Cancer Res Treat.
2022 Jan;54(1):259-268. 10.4143/crt.2021.010.
Absolute Neutrophil Count after the First Chemotherapy Cycle as a Surrogate Marker for Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Neuroblastoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Research Institute for Future Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Clinical Precision Medicine Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 4Statistics and Data Center, Research Institute for Future Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2524607
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2021.010
Abstract
- Purpose
We performed this study to determine whether the degree of neutropenia after the first chemotherapy cycle can be used as a surrogate marker of individual susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents affecting treatment outcome in patients with neuroblastoma.
Materials and Methods
The study included 313 patients who received the first cycle chemotherapy with a CEDC (cisplatin+etoposide+doxorubicin+cyclophosphamide) regimen and had absolute neutrophil count (ANC) data available. The cumulative incidences of progression and treatment-related mortality (TRM) were estimated. To identify genetic variations associated with the ANC, a genome-wide association study (GWAS) was performed.
Results
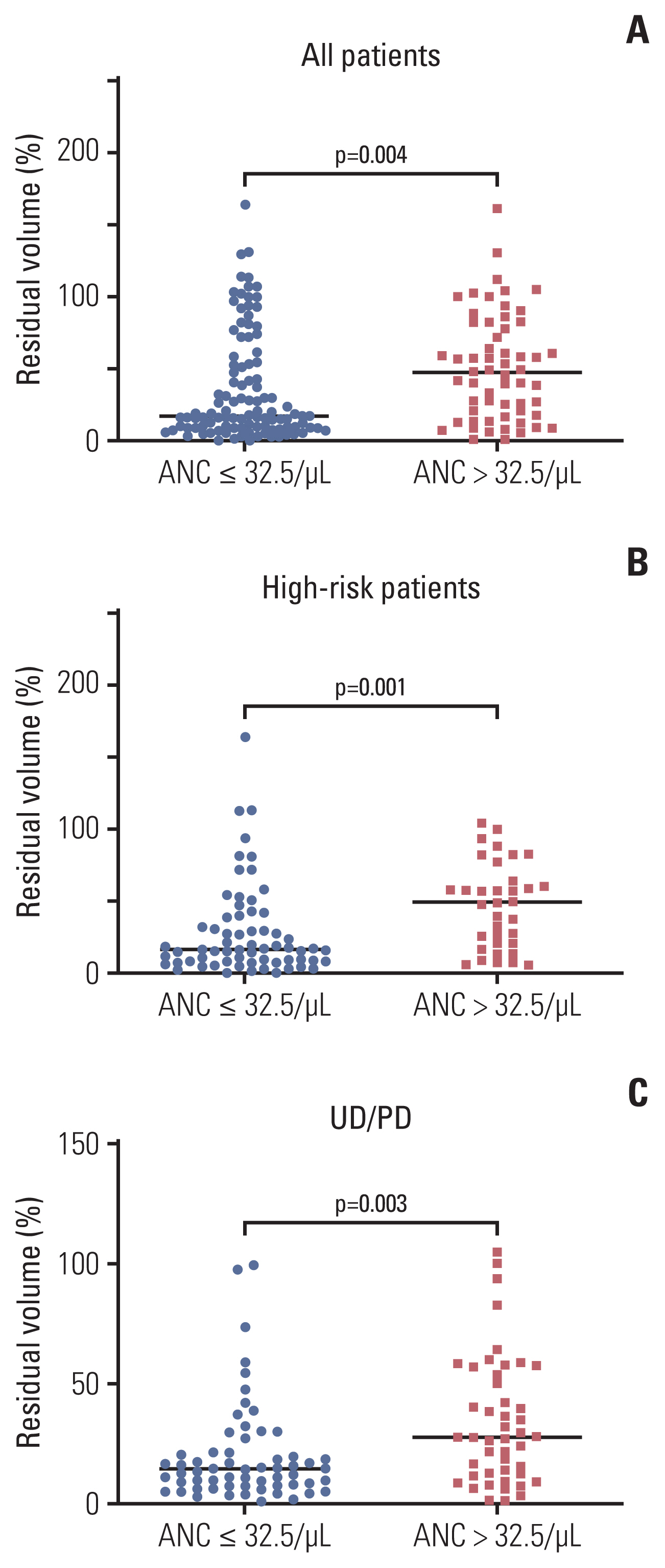
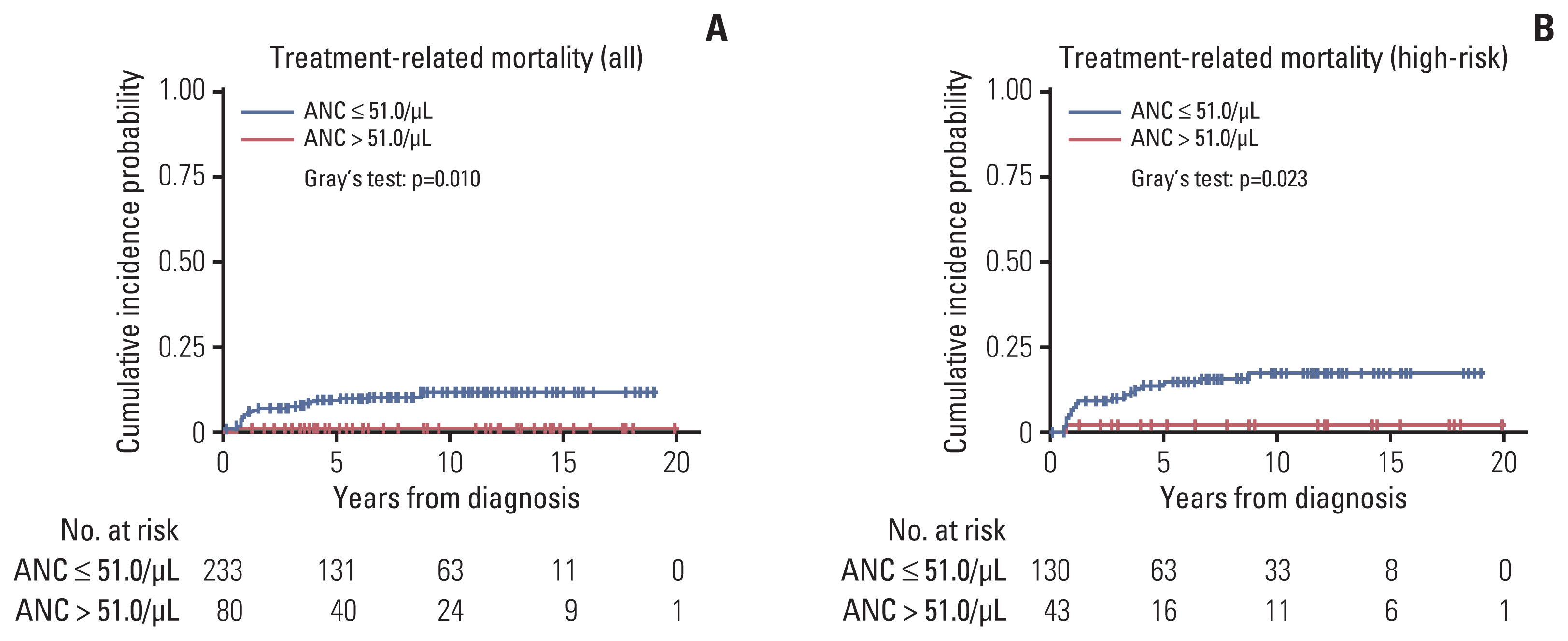
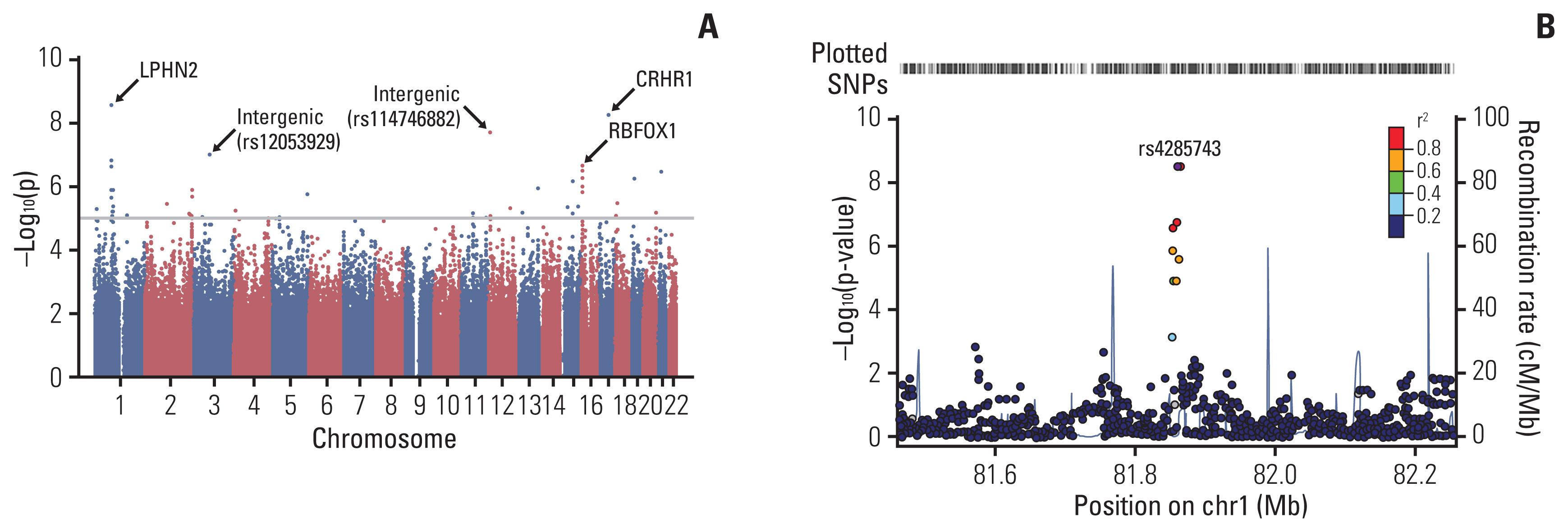
An ANC of 32.5/μL was determined as the cutoff point to categorize patients into the good and poor prognosis subgroups in terms of progression. Patients with a high nadir ANC had a higher cumulative incidence of progression than those with a low nadir ANC (p < 0.001). In multivariate analysis, high nadir ANC, age, bone marrow involvement, and unfavorable histology were poor prognostic factors. With regard to the TRM, patients with a low nadir ANC (ANC < 51.0/μL) had a higher cumulative incidence of TRM than those with a high nadir ANC (p=0.010). In GWAS, single-nucleotide polymorphisms of LPHN2 and CRHR1 were significantly associated with the nadir ANC.
Conclusion
In neuroblastoma patients, the degree of neutropenia after the first chemotherapy cycle can be used as a surrogate marker to predict an individual’s susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents. Tailoring of treatment based on the degree of neutropenia needs to be considered.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL. Neuroblastoma. Lancet. 2007; 369:2106–20.
Article2. Brodeur GM. Neuroblastoma: biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003; 3:203–16.
Article3. Hero B, Simon T, Spitz R, Ernestus K, Gnekow AK, Scheel-Walter HG, et al. Localized infant neuroblastomas often show spontaneous regression: results of the prospective trials NB95-S and NB97. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:1504–10.
Article4. Moen EL, Godley LA, Zhang W, Dolan ME. Pharmacogenomics of chemotherapeutic susceptibility and toxicity. Genome Med. 2012; 4:90.
Article5. Roden DM, McLeod HL, Relling MV, Williams MS, Mensah GA, Peterson JF, et al. Pharmacogenomics. Lancet. 2019; 394:521–32.
Article6. Lennard L, Lilleyman JS, Van Loon J, Weinshilboum RM. Genetic variation in response to 6-mercaptopurine for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 1990; 336:225–9.
