J Stroke.
2022 Jan;24(1):108-117. 10.5853/jos.2021.02061.
Deep Learning Approach Using Diffusion-Weighted Imaging to Estimate the Severity of Aphasia in Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Nunaps Inc., Seoul, Korea
- 3Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2021.02061
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the applicability of deep learning (DL) model using diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) data to predict the severity of aphasia at an early stage in acute stroke patients.
Methods
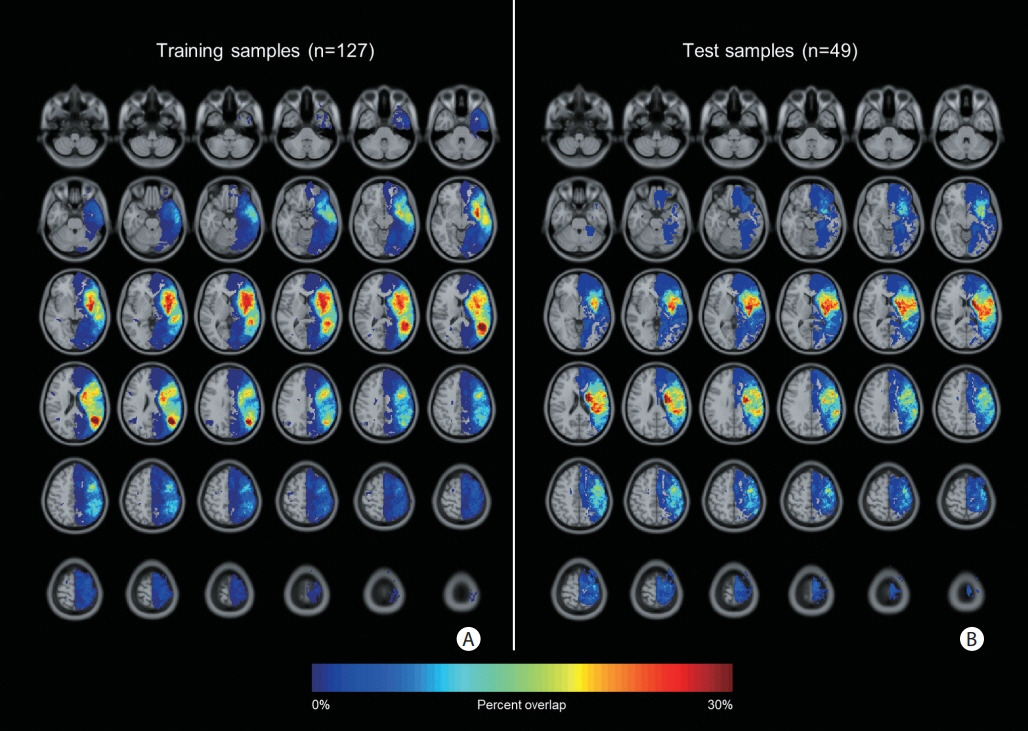
We retrospectively analyzed consecutive patients with aphasia caused by acute ischemic stroke in the left middle cerebral artery territory, who visited Asan Medical Center between 2011 and 2013. To implement the DL model to predict the severity of post-stroke aphasia, we designed a deep feed-forward network and utilized the lesion occupying ratio from DWI data and established clinical variables to estimate the aphasia quotient (AQ) score (range, 0 to 100) of the Korean version of the Western Aphasia Battery. To evaluate the performance of the DL model, we analyzed Cohen’s weighted kappa with linear weights for the categorized AQ score (0–25, very severe; 26–50, severe; 51–75, moderate; ≥76, mild) and Pearson’s correlation coefficient for continuous values.
Results
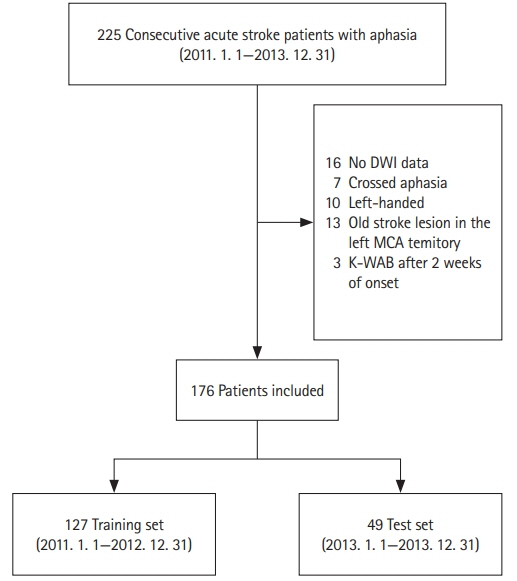
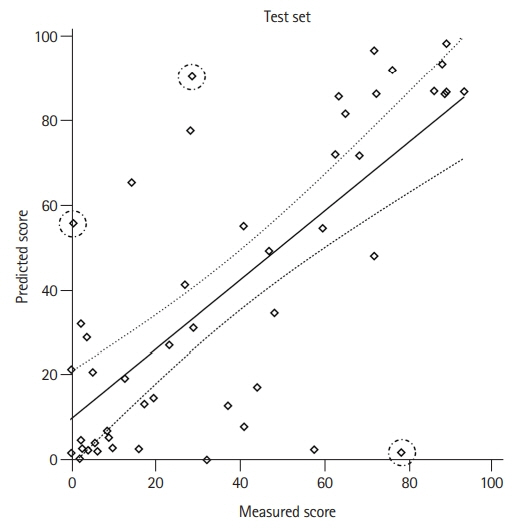
We identified 225 post-stroke aphasia patients, of whom 176 were included and analyzed. For the categorized AQ score, Cohen’s weighted kappa coefficient was 0.59 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.42 to 0.76; P<0.001). For continuous AQ score, the correlation coefficient between true AQ scores and model-estimated values was 0.72 (95% CI, 0.55 to 0.83; P<0.001).
Conclusions
DL approaches using DWI data may be feasible and useful for estimating the severity of aphasia in the early stage of stroke.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019; 139:e56–e528.2. Ellis C, Dismuke C, Edwards KK. Longitudinal trends in aphasia in the United States. NeuroRehabilitation. 2010; 27:327–333.
Article3. Ellis C, Simpson AN, Bonilha H, Mauldin PD, Simpson KN. The one-year attributable cost of poststroke aphasia. Stroke. 2012; 43:1429–1431.
Article4. Charidimou A, Kasselimis D, Varkanitsa M, Selai C, Potagas C, Evdokimidis I. Why is it difficult to predict language impairment and outcome in patients with aphasia after stroke? J Clin Neurol. 2014; 10:75–83.
Article5. Pedersen PM, Jørgensen HS, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS. Aphasia in acute stroke: incidence, determinants, and recovery. Ann Neurol. 1995; 38:659–666.
Article6. Nouwens F, de Jong-Hagelstein M, De Lau LM, Dippel DW, Koudstaal PJ, van de Sandt-Koenderman WM, et al. Severity of aphasia and recovery after treatment in patients with stroke. Aphasiology. 2014; 28:1168–1177.
Article7. El Hachioui H, Lingsma HF, van de Sandt-Koenderman MW, Dippel DW, Koudstaal PJ, Visch-Brink EG. Long-term prognosis of aphasia after stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013; 84:310–315.
Article8. Nouwens F, Visch-Brink EG, El Hachioui H, Lingsma HF, van de Sandt-Koenderman MW, Dippel DWJ, et al. Validation of a prediction model for long-term outcome of aphasia after stroke. BMC Neurol. 2018; 18:170.
Article9. Payabvash S, Kamalian S, Fung S, Wang Y, Passanese J, Kamalian S, et al. Predicting language improvement in acute stroke patients presenting with aphasia: a multivariate logistic model using location-weighted atlas-based analysis of admission CT perfusion scans. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:1661–1668.
Article10. Lee EJ, Kim YH, Kim N, Kang DW. Deep into the brain: artificial intelligence in stroke imaging. J Stroke. 2017; 19:277–285.11. Lee H, Lee EJ, Ham S, Lee HB, Lee JS, Kwon SU, et al. Machine learning approach to identify stroke within 4.5 hours. Stroke. 2020; 51:860–866.
Article12. Kassner A, Thornhill RE. Texture analysis: a review of neurologic MR imaging applications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:809–816.
Article13. Wernick MN, Yang Y, Brankov JG, Yourganov G, Strother SC. Machine learning in medical imaging. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2010; 27:25–38.
Article14. Kim H, Na DL. Normative data on the Korean version of the Western Aphasia Battery. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2004; 26:1011–1020.
Article15. Brott T, Adams HP Jr, Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, et al. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke. 1989; 20:864–870.
Article16. Forsting M, Janen O. MR Neuroimaging: Brain, Spine, Peripheral Nerves. New York, NY: Thieme;2017.17. Kim BJ, Kim YH, Kim N, Kwon SU, Kim SJ, Kim JS, et al. Lesion location-based prediction of visual field improvement after cerebral infarction. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0143882.
Article18. Plowman E, Hentz B, Ellis C Jr. Post-stroke aphasia prognosis: a review of patient-related and stroke-related factors. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012; 18:689–694.
Article19. Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J Mach Learn Res. 2014; 15:1929–1958.20. Raita Y, Goto T, Faridi MK, Brown DF, Camargo CA Jr, Hasegawa K. Emergency department triage prediction of clinical outcomes using machine learning models. Crit Care. 2019; 23:64.
Article21. Chung MK. Statistical and Computational Methods in Brain Image Analysis. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press;2013.22. Martinez-Martin P, Radicati FG, Rodriguez Blazquez C, Wetmore J, Kovacs N, Ray Chaudhuri K, et al. Extensive validation study of the Parkinson’s disease composite scale. Eur J Neurol. 2019; 26:1281–1288.23. Kertesz A. Western Aphasia Battery-Revised (WAB-R): Examiner’s Manual. San Antonio, TX: PsychCorp;2006.24. Andersen R. Modern Methods for Robust Regression. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications;2007.25. Watila MM, Balarabe SA. Factors predicting post-stroke aphasia recovery. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 352:12–18.26. Laska AC, Hellblom A, Murray V, Kahan T, Von Arbin M. Aphasia in acute stroke and relation to outcome. J Intern Med. 2001; 249:413–422.
Article27. Lazar RM, Minzer B, Antoniello D, Festa JR, Krakauer JW, Marshall RS. Improvement in aphasia scores after stroke is well predicted by initial severity. Stroke. 2010; 41:1485–1488.
Article28. Glize B, Villain M, Richert L, Vellay M, de Gabory I, Mazaux JM, et al. Language features in the acute phase of poststroke severe aphasia could predict the outcome. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017; 53:249–255.
Article29. Blom-Smink MR, van de Sandt-Koenderman MW, Lingsma HF, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Ribbers GM. Predicting everyday verbal communicative ability after inpatient stroke rehabilitation in patients with moderate and severe aphasia at admission: validation of a prognostic model. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019; 55:532–534.
Article30. Godecke E, Rai T, Ciccone N, Armstrong E, Granger A, Hankey GJ. Amount of therapy matters in very early aphasia rehabilitation after stroke: a clinical prognostic model. Semin Speech Lang. 2013; 34:129–141.
Article31. Liu X, Gao K, Liu B, Pan C, Liang K, Yan L, et al. Advances in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Health Data Sci. 2021; 2021:8786793.
Article32. Das JM, Saadabadi A. Abulia. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing;2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537093. Assessed December 1, 2021.33. Siegel JS, Snyder AZ, Metcalf NV, Fucetola RP, Hacker CD, Shimony JS, et al. The circuitry of abulia: insights from functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage Clin. 2014; 6:320–326.
Article34. Labeyrie MA, Turc G, Hess A, Hervo P, Mas JL, Meder JF, et al. Diffusion lesion reversal after thrombolysis: a MR correlate of early neurological improvement. Stroke. 2012; 43:2986–2991.35. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, NV. IEEE; 2016;770-778. https://www.computer.org/csdl/proceedings-article/cvpr/2016/8851a770/12OmNxvwoXv. Assessed December 1, 2021.36. Srivastava RK, Greff K, Schmidhuber J. Highway networks. arXiv 2015 Nov 3. https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.00387.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Applications and Future Perspectives of Brain Tumor Imaging
- Global Aphasia without Hemiparesis: Lesion Analysis and its Mechanism in 12 Patients
- Prolonged Ictal Aphasia Presenting as Clinical-Diffusion Mismatch in a Patient with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Characteristics of Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Post-stroke Aphasia
- Analysis of Aphasia Patients Resulting from Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Quantitative Methods of Aphasia Test