J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2022 Jan;39(1):58-61. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00864.
Mega cisterna magna in bipolar mood disorder: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, Sakarya University, Sakarya, Turkey
- 2Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Sakarya University, Sakarya, Turkey
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Diyarbakır Dağkapı State Hospital, Diyarbakır, Turkey
- KMID: 2525029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00864
Abstract
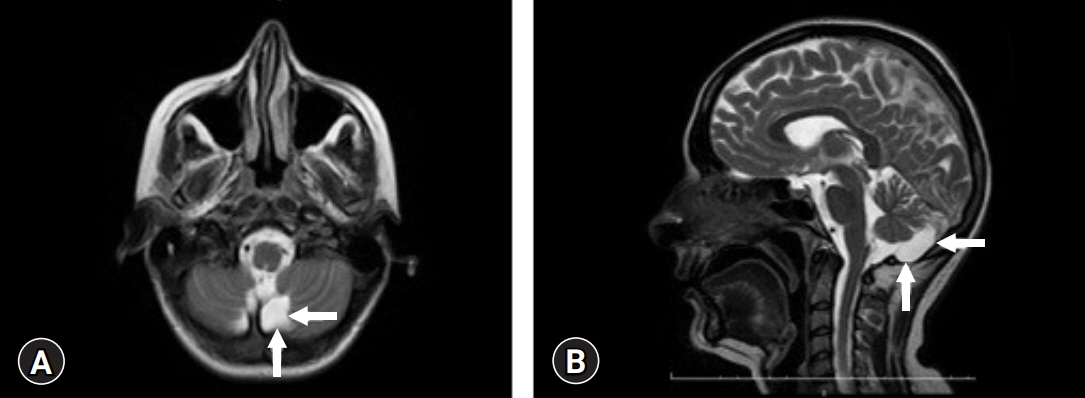
- Mega cisterna magna (MCM), one of the members of the Dandy-Walker complex, is a developmental malformation of the posterior fossa that is larger than 10 mm but morphologically does not affect the vermis and cerebellar hemispheres. Reports of psychiatric disorders associated with this anomaly are rare. We present the case of a patient with MCM who presented with a psychotic manic attack and was diagnosed with bipolar disorder. A 28-year-old female, single housewife, university graduate, presented with irritability, decreased sleep and appetite, distraction, and agitation. The patient also had a delusion of reference. In the clinical follow-up, an increase in energy and an increase in the amount of speech were observed. Her neurological examination was normal, and cranial magnetic resonance imaging revealed an MCM. The relationship and clinical significance of MCM with psychosis and mood disorders have not yet been fully elucidated. It is not known whether this association is accidental or based on etiological commonality. The purpose of this case report is to review the relationship between the cerebellum and psychiatric symptoms and to contribute to the literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Roostaei T, Nazeri A, Sahraian MA, Minagar A. The human cerebellum: a review of physiologic neuroanatomy. Neurol Clin. 2014; 32:859–69.2. Phillips JR, Hewedi DH, Eissa AM, Moustafa AA. The cerebellum and psychiatric disorders. Front Public Health. 2015; 3:66.3. Zimmer EZ, Lowenstein L, Bronshtein M, Goldsher D, Aharon-Peretz J. Clinical significance of isolated mega cisterna magna. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2007; 276:487–90.4. Karayilan S, Erol A. Schizophrenia and mega cisterna magna: case report. Anadolu Psikiyatri Derg. 2013; 14:90–2.5. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of medical disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association;2013.6. Langarica M, Peralta V. Psychosis associated to megacisterna magna. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2005; 28:119–21.7. Ferentinos PP, Kontaxakis VP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Paplos KG, Pappa DA, Soldatos CR. Refractory psychosis and prominent cognitive deficits in a patient with mega-cisterna magna. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007; 31:561–3.8. Turan T, Beşirli A, Asdemir A, Ozsoy S, Eşel E. Manic episode associated with mega cisterna magna. Psychiatry Investig. 2010; 7:305–7.9. Kumar S, Sur S, Singh A. Mega cisterna magna associated with recurrent catatonia: a case report. Biol Psychiatry. 2011; 70:e19.10. Kani AS, Poyraz CA, İnce E, Duran A. Comorbid schizophrenia and obsessive compulsive disorder associated with mega cisterna magna: a case report. Yeni Symp. 2015; 53:45–6.11. Erzin G. Psychosis and mega cisterna magna: case report. Eur Psychiatry. 2016; 33(Suppl):S613–4.12. Balcioğlu YH, Kirlioğlu SS, Berkol TD, Özgen G. Coincidental mega cisterna magna with psychotic disorder: a possible neuroanatomical liability for a shared psychotic disorder. Anadolu Psikiyatri Dergisi. 2018; 19:106–9.13. Öztürrk SS, Seven H, Demiröz D, Özbek S, Çiçek İE, Eren I. A case of late onset bipolar disorder with mega cisterna magna. Psychiatr Clin Psychopharmacol. 2018; 28(Suppl 1):137.14. Tréhout M, Zhang N, Blouet M, Borha A, Dollfus S. Dandy-Walker malformation-like condition revealed by refractory schizophrenia: a case report and literature review. Neuropsychobiology. 2019; 77:59–66.15. Batmaz M, Balçik ZE, Özer Ü, Hamurişçi Yalçin B, Özen Ş. Dandy-Walker malformation presenting with affective symptoms. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2017; 54:277–81.16. Adamaszek M, D’Agata F, Ferrucci R, Habas C, Keulen S, Kirkby KC, et al. Consensus paper: cerebellum and emotion. Cerebellum. 2017; 16:552–76.17. Fatemi SH, Stary JM, Earle JA, Araghi-Niknam M, Eagan E. GABAergic dysfunction in schizophrenia and mood disorders as reflected by decreased levels of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 kDa and Reelin proteins in cerebellum. Schizophr Res. 2005; 72:109–22.18. Maloku E, Covelo IR, Hanbauer I, Guidotti A, Kadriu B, Hu Q, et al. Lower number of cerebellar Purkinje neurons in psychosis is associated with reduced reelin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:4407–11.19. Siebert JR. A pathological approach to anomalies of the posterior fossa. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2006; 76:674–84.