Kosin Med J.
2021 Dec;36(2):144-147. 10.7180/kmj.2021.36.2.144.
Usefulness of Kaloderm® in Finger Tip Necrosis : A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2524657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2021.36.2.144
Abstract
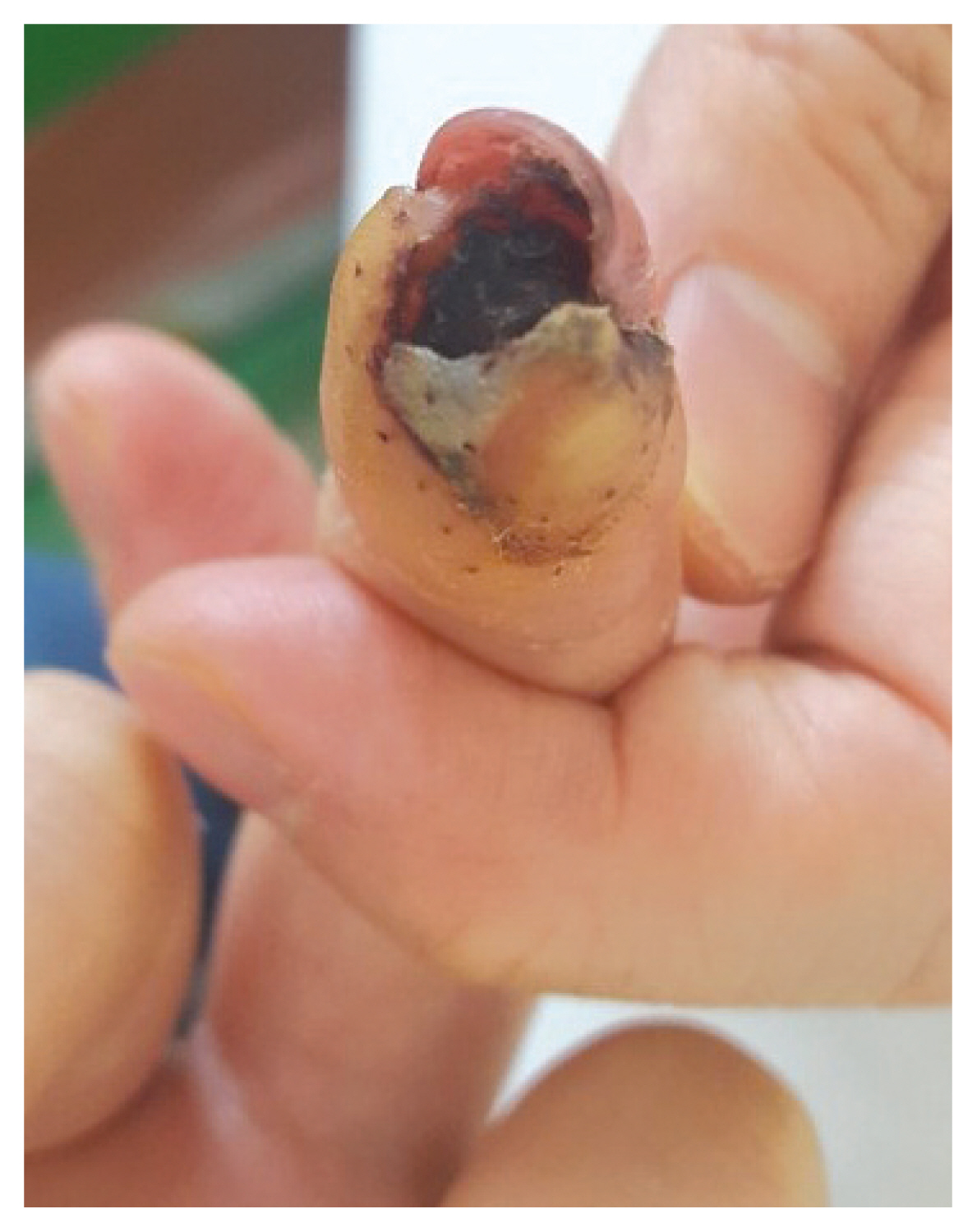
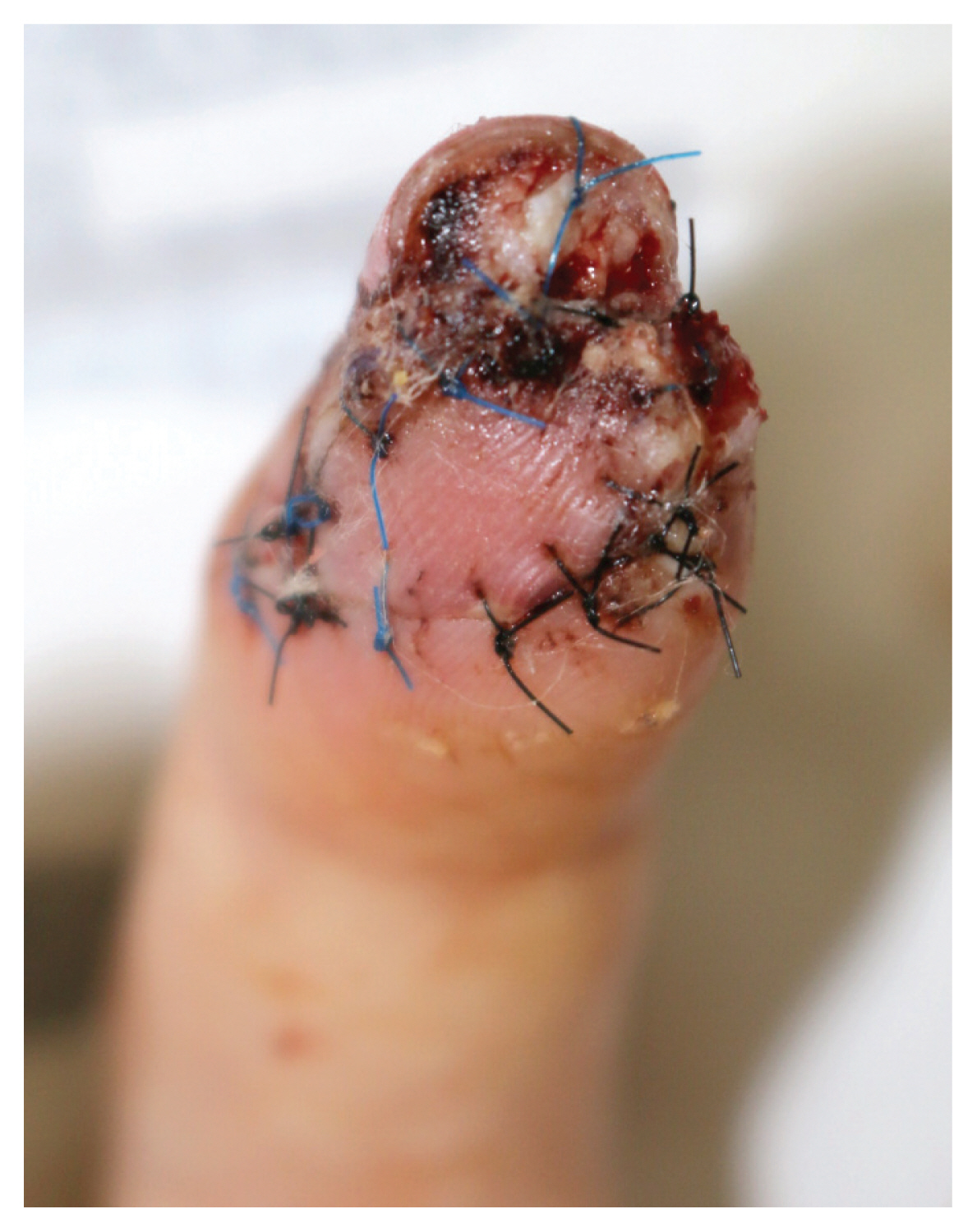
- We experienced a case of crush injury of the hand for which we performed a flap surgery and treated the necrotic parts placement using cultured allogeneic keratinocytes (Kaloderm® ) with good results. The patient was a 31-year-old woman whose left middle finger was caught in a door, causing a crush injury. Although primary repair was performed, a 2 × 2.5-cm-sized necrosis developed, and a V-Y advancement flap was performed after the removal of dead tissues. However, a 1 × 2-cm-sized partial necrosis occurred and was treated using Kaloderm ® . After the use of Kaloderm® , the patient’s wound was healed, and no complications, except for mild pain, were observed for 1 year after the surgery. If a necrotic site appears after flap placement of fingertip, its treatment is difficult. If used well, Kaloderm® may be a good option for necrosis of the fingertips and other areas that are difficult to cure.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Russell RC, Van Beek AL, Wavak P, Zook EG. Alternative hand flaps for amputations and digital defects. J Hand Surg Am. 1981; 6:399–405.
