Intest Res.
2022 Jan;20(1):64-71. 10.5217/ir.2020.00100.
Maintaining infliximab induced clinical remission with azathioprine and 5-aminosalicylates in acute severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis has lower cost and high efficacy (MIRACLE): a multicenter study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana, India
- 2Department of Gastroenterology and Human Nutrition, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
- 3Department of Pharmacology, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana, India
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana, India
- 5Department of CRC, Research and Development Centre, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana, India
- 6Research and Development Centre, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana, India
- 7School of Business Studies, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
- KMID: 2525073
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2020.00100
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Infliximab (IFX) has been used to induce and maintain remission in patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis (UC). Long-term use of biologics in developing countries is limited by high cost and frequent side effects. An optimal maintenance strategy in these patients needs to be established.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of maintenance of clinical remission with combination of azathioprine (AZA) and 5-aminosalicylates (5-ASA) in patients with severe steroidrefractory UC where IFX (5 mg/kg intravenously at weeks 0, 2, 6) had been used only as an induction therapy was done at 2 centers in India. Primary outcome was the proportion of patients maintaining corticosteroid-free sustained clinical remission (SCR) at the end of study period. Rates of relapse and cost of therapy were also analyzed.
Results
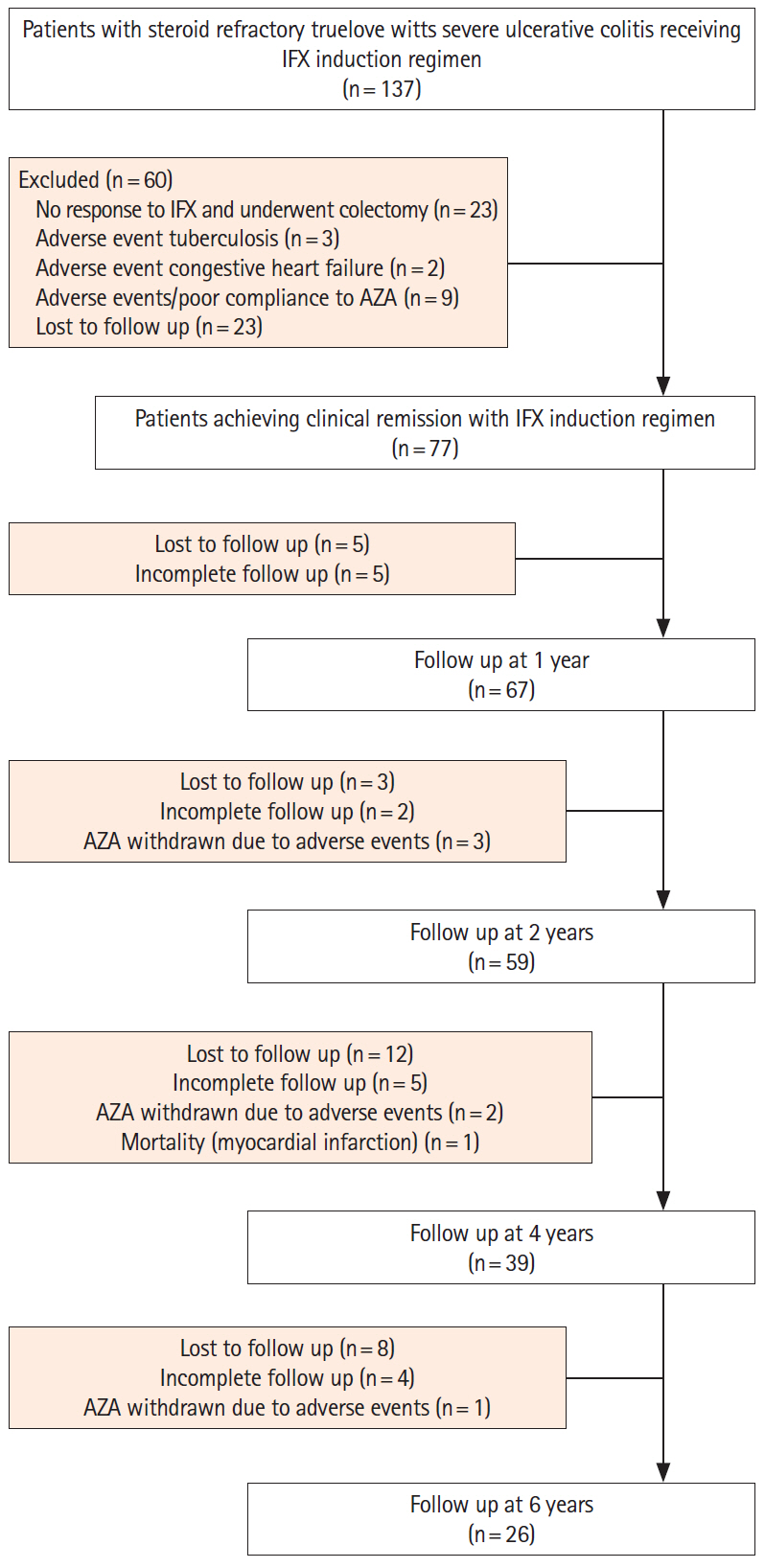
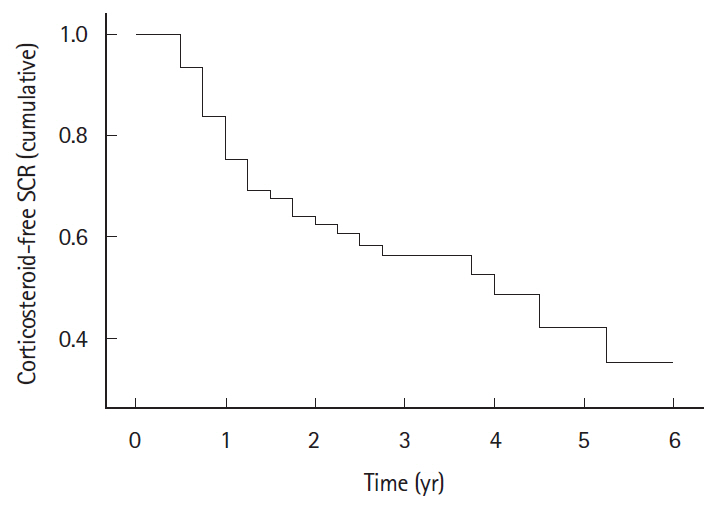
Of the 137 patients who received rescue IFX induction therapy, 77 (56.2%) achieved clinical remission (mean age 34.81 ± 13.32 years, 68.83% males, median follow-up 4 years, range 3 months to 6 years) and were included. Cumulative corticosteroid-free SCR was maintained in 68%, 59%, 42%, and 35% patients at 1, 2, 4, and 6 years respectively. Sixty-seven relapses were observed in 33 patients. Majority of the relapses (45/67, 67.16%) occurred within first 2 years of follow-up. Two relapses were managed with re-induction with IFX, one required colectomy, whereas all other responded to repeat course(s) of corticosteroids. Annual per capita maintenance therapy with 5-ASA and AZA was cheaper by US$ 4,526 compared to maintaining remission with IFX.
Conclusions
