Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2021 Oct;9(2):106-110. 10.14791/btrt.2021.9.e22.
Anterior Craniocervical Junctional Neurenteric Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2522228
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2021.9.e22
Abstract
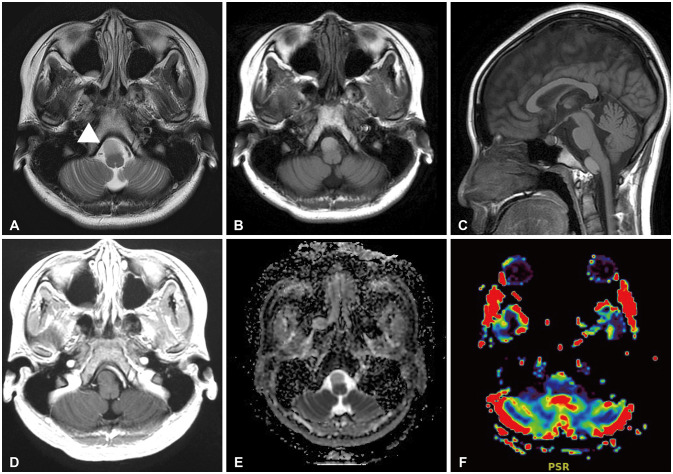
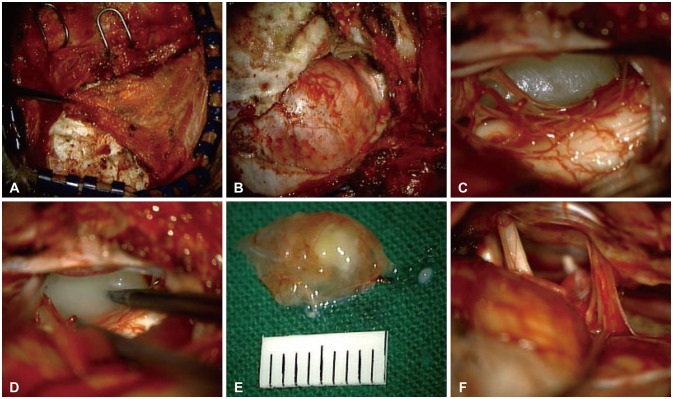
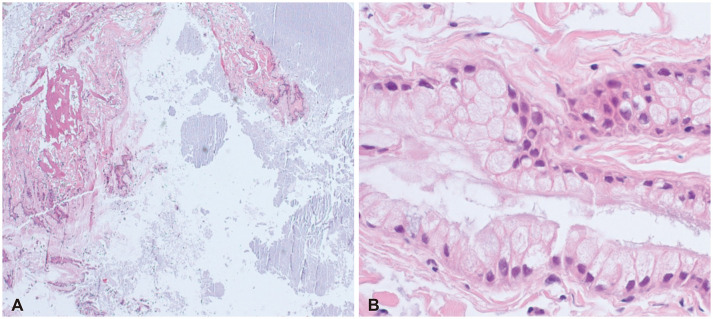
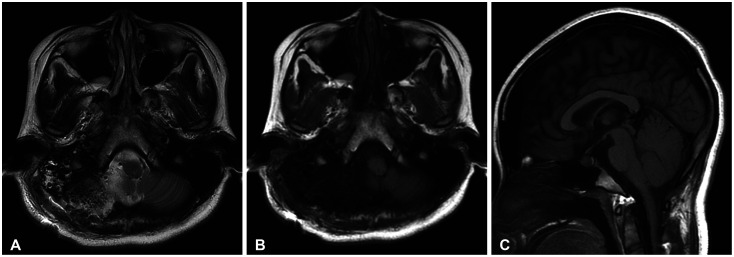
- Intracranial neurenteric cyst at the anterior craniocervical junction is very rare, and its treatment and prognosis have not been established. We report a case of neurenteric cyst at the anterior craniocervical junction and review the relevant literature. A 16-year-old girl presented with a 2-month history of slowly progressive headache. MRI revealed a well-defined intradural extramedullary cyst in the anterior medulla and brain stem with C1 cord compression. We performed gross total resection of the cyst using a far-lateral transcondylar approach. Surgical resection is the treatment of choice for neurenteric cysts at anterior craniocervical junction, the far-lateral transcondylar approach might be the optimal surgical approach.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sundaram C, Paul TR, Raju BV, et al. Cysts of the central nervous system: a clinicopathologic study of 145 cases. Neurol India. 2001; 49:237–242. PMID: 11593239.2. Guilburd JN, Arieh YB, Peyser E. Spinal intradural enterogenous cyst: report of a case. Surg Neurol. 1980; 14:359–362. PMID: 7444743.3. Al Qadhi S, Laiq S, Salhotra N, et al. Neurenteric cyst at craniovertebral junction: an uncommon presentation. Am J Med Case Rep. 2021; 9:407–410.4. Prasad GL, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK. Ventral foramen magnum neurenteric cysts: a case series and review of literature. Neurosurg Rev. 2016; 39:535–544. PMID: 26662045.5. Haque M, Rahman A, Ahmed N, Alam S. Huge ventral cervicomedullary neurenteric cyst: a rare entity with good surgical outcome and appraisal. Asian J Neurosurg. 2020; 15:1016–1019. PMID: 33708680.6. Wang L, Zhang J, Wu Z, et al. Diagnosis and management of adult intracranial neurenteric cysts. Neurosurgery. 2011; 68:44–52. PMID: 21150754.7. Preece MT, Osborn AG, Chin SS, Smirniotopoulos JG. Intracranial neurenteric cysts: imaging and pathology spectrum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1211–1216. PMID: 16775266.8. Anderson T, Kaufman T, Murtagh R. Intracranial neurenteric cyst: a case report and differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions. Radiol Case Rep. 2020; 15:2649–2654. PMID: 33093931.9. Perry A, Scheithauer BW, Zaias BW, Minassian HV. Aggressive enterogenous cyst with extensive craniospinal spread: case report. Neurosurgery. 1999; 44:401–404. PMID: 9932896.10. Gavrjushin AV, Chelushkin DM. Intra-axial neurenteric cyst of medulla: case report and literature review. Cureus. 2021; 13:e15361. PMID: 34239793.11. Nelson SM, Mathis DA, Hobbs JK, Timpone VM. Intracranial neurenteric cyst mimicking an ependymoma: imaging features, pathologic correlation and review of literature. Clin Imaging. 2017; 