Article2. Lavker RM, Sun TT. Heterogeneity in epidermal basal keratinocytes: morphological and functional correalations. Science. 1982; 215:1239–41.3. Lavker RM, Sun TT. Epidermal stem cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1983; 81:121s–7s.
Article4. Park JM, Heo J, Ha JS, Lee KC, Kim SK, Kim JH. Finger reconstruction by inguinal tube flap. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2005; 10:149–55.5. Lineen E, Namias N. Biologic dressing in burns. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19:923–8.
Article6. Lee JS, Chu SG, Lee JW, Choi KY, Yang JD, Cho BC, et al. Application of cultured epidermal homograft(Kaloderm) for wide scar treatment. J Craniofac Surg. 2019; 30:e535–9.7. Joo HS, Lee SJ, Sung KY. Early debridement and cultured allogenic keratinocyte dressing prevent hypertrophic scarring in infants with deep dermal burns. Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018; 24:111–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Cultured Allogenic Keratinocyte (Kaloderm(R)) for 2nd Degree Burn Patient Treatment
- Bilateral Free 2nd Toe Pulp Flap for Reconstruction of Soft Tissue Defect in Traumatic Finger Injuries
- Afferent Arteriovenous Anastomosis For Finger Tip Replantation
- Bilateral Ring Finger Necrosis in a Hemodialysis Patient: A Case Report
- The Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Presenting with Raynaud's Disease and Digital Necrosis