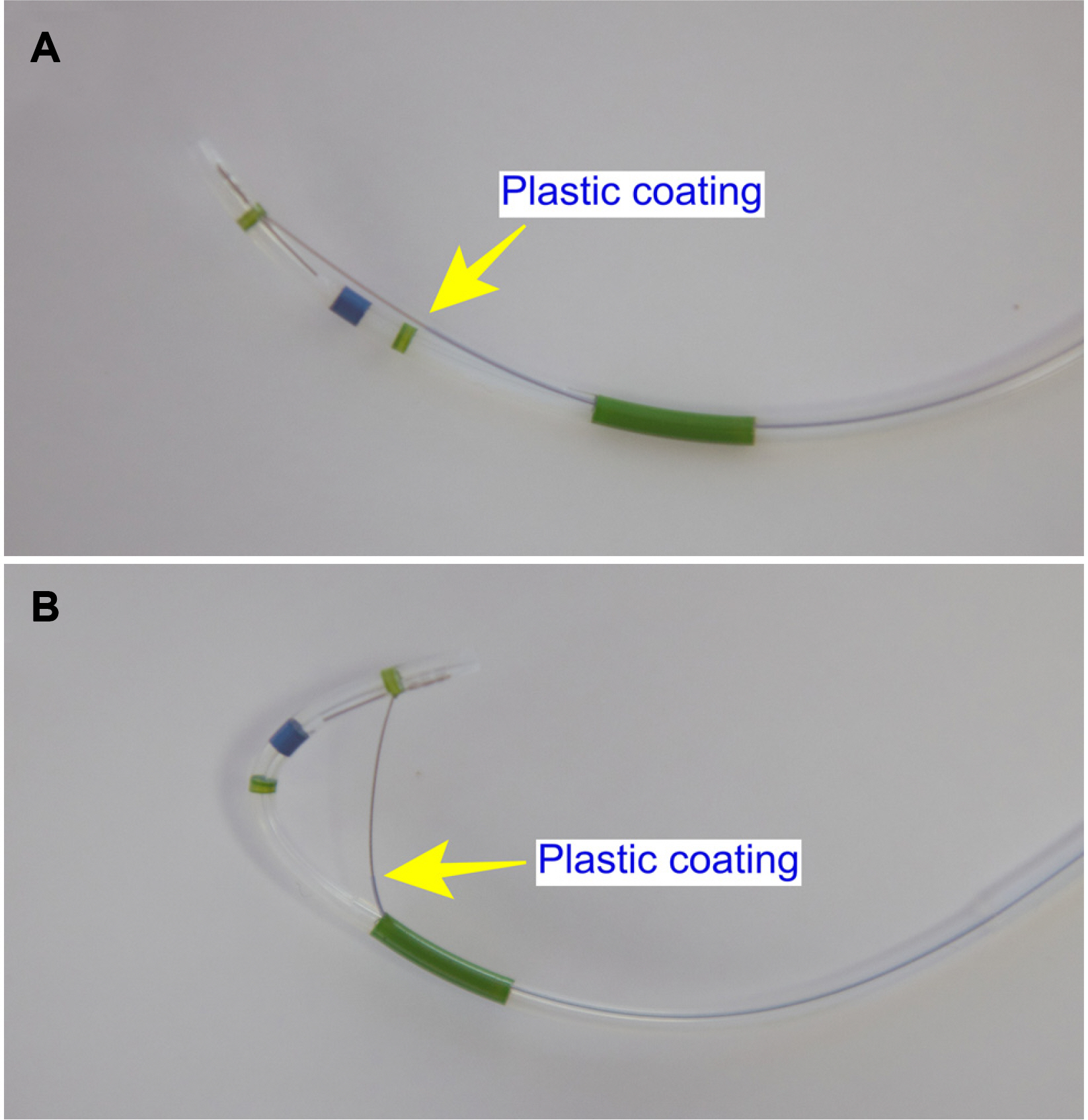
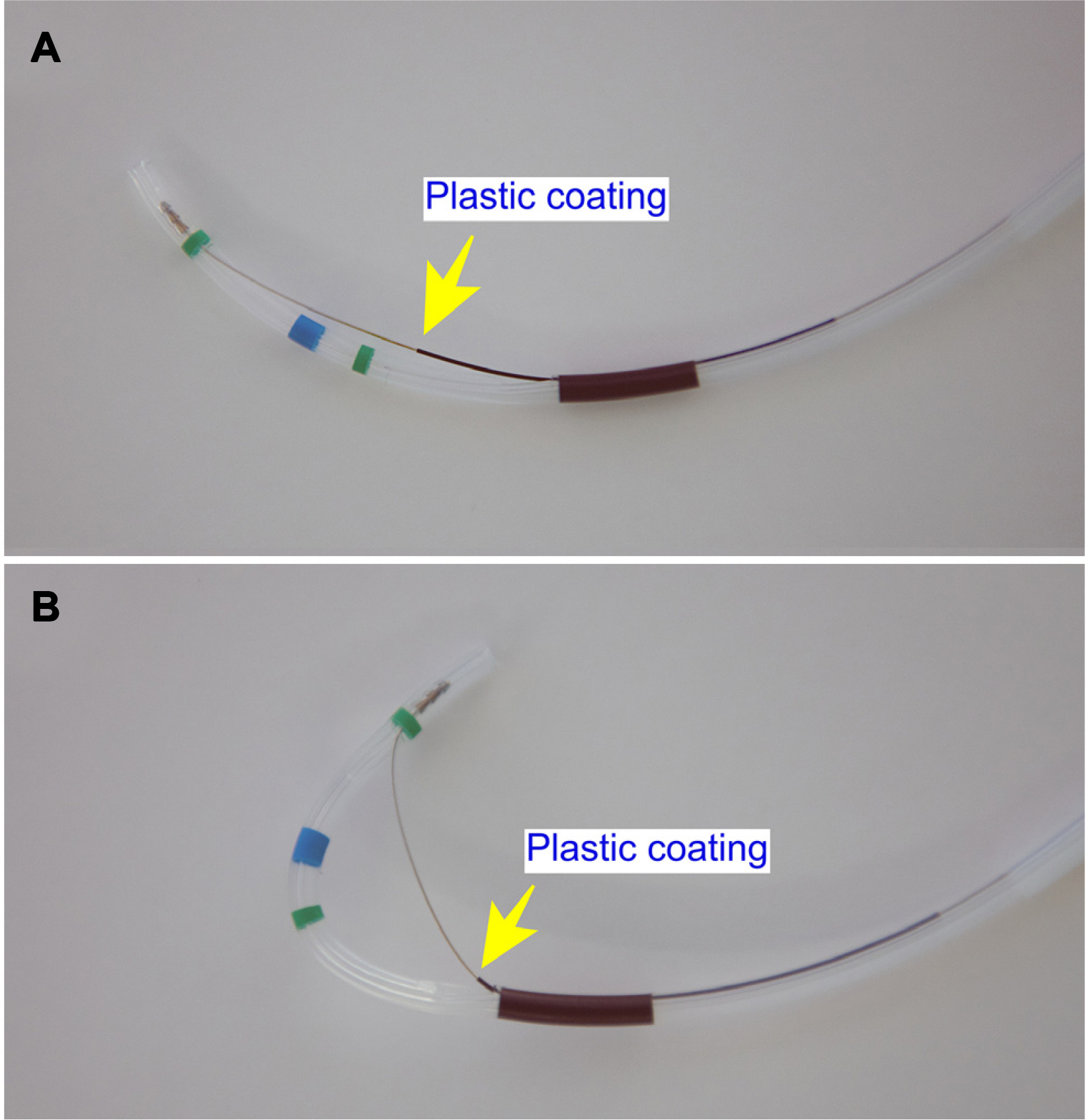
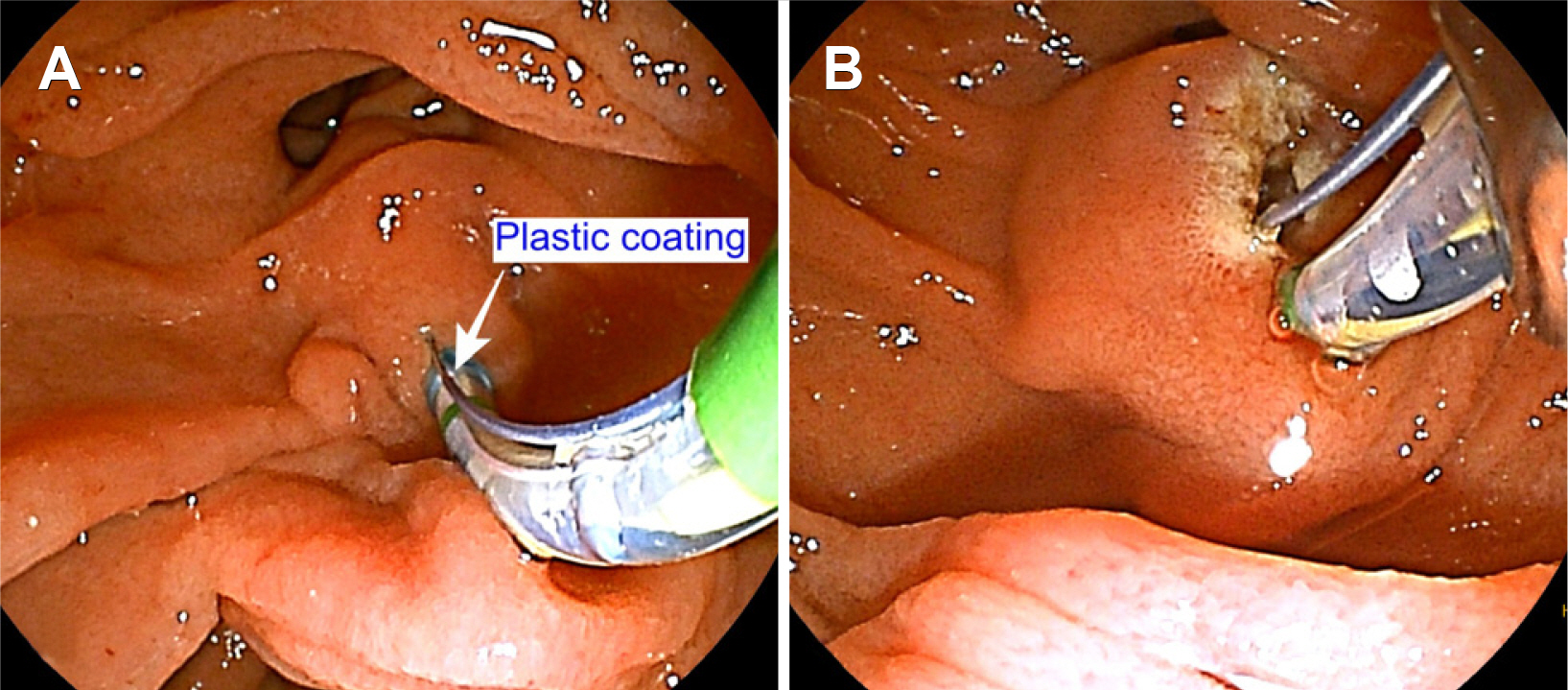
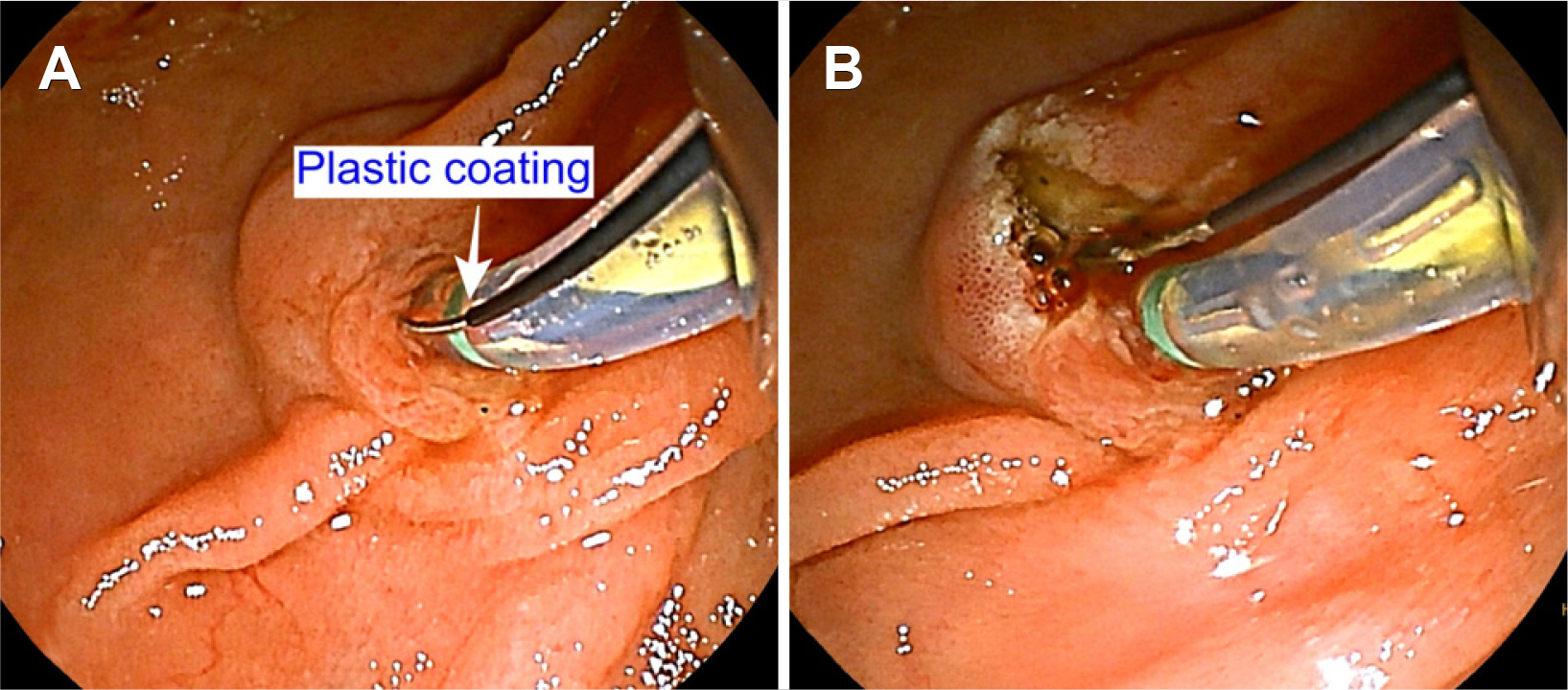
Sphincterotomes are essential for endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) and can also be used for cannulation in ERCP. A domestic new pull-type sphincterotome (Optimos™, Taewoong, Goyang, Korea) provides acceptable technical feasibility and safety, but there are no comparison results. Thus, this study compared the clinical performance and safety of Optimos™ sphincterotome to a conventional sphincterotome (CleverCut3™, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) in patients who underwent ERCP.
Methods
From April 2021 to July 2021, a randomized prospective comparative study was conducted on 104 consecutive patients who underwent ERCP in three medical centers. The primary endpoint was the clinical performance and safety of sphincterotomes during ERCP.
Results
One hundred and four patients were assigned randomly to the Optimos™ group (n=51) or CleverCut3™ group (n=53). All demographic characteristics did not differ between the groups except the BMI. The technical success rate for cannulation, performance of EST, and total procedure time were similar in the two groups. The adverse events did not differ, even though two cases of post-ERCP pancreatitis occurred in CleverCut3™. On the other hand, in questionnaire analysis, CleverCut™ showed a better user’s convenience (median [interquartile range] 4.0 [3.0-4.0] vs. 3.0 [3.0-4.0], p=0.013) and manipulability (median [interquartile range], 4.0 [3.0-4.0] vs. 3.0 [3.0-4.0], p=0.039) than Optimos™, even though the other profiles did not reveal any differences.
Conclusions
New domestic pull-type sphincterotome can offer comparable clinical performance and safety profiles to conventional sphincterotome, but it needs refinements to increase the user’s convenience and manipulability. Further improvement and innovation will be required to advance domestic medical devices.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development and Utilization of Sphincterotome for Successful Biliary Cannulation and Safe Endoscopic Sphincterotomy
Huapyong Kang
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022;79(1):1-3. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.002.
Reference
-
1. Cotton PB. 2012; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: maximizing benefits and minimizing risks. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 22:587–599. DOI: 10.1016/j.giec.2012.05.002. PMID: 22748250.2. Statements and guidelines developed by the Standards of Training and Practice Committee of the ASGE. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988; 34 Suppl 3:1S–40S. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.09.007. PMID: 31791596.3. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Chandrasekhara V, Khashab MA, et al. Adverse events associated with ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:32–47. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.06.051. PMID: 27546389.
Article4. Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, et al. 2007; Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol. 102:1781–1788. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01279.x. PMID: 17509029.
Article5. Herreros de Tejada A, Calleja JL, Díaz G, et al. 2009; Double-guidewire technique for difficult bile duct cannulation: a multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 70:700–709. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.03.031. PMID: 19560764.
Article6. Park CH, Park SW, Yang MJ, et al. Pre- and post-procedure risk prediction models for post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. Surg Endosc. 2021; [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-021-08491-1. PMID: 34231067.
Article7. Park CH, Jung JH, Nam E, et al. 2018; Comparative efficacy of various endoscopic techniques for the treatment of common bile duct stones: a network meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 87:43–57.e10. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.07.038. PMID: 28756105.
Article8. Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, et al. 1991; Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc. 37:383–393. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(91)70740-2. PMID: 2070995.
Article9. Kawai K, Akasaka Y, Murakami K, Tada M, Koli Y. 1974; Endoscopic sphincterotomy of the ampulla of Vater. Gastrointest Endosc. 20:148–151. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(74)73914-1. PMID: 4825160.
Article10. Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, et al. 1996; Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med. 335:909–918. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199609263351301. PMID: 8782497.
Article11. Loperfido S, Angelini G, Benedetti G, et al. 1998; Major early complications from diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: a prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 48:1–10. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(98)70121-X. PMID: 9684657.
Article12. Syrén E, Eriksson S, Enochsson L, Eklund A, Sandblom G. 2019; Risk factors for pancreatitis following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. BJS Open. 3:485–489. DOI: 10.1002/bjs5.50162. PMID: 31406957. PMCID: PMC6681151.
Article13. Masci E, Mariani A, Curioni S, Testoni PA. 2003; Risk factors for pancreatitis following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 35:830–834. DOI: 10.1055/s-2003-42614. PMID: 14551860.
Article14. Chen JJ, Wang XM, Liu XQ, et al. 2014; Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: a systematic review of clinical trials with a large sample size in the past 10 years. Eur J Med Res. 19:26. DOI: 10.1186/2047-783X-19-26. PMID: 24886445. PMCID: PMC4035895.
Article15. Kethu SR, Adler DG, et al. ASGE Technology Committee. 2010; ERCP cannulation and sphincterotomy devices. Gastrointest Endosc. 71:435–445. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.07.038. PMID: 20189502.
Article16. Tse F, Yuan Y, Moayyedi P, Leontiadis GI. 2013; Guide wire-assisted cannulation for the prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 45:605–618. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1326640. PMID: 23807804.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rotatable sphincterotome as a rescue device for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography cannulation: a single-center experience
- Selective Biliary Cannulation for a Papilla in the 9 o'clock Position Using Pull and Rotatable Sphincterotome
- Development and Utilization of Sphincterotome for Successful Biliary Cannulation and Safe Endoscopic Sphincterotomy
- Sphincterotomy - Induced Hemorrhage: Prevalence, Risk Factors and Endoscopic Hemostasis
- Burdick's Technique for Biliary Access Revisited