Article7. Yang JJ, Landier W, Yang W, Liu C, Hageman L, Cheng C, et al. Inherited NUDT15 variant is a genetic determinant of mercaptopurine intolerance in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:1235–42.
Article8. Bagatell R, McHugh K, Naranjo A, Van Ryn C, Kirby C, Brock P, et al. Assessment of primary site response in children with high-risk neuroblastoma: an international multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:740–6.
Article9. Lee JW, Lee S, Cho HW, Ma Y, Yoo KH, Sung KW, et al. Incorporation of high-dose (131)I-metaiodobenzylguanidine treatment into tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for high-risk neuroblastoma: results of the SMC NB-2009 study. J Hematol Oncol. 2017; 10:108.
Article10. Sung KW, Son MH, Lee SH, Yoo KH, Koo HH, Kim JY, et al. Tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma: results of SMC NB-2004 study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013; 48:68–73.
Article11. Laska E, Meisner M, Wanderling J. A maximally selected test of symmetry about zero. Stat Med. 2012; 31:3178–91.
Article12. Kim HT. Cumulative incidence in competing risks data and competing risks regression analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:559–65.
Article13. Pruim RJ, Welch RP, Sanna S, Teslovich TM, Chines PS, Gliedt TP, et al. LocusZoom: regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics. 2010; 26:2336–7.
Article14. Kishida Y, Kawahara M, Teramukai S, Kubota K, Komuta K, Minato K, et al. Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia as a prognostic factor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from Japan Multinational Trial Organization LC00-03. Br J Cancer. 2009; 101:1537–42.
Article15. Ma RM, Chen CZ, Zhang W, You J, Huang DP, Guo GL. Prognostic value of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia at the first cycle in invasive breast cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3240.
Article16. Kasi PM, Kotani D, Cecchini M, Shitara K, Ohtsu A, Ramanathan RK, et al. Chemotherapy induced neutropenia at 1-month mark is a predictor of overall survival in patients receiving TAS-102 for refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a cohort study. BMC Cancer. 2016; 16:467.
Article17. Chen Y, Wang Y, Shi Y, Dai G. Timing of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia predicts prognosis in metastatic colon cancer patients: a retrospective study in mFOLFOX6-treated patients. BMC Cancer. 2017; 17:242.
Article18. Sung L, Aplenc R, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Wang YC, Meshinchi S, et al. Association between prolonged neutropenia and reduced relapse risk in pediatric AML: a report from the children’s oncology group. Int J Cancer. 2016; 139:1930–5.
Article19. Alexander S, Pole JD, Gibson P, Lee M, Hesser T, Chi SN, et al. Classification of treatment-related mortality in children with cancer: a systematic assessment. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:e604–10.
Article20. White GR, Varley JM, Heighway J. Genomic structure and expression profile of LPHH1, a 7TM gene variably expressed in breast cancer cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000; 1491:75–92.
Article21. Eng L, Ibrahimzada I, Jarjanazi H, Savas S, Meschian M, Pritchard KI, et al. Bioinformatic analyses identifies novel protein-coding pharmacogenomic markers associated with paclitaxel sensitivity in NCI60 cancer cell lines. BMC Med Genomics. 2011; 4:18.
Article22. Perez-Ortiz AC, Ramirez I, Cruz-Lopez JC, Villarreal-Garza C, Luna-Angulo A, Lira-Romero E, et al. Pharmacogenetics of response to neoadjuvant paclitaxel treatment for locally advanced breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:106454–67.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Risk Factor of Bacteremia in Children with Febrile Neutropenia due to Chemotherapy
- Prognostic Value of Hematological Markers in Head and Neck Cancer Patients With a History of Hematological Malignancy
- The Effect of Empirical Antibiotics in Febrile Neutropenia
- Diagnostic Usefulness of Basic Hematologic Tests for the Detection of Bacteremia in Febrile Patients with Neutrophilia
- Clinical Effects of Recombinant Human G-CSF (Neutrogin) on Neutropenia Induced by the Cancer Chemotherapy for Gynecologic Malignancy