Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 Nov;25(4):562-565. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.562.
Monosegment associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy: Preserving segment 1 as the only liver remnant after hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Abdominal Surgery, Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplasicas (INEN), Lima, Peru
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplasicas (INEN), Lima, Peru
- KMID: 2523064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.562
Abstract
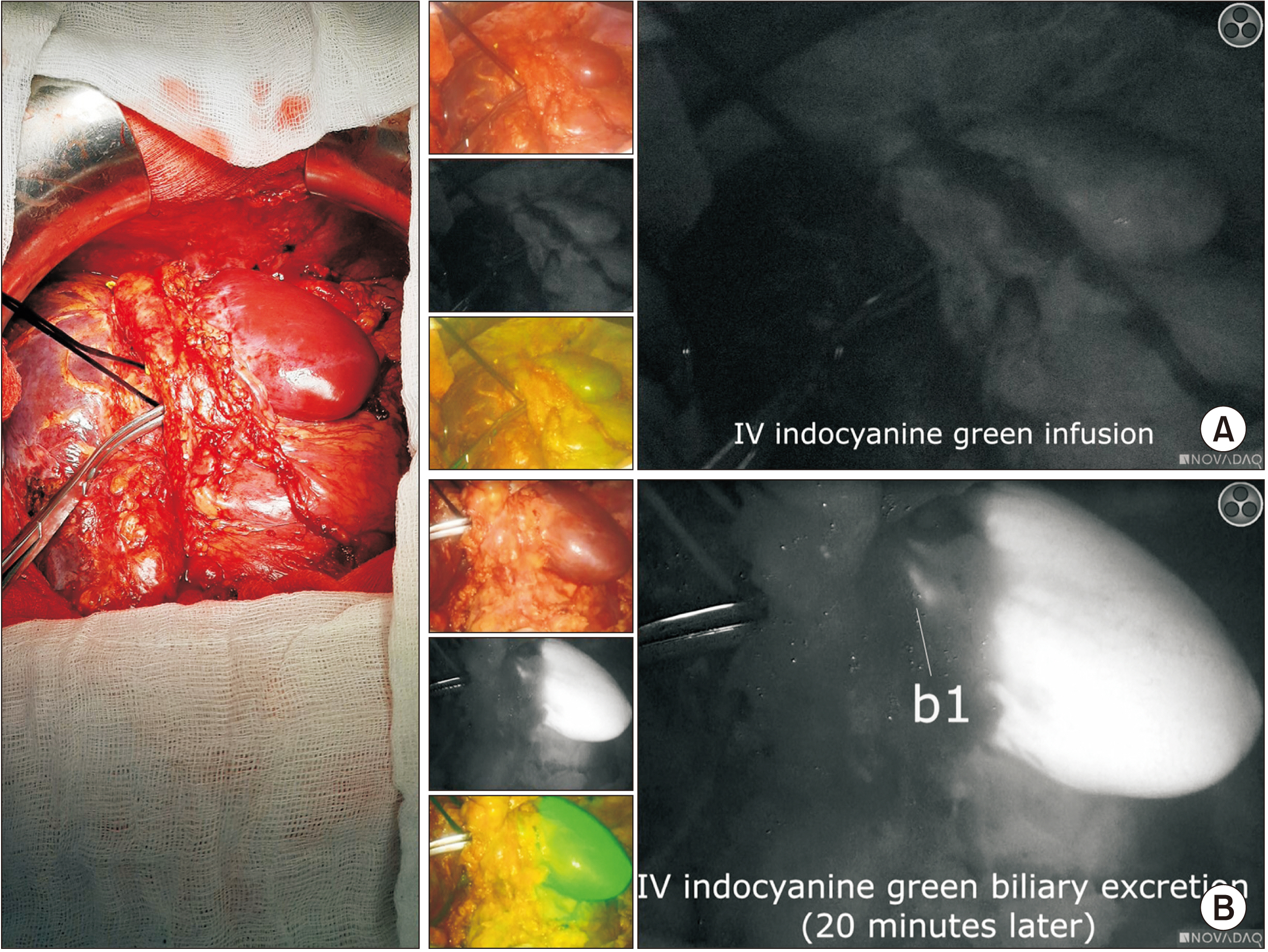
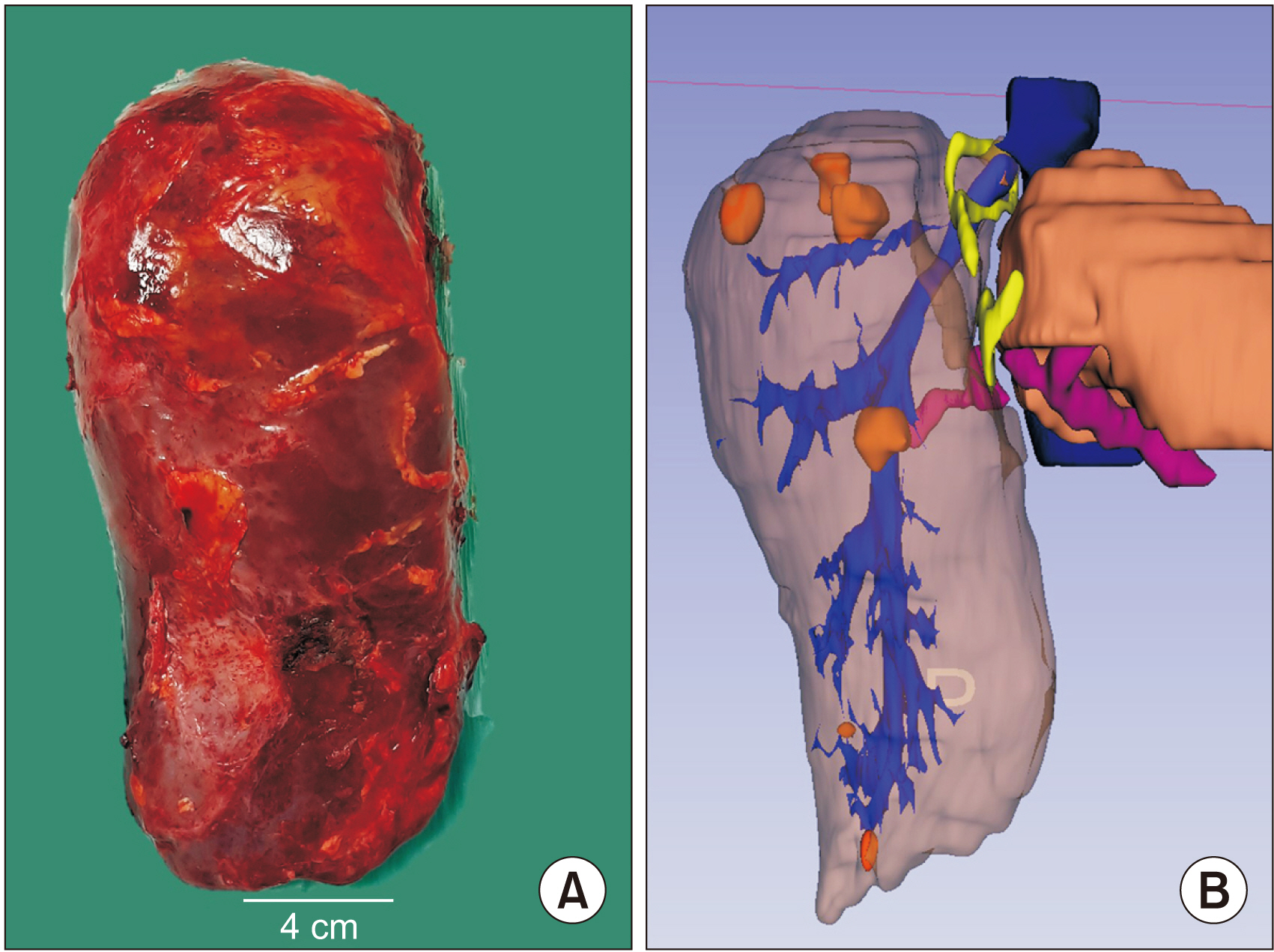
- Since the inception of the associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) procedure, many centres have used this technique for patients who would otherwise be considered unresectable due to insufficient future liver remnant. In this report, we presented the case of a paediatric patient with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent monosegment ALPPS (M-ALPPS) hepatectomy preserving segment 1 as the sole liver remnant using indocyanine green (ICG) as a f luorescence guide.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schadde E, Malagó M, Hernandez-Alejandro R, Li J, Abdalla E, Ardiles V, et al. 2015; Monosegment ALPPS hepatectomy: extending resectability by rapid hypertrophy. Surgery. 157:676–689. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.11.015. PMID: 25712199.
Article2. Ruiz Figueroa EF, Fernández-Placencia RM, Berrospi Espinoza FE, Gomez HF, Chávez Passiuri IK. 2019; Monosegmental ALPPS: a long-term survival alternative to liver transplant in PRETEXT IV hepatoblastoma. J Surg Case Rep. 2019:rjz144. DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjz144. PMID: 31086654. PMCID: PMC6507791.
Article3. Rahbari NN, Garden OJ, Padbury R, Brooke-Smith M, Crawford M, Adam R, et al. 2011; Posthepatectomy liver failure: a definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery (ISGLS). Surgery. 149:713–724. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.10.001. PMID: 21236455.
Article4. Wang W, Zhang Z, Wang J. 2020; Subtotal (segment II-VIII) hepatectomy for bilateral diffuse hepatolithiasis with compensatory caudate lobe hypertrophy: a report of two cases. BMC Gastroenterol. 20:350. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01503-9. PMID: 33081716. PMCID: PMC7576830.
Article5. Dong J, Lau WY, Lu W, Zhang W, Wang J, Ji W. 2012; Caudate lobe-sparing subtotal hepatectomy for primary hepatolithiasis. Br J Surg. 99:1423–1428. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.8888. PMID: 22961524.
Article6. Shuto T, Kinoshita H, Yamada C, Hirohashi K, Shiokawa C, Kubo S, et al. 1993; Bilateral lobectomy excluding the caudate lobe for giant mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver. Surgery. 113:215–222. PMID: 8430370.7. Aijun L, Jiamei Y, Qinhe T, Mengchao W. 2014; Caudate lobe as the sole remnant liver following extended liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Surg Case Rep. 5:462–464. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2014.05.003. PMID: 24973528. PMCID: PMC4147654.
Article8. Lai Q, Mennini G, Larghi Laureiro Z, Rossi M. 2021; Uncommon indications for associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy: a systematic review. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 10:210–225. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn-20-355. PMID: 33898561. PMCID: PMC8050569.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Associating microwave ablation and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy for the treatment of huge hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis
- Totally laparoscopic associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy using anterior approach in HCC patient with Type II portal vein anomaly: a case report
- Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) procedure for hepatocellular carcinoma with chronic liver disease: a case report and review of literature
- Associated Liver Partition and Portal Vein Ligation for Staged Hepatectomy (ALPPS) Registry: What Have We Learned?
- Two-Stage Hepatectomy for Bilateral Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Tumor Thrombi