Clinical remission achieved with IFX induction therapy in severe steroid-refractory UC can be sustained over long time with a combination of AZA and 5-ASA.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Physician education can minimize inappropriate steroid use in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the ACTION study
Yehyun Park, Chang Hwan Choi, Hyun Soo Kim, Hee Seok Moon, Do Hyun Kim, Jin Ju Kim, Dennis Teng, Dong Il Park
Intest Res. 2022;20(4):452-463. doi: 10.5217/ir.2021.00125.
Reference
-
1. Baumgart DC, Carding SR. Inflammatory bowel disease: cause and immunobiology. Lancet. 2007; 369:1627–1640.
Article2. Travis SP, Farrant JM, Ricketts C, et al. Predicting outcome in severe ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1996; 38:905–910.
Article3. Turner D, Walsh CM, Steinhart AH, Griffiths AM. Response to corticosteroids in severe ulcerative colitis: a systematic review of the literature and a meta-regression. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:103–110.
Article4. Gustavsson A, Halfvarson J, Magnuson A, Sandberg-Gertzén H, Tysk C, Järnerot G. Long-term colectomy rate after intensive intravenous corticosteroid therapy for ulcerative colitis prior to the immunosuppressive treatment era. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:2513–2519.
Article5. Lichtiger S, Present DH, Kornbluth A, et al. Cyclosporine in severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:1841–1845.
Article6. Sood A, Midha V, Sood N, et al. Cyclosporine in the treatment of severe steroid refractory ulcerative colitis: a retrospective analysis of 24 cases. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2008; 27:232–235.7. Sood A, Midha V, Sharma S, et al. Infliximab in patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis: Indian experience. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2014; 33:31–34.
Article8. Reinisch W, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, et al. Long-term infliximab maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis: the ACT-1 and -2 extension studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012; 18:201–211.
Article9. Roda G, Jharap B, Neeraj N, Colombel JF. Loss of response to anti-TNFs: definition, epidemiology, and management. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016; 7:e135.
Article10. Turner D, Seow CH, Greenberg GR, Griffiths AM, Silverberg MS, Steinhart AH. A systematic prospective comparison of noninvasive disease activity indices in ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7:1081–1088.
Article11. Ferrante M, Vermeire S, Fidder H, et al. Long-term outcome after infliximab for refractory ulcerative colitis. J Crohns Colitis. 2008; 2:219–225.
Article12. Ozaki R, Kobayashi T, Okabayashi S, et al. Histological risk factors to predict clinical relapse in ulcerative colitis with endoscopically normal mucosa. J Crohns Colitis. 2018; 12:1288–1294.
Article13. Rubin DT, Ananthakrishnan AN, Siegel CA, Sauer BG, Long MD. ACG clinical guideline: ulcerative colitis in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019; 114:384–413.
Article14. Harbord M, Eliakim R, Bettenworth D, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2017; 11:769–784.
Article15. Puri AS, Desai D, Sood A, Sachdeva S. Infliximab-induced tuberculosis in patients with UC: experience from India-a country with high prevalence of tuberculosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32:1191–1194.
Article16. Gustavsson A, Järnerot G, Hertervig E, et al. Clinical trial: colectomy after rescue therapy in ulcerative colitis: 3-year follow-up of the Swedish-Danish controlled infliximab study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 32:984–989.
Article17. Lamers CB, Griffioen G, van Hogezand RA, Veenendaal RA. Azathioprine: an update on clinical efficacy and safety in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1999; 230:111–115.18. Nikolaus S, Raedler A, Kühbacker T, Sfikas N, Fölsch UR, Schreiber S. Mechanisms in failure of infliximab for Crohn’s disease. Lancet. 2000; 356:1475–1479.
Article19. Laharie D, Bourreille A, Branche J, et al. Ciclosporin versus infliximab in patients with severe ulcerative colitis refractory to intravenous steroids: a parallel, open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012; 380:1909–1915.
Article20. Roda G, Marocchi M, Sartini A, Roda E. Cytokine networks in ulcerative colitis. Ulcers. 2011; 2011:e391787.
Article21. Hindryckx P, Jairath V, D’Haens G. Acute severe ulcerative colitis: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 13:654–664.
Article22. Yokoyama Y, Kamikozuru K, Watanabe K, Nakamura S. Inflammatory bowel disease patients experiencing a loss of response to infliximab regain long-term response after undergoing granulocyte/monocyte apheresis: a case series. Cytokine. 2018; 103:25–28.
Article23. Yamada S, Yoshino T, Matsuura M, et al. Long-term efficacy of infliximab for refractory ulcerative colitis: results from a single center experience. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14:80.
Article24. Nasuno M, Miyakawa M, Tanaka H, Motoya S. Short- and long-term outcomes of infliximab treatment for steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis and related prognostic factors: a single-center retrospective study. Digestion. 2017; 95:67–71.
Article25. Louis E, Mary JY, Vernier-Massouille G, et al. Maintenance of remission among patients with Crohn’s disease on antimetabolite therapy after infliximab therapy is stopped. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:63–70.
Article26. Kang B, Choi SY, Choi YO, et al. Subtherapeutic infliximab trough levels and complete mucosal healing are associated with sustained clinical remission after infliximab cessation in paediatric-onset Crohn’s disease patients treated with combined immunosuppressive therapy. J Crohns Colitis. 2018; 12:644–652.
Article27. Papamichael K, Vande Casteele N, Gils A, et al. Long-term outcome of patients with Crohn’s disease who discontinued infliximab therapy upon clinical remission. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:1103–1110.
Article28. Gisbert JP, Marín AC, Chaparro M. The risk of relapse after anti-TNF discontinuation in inflammatory bowel disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111:632–647.
Article29. Huang G, Xiong J. Effect of azathioprine upon inflammation in rats with ulcerative colitis induced by immune complex-combined TNBS/ethanol. Biomed Res. 2017; 28:2604–2608.30. Refojo D, Liberman AC, Holsboer F, Arzt E. Transcription factor-mediated molecular mechanisms involved in the functional cross-talk between cytokines and glucocorticoids. Immunol Cell Biol. 2001; 79:385–394.
Article31. Goleva E, Kisich KO, Leung DY. A role for STAT5 in the pathogenesis of IL-2-induced glucocorticoid resistance. J Immunol. 2002; 169:5934–5940.
Article32. Bantel H, Domschke W, Schulze-Osthoff K, Kaskas B, Gregor M. Abnormal activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB involved in steroid resistance in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:1845–1846.
Article33. Bach JF. The mode of action of immunosuppressive agents. In : Neuberger A, Tatum EL, editors. Frontiers of biology. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Co.;1975. p. 21.34. Reinink AR, Gregory M, Kymes S, Dassopoulos T. Cost-effectiveness analysis of azathioprine vs. infliximab vs. combination therapy for Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140(5 Suppl 1):S–175.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Steroid-resistant Ulcerative Colitis in Acute Exacervation Phase Remitted by Cyclosporine and Azathioprine: A case report
- Effect of Infliximab in the Treatment of Refractory Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Complication
- Efficacy of Infliximab Rescue Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with Steroid-Refractory Ulcerative Colitis: Single Center Experience
- Infliximab versus Cyclosporine Treatment for Severe Corticosteroid-Refractory Ulcerative Colitis: A Korean, Retrospective, Single Center Study
- Efficacy and safety of the adalimumab biosimilar Exemptia as induction therapy in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis