J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Nov;36(46):e307. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e307.
Controlling an Outbreak of Multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: a Retrospective Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Children's Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 3Infection Prevention and Control Department, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 4Department of Nursing, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2522882
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e307
Abstract
- Background
Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (MDRAB) is widespread among intensive care units worldwide, posing a threat to patients and the health system. We describe the successful management of a MDRAB outbreak by implementing an infection-control strategy in a pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Methods
This retrospective study investigated the patients admitted to the PICU in periods 1 (8 months) and 2 (7 months), from the index MDRAB case to intervention implementation, and from intervention implementation to cessation of MDRAB spread. An infection-control strategy was designed following six concepts: 1) cohort isolation of colonized patients, 2) enforcement of hand hygiene, 3) universal contact precautions, 4) environmental management, 5) periodic surveillance culture study, and 6) monitoring and feedback.
Results
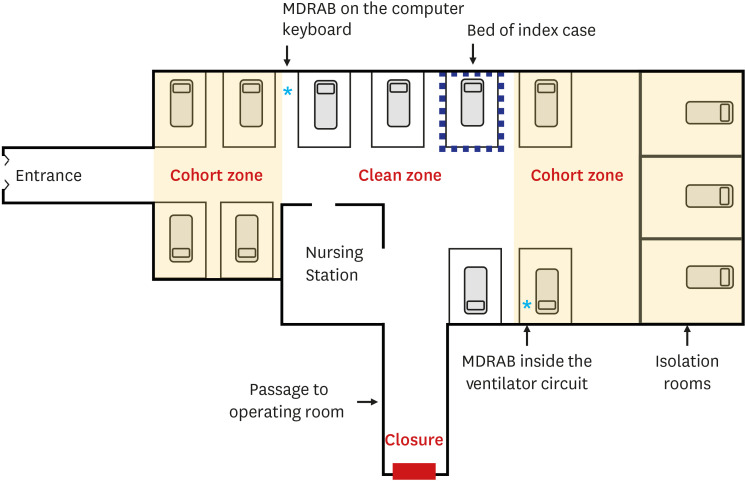
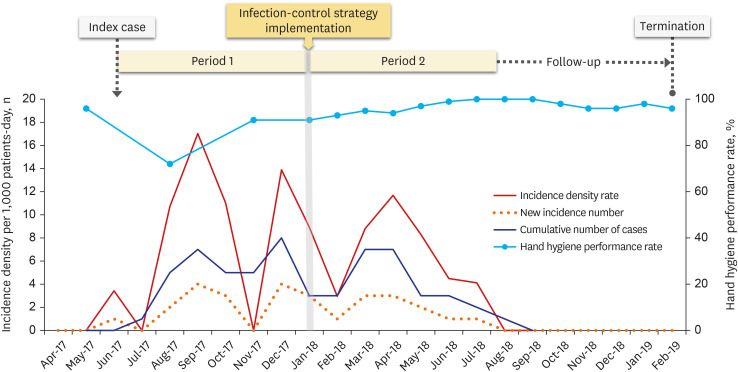
Of the 427 patients, 29 were confirmed to have MDRAB colonization, of which 18 had MDRAB infections. Overall incidence per 1,000 patient days decreased from 7.8 (period 1) to 5.8 (period 2). The MDRAB outbreak was declared terminated after the 6-month followup following period 2. MDRAB was detected on the computer keyboard and in condensed water inside the ventilator circuits. The rate of hand hygiene performance was the lowest in the three months before and after index case admission and increased from 84% (period 1) to 95% (period 2). Patients with higher severity, indicated by a higher Pediatric Risk of Mortality III score, were more likely to develop colonization (P = 0.030), because they had invasive devices and required more contact with healthcare workers. MDRAB colonization contributed to an increase in the duration of mechanical ventilation and PICU stay (P < 0.001), but did not affect mortality (P = 0.273).
Conclusion
The MDRAB outbreak was successfully terminated by the implementation of a comprehensive infection-control strategy focused on the promotion of hand hygiene, universal contact precautions, and environmental management through multidisciplinary teamwork.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weber DJ, Rutala WA, Miller MB, Huslage K, Sickbert-Bennett E. Role of hospital surfaces in the transmission of emerging health care-associated pathogens: norovirus, Clostridium difficile, and Acinetobacter species. Am J Infect Control. 2010; 38(5):Suppl 1. S25–S33. PMID: 20569853.2. Choi IS, Choi JA, Jang SJ, Park G, Jeong SH, Kim CM, et al. Distribution of adeG, adeB, adeE, adeY, abeM, and adeJ efflux pump genes in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter species from Korea. Lab Med Online. 2019; 9(4):201–209.3. Wendt C, Dietze B, Dietz E, Rüden H. Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on dry surfaces. J Clin Microbiol. 1997; 35(6):1394–1397. PMID: 9163451.4. Hong KB, Oh HS, Song JS, Lim JH, Kang DK, Son IS, et al. Investigation and control of an outbreak of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection in a pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012; 31(7):685–690. PMID: 22466324.5. Lee H, Lee H. Clinical and economic evaluation of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii colonization in the intensive care unit. Infect Chemother. 2016; 48(3):174–180. PMID: 27659440.6. Kim YJ, Kim SI, Hong KW, Kim YR, Park YJ, Kang MW. Risk factors for mortality in patients with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia: impact of appropriate antimicrobial therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27(5):471–475. PMID: 22563209.7. Choi JY, Kwak YG, Yoo H, Lee SO, Kim HB, Han SH, et al. Trends in the distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of causative pathogens of device-associated infection in Korean intensive care units from 2006 to 2013: results from the Korean Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System (KONIS). J Hosp Infect. 2016; 92(4):363–371. PMID: 26876746.
Article8. Tabah A, Koulenti D, Laupland K, Misset B, Valles J, Bruzzi de Carvalho F, et al. Characteristics and determinants of outcome of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections in intensive care units: the EUROBACT International Cohort Study. Intensive Care Med. 2012; 38(12):1930–1945. PMID: 23011531.
Article9. Kadri SS, Adjemian J, Lai YL, Spaulding AB, Ricotta E, Prevots DR, et al. Difficult-to-treat resistance in Gram-negative bacteremia at 173 US hospitals: retrospective cohort analysis of prevalence, predictors, and outcome of resistance to all first-line agents. Clin Infect Dis. 2018; 67(12):1803–1814. PMID: 30052813.
Article10. Teerawattanapong N, Panich P, Kulpokin D, Na Ranong S, Kongpakwattana K, Saksinanon A, et al. A systematic review of the burden of multidrug-resistant healthcare-associated infections among intensive care unit patients in Southeast Asia: the rise of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii . Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2018; 39(5):525–533. PMID: 29580299.11. Cheon S, Kim MJ, Yun SJ, Moon JY, Kim YS. Controlling endemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in intensive care units using antimicrobial stewardship and infection control. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31(2):367–374. PMID: 26874513.12. Warde E, Davies E, Ward A. Control of a multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak. Br J Nurs. 2019; 28(4):242–248. PMID: 30811227.13. Shi HJ, Kim JH, Kim NY, Lee JB, Eom JS. Environmental culture of bacteria at the intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital in Korea: a consideration for improving medical environmental safety and healthcare-associated infection. Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2020; 25(2):105–114.
Article14. Ray A, Perez F, Beltramini AM, Jakubowycz M, Dimick P, Jacobs MR, et al. Use of vaporized hydrogen peroxide decontamination during an outbreak of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection at a long-term acute care hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010; 31(12):1236–1241. PMID: 20973723.15. Gramatniece A, Silamikelis I, Zahare I, Urtans V, Zahare I, Dimina E, et al. Control of Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak in the neonatal intensive care unit in Latvia: whole-genome sequencing powered investigation and closure of the ward. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019; 8(1):84. PMID: 31143444.
Article16. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Infection control guidelines for multidrug resistant microorganisms in healthcare facilities (Korean). Updated 2012. Accessed August 20, 2021. http://www.kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20507020000&bid=0019&act=view&list_no=138310&tag=&nPage=1 .17. Kim YA, Kim H, Kim YM, Park SE. A successful application of adult polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column hemoperfusion to a neonate with septic shock. Acute Crit Care. 2019; 34(4):284–288. PMID: 31743641.
Article18. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, Twenty-fifth Informational Supplement, M100-S25. Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI;2015.19. Park HJ, Kim JM, Kim KH, Kim DS. Current analysis of Acintobacter baumannii infection among pediatric patients in a single-centered study. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2011; 18(1):23–30.20. Nutman A, Lerner A, Schwartz D, Carmeli Y. Evaluation of carriage and environmental contamination by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii . Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016; 22(11):949.e5–949.e7.21. Ng DH, Marimuthu K, Lee JJ, Khong WX, Ng OT, Zhang W, et al. Environmental colonization and onward clonal transmission of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) in a medical intensive care unit: the case for environmental hygiene. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018; 7(1):51. PMID: 29644052.
Article22. Dekic S, Hrenovic J, van Wilpe E, Venter C, Goic-Barisic I. Survival of emerging pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii in water environment exposed to different oxygen conditions. Water Sci Technol. 2019; 80(8):1581–1590. PMID: 31961820.23. Mousa M, Schwartz D, Carmeli Y, Nutman A. Droplet aerosol dissemination of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii surrounding ventilated patients. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019; 40(3):365–367. PMID: 30773156.24. Harris AD, Morgan DJ, Pineles L, Perencevich EN, Barnes SL. Deconstructing the relative benefits of a universal glove and gown intervention on MRSA acquisition. J Hosp Infect. 2017; 96(1):49–53. PMID: 28410760.
Article25. Harris AD, Morgan DJ, Pineles L, Magder L, O'Hara LM, Johnson JK. Acquisition of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in the Benefits of Universal Glove and Gown (BUGG) cluster randomized trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 72(3):431–437. PMID: 31970393.
Article26. Harris AD, Pineles L, Belton B, Johnson JK, Shardell M, Loeb M, et al. Universal glove and gown use and acquisition of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the ICU: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2013; 310(15):1571–1580. PMID: 24097234.27. Tawney A, Semproch L, Lephart P, Valentine K, Thomas R, Asmar BI, et al. Impact of contact isolation precautions on multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in the pediatric intensive care unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2015; 36(9):1108–1110. PMID: 26047364.28. Park SY, Lee EJ, Kim T, Yu SN, Park KH, Lee MS, et al. Early administration of appropriate antimicrobial agents to improve the outcome of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii complex bacteraemic pneumonia. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018; 51(3):407–412. PMID: 29122697.29. Kim B, Kim K, Yoon JS. Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii infection in children in adult versus pediatric intensive care units. Pediatr Int. 2020; 62(4):451–458. PMID: 31887243.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection in the intensive care unit
- Clinical and Molecular-epidemiologic Analysis of A Nosocomial Outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Outbreak of Acinetobacter septicemia in a neonatal intensive care unit
- The Analysis of Risk Factor and Infection Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Medical Intensive Care Unit
- Risk Factors of Invasive Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit during Outbreak