Korean Circ J.
2022 Feb;52(2):150-161. 10.4070/kcj.2021.0240.
Ischemic Burden Assessment Using Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography in Single Vessel Chronic Total Occlusion of Coronary Artery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Sejong, Korea
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Eunpyeong St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Cardiology, Daejeon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 5Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525455
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2021.0240
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
Studies evaluating the nature of ischemic burden of chronic total occlusion (CTO) vessels are still lacking.
Methods
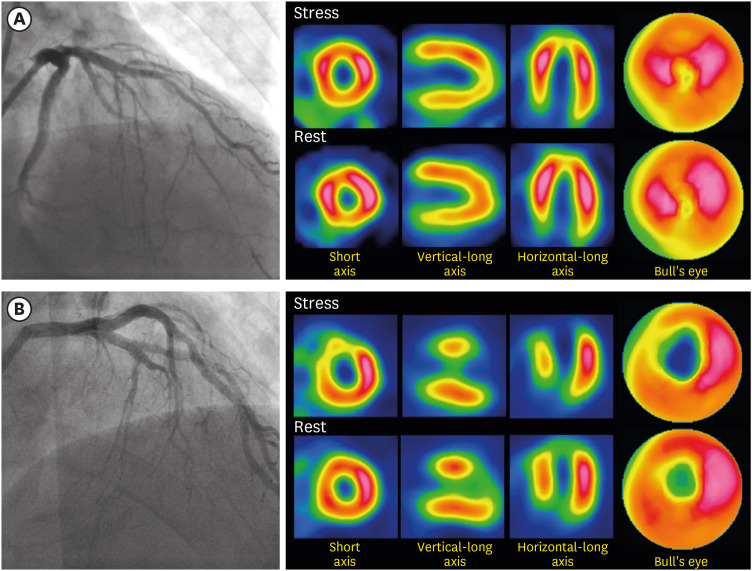
A total of 165 patients with single vessel CTO >2.5 mm in an epicardial coronary artery who underwent single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) were enrolled in the study. Ischemic burden was calculated with the use of semi-quantitative SPECT analysis, and was defined as the summed difference score (SDS) divided by the maximal limit of the score (=SDS/68).
Results
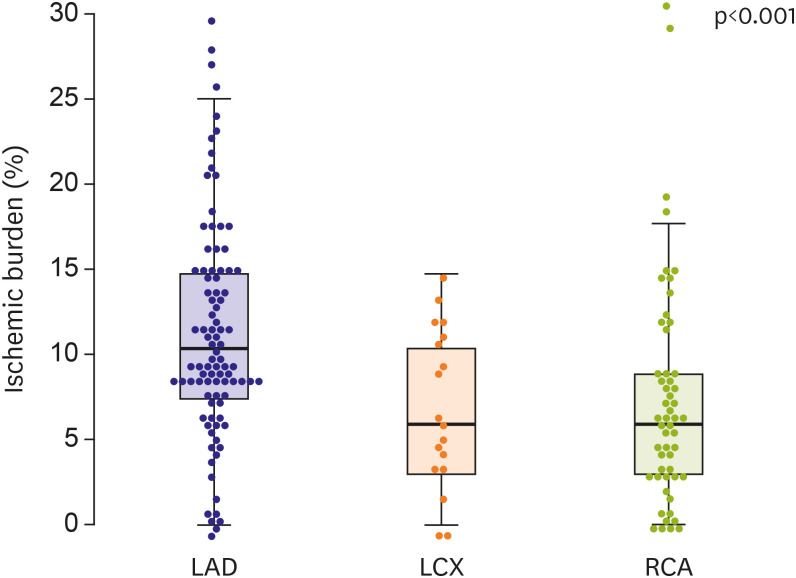
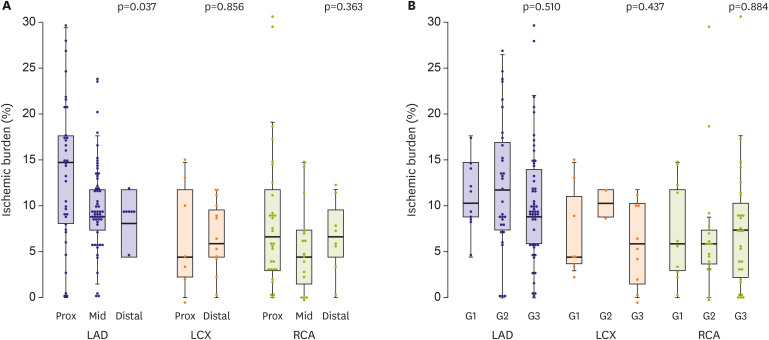
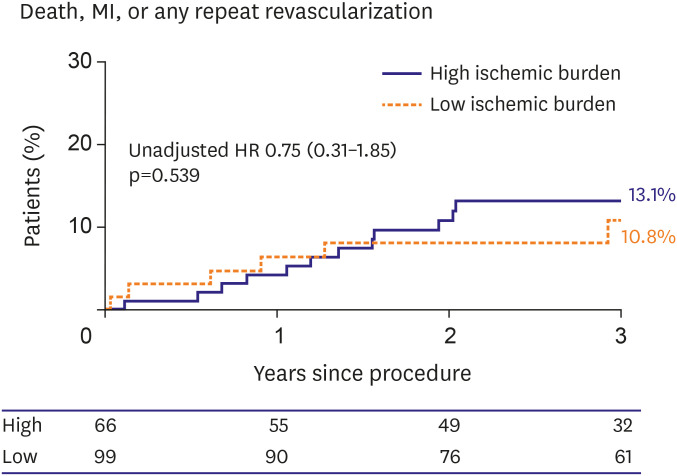
The mean age of the participants was 59.5 years and the CTO of the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD), left circumplex coronary artery (LCX), and right coronary artery (RCA) accounted for 93 (56.4%), 18 (10.9%), and 54 (32.7%) patients, respectively. The median ischemic burden of the total population was 8.8%, and it was highest in the LAD CTO (10.3%) compared with the LCX (5.9%) and RCA CTO (5.9%, p<0.001). High-ischemic burden (ischemic burden >10%) was observed in 66 patients (40.0%), and in 47 patients (50.5%) of the LAD CTO. Ischemic burden was different according to the CTO location only in LAD CTO. The statistically significant predictors for high-ischemic burden were hypertension, baseline ejection fraction >45%, LAD CTO, proximal CTO location, and de novo CTO. Japanese-CTO score and Rentrop scale collateral grade were not associated with high-ischemic burden.
Conclusions
Only 40% of patients with single vessel CTO had ischemic burden >10%. For CTO vessels, measurement of ischemic burden using SPECT prior to revascularization may be helpful in identifying beneficial subjects.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Before Coronary CTO PCI: Burden or Location?
Woong Gil Choi
Korean Circ J. 2022;52(2):162-165. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2021.0393.
Reference
-
1. Lee PH, Lee SW, Park HS, et al. Successful recanalization of native coronary chronic total occlusion is not associated with improved long-term survival. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016; 9:530–538. PMID: 26947387.
Article2. Christakopoulos GE, Christopoulos G, Carlino M, et al. Meta-analysis of clinical outcomes of patients who underwent percutaneous coronary interventions for chronic total occlusions. Am J Cardiol. 2015; 115:1367–1375. PMID: 25784515.
Article3. George S, Cockburn J, Clayton TC, et al. Long-term follow-up of elective chronic total coronary occlusion angioplasty: analysis from the U.K. Central Cardiac Audit Database. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 64:235–243. PMID: 25034057.
Article4. Patel VG, Brayton KM, Tamayo A, et al. Angiographic success and procedural complications in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary chronic total occlusion interventions: a weighted meta-analysis of 18,061 patients from 65 studies. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013; 6:128–136. PMID: 23352817.
Article5. Michael TT, Karmpaliotis D, Brilakis ES, et al. Procedural outcomes of revascularization of chronic total occlusion of native coronary arteries (from a multicenter United States registry). Am J Cardiol. 2013; 112:488–492. PMID: 23672987.
Article6. Lee SW, Lee PH, Ahn JM, et al. Randomized trial evaluating percutaneous coronary intervention for the treatment of chronic total occlusion. Circulation. 2019; 139:1674–1683. PMID: 30813758.
Article7. Werner GS, Martin-Yuste V, Hildick-Smith D, et al. A randomized multicentre trial to compare revascularization with optimal medical therapy for the treatment of chronic total coronary occlusions. Eur Heart J. 2018; 39:2484–2493. PMID: 29722796.
Article8. Henriques JP, Hoebers LP, Råmunddal T, et al. Percutaneous intervention for concurrent chronic total occlusions in patients with STEMI: the EXPLORE trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 68:1622–1632. PMID: 27712774.9. Hachamovitch R, Hayes SW, Friedman JD, Cohen I, Berman DS. A prognostic score for prediction of cardiac mortality risk after adenosine stress myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:722–729. PMID: 15734617.
Article10. Hachamovitch R, Rozanski A, Hayes SW, et al. Predicting therapeutic benefit from myocardial revascularization procedures: are measurements of both resting left ventricular ejection fraction and stress-induced myocardial ischemia necessary? J Nucl Cardiol. 2006; 13:768–778. PMID: 17174808.
Article11. Hachamovitch R, Rozanski A, Shaw LJ, et al. Impact of ischaemia and scar on the therapeutic benefit derived from myocardial revascularization vs. medical therapy among patients undergoing stress-rest myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Eur Heart J. 2011; 32:1012–1024. PMID: 21258084.
Article12. Shaw LJ, Berman DS, Maron DJ, et al. Optimal medical therapy with or without percutaneous coronary intervention to reduce ischemic burden: results from the Clinical Outcomes Utilizing Revascularization and Aggressive Drug Evaluation (COURAGE) trial nuclear substudy. Circulation. 2008; 117:1283–1291. PMID: 18268144.13. Task Force Members. Montalescot G, Sechtem U, et al. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: the Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2013; 34:2949–3003. PMID: 23996286.
Article14. Sianos G, Morel MA, Kappetein AP, et al. The SYNTAX Score: an angiographic tool grading the complexity of coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention. 2005; 1:219–227. PMID: 19758907.15. Morino Y, Abe M, Morimoto T, et al. Predicting successful guidewire crossing through chronic total occlusion of native coronary lesions within 30 minutes: the J-CTO (Multicenter CTO Registry in Japan) score as a difficulty grading and time assessment tool. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011; 4:213–221. PMID: 21349461.
Article16. Werner GS, Ferrari M, Betge S, Gastmann O, Richartz BM, Figulla HR. Collateral function in chronic total coronary occlusions is related to regional myocardial function and duration of occlusion. Circulation. 2001; 104:2784–2790. PMID: 11733395.
Article17. Kim YH, Ahn JM, Park DW, et al. Impact of ischemia-guided revascularization with myocardial perfusion imaging for patients with multivessel coronary disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 60:181–190. PMID: 22789882.
Article18. Berman DS, Abidov A, Kang X, et al. Prognostic validation of a 17-segment score derived from a 20-segment score for myocardial perfusion SPECT interpretation. J Nucl Cardiol. 2004; 11:414–423. PMID: 15295410.
Article19. Dorbala S, Ananthasubramaniam K, Armstrong IS, et al. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) myocardial perfusion imaging guidelines: instrumentation, acquisition, processing, and interpretation. J Nucl Cardiol. 2018; 25:1784–1846. PMID: 29802599.
Article20. Hachamovitch R, Hayes SW, Friedman JD, Cohen I, Berman DS. Stress myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography is clinically effective and cost effective in risk stratification of patients with a high likelihood of coronary artery disease (CAD) but no known CAD. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 43:200–208. PMID: 14736438.
Article21. Hachamovitch R, Hayes SW, Friedman JD, Cohen I, Berman DS. Comparison of the short-term survival benefit associated with revascularization compared with medical therapy in patients with no prior coronary artery disease undergoing stress myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography. Circulation. 2003; 107:2900–2907. PMID: 12771008.
Article22. Brilakis ES, Grantham JA, Rinfret S, et al. A percutaneous treatment algorithm for crossing coronary chronic total occlusions. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2012; 5:367–379. PMID: 22516392.
Article23. Harding SA, Wu EB, Lo S, et al. A new algorithm for crossing chronic total occlusions from the Asia Pacific Chronic Total Occlusion Club. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017; 10:2135–2143. PMID: 29122129.
Article24. Bagnall A, Spyridopoulos I. The evidence base for revascularisation of chronic total occlusions. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2014; 10:88–98. PMID: 24694105.
Article25. Safley DM, Koshy S, Grantham JA, et al. Changes in myocardial ischemic burden following percutaneous coronary intervention of chronic total occlusions. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011; 78:337–343. PMID: 21413136.
Article26. Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Auger D, Di Mario C, et al. CMR guidance for recanalization of coronary chronic total occlusion. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016; 9:547–556. PMID: 27085432.27. Meier P, Gloekler S, Zbinden R, et al. Beneficial effect of recruitable collaterals: a 10-year follow-up study in patients with stable coronary artery disease undergoing quantitative collateral measurements. Circulation. 2007; 116:975–983. PMID: 17679611.28. Werner GS, Fritzenwanger M, Prochnau D, et al. Determinants of coronary steal in chronic total coronary occlusions donor artery, collateral, and microvascular resistance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:51–58. PMID: 16814648.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of ischemic myocardium with simultaneous dobutamine stress echocardiography and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT in patients with suspected coronary artery disease
- Comparison of Silent Patients with Painful Patients in Patients with Coronary Artery Stenoses during Exercise Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy
- A Single Coronary Artery: Right Coronary Artery Originating From the Distal Left Circumflex Artery
- Redo-Coronary Artery Bypass due to Progression of the Celiac Axis Stenosis
- Clinical Application of Cardiac Hybrid Imaging in Coronary Artery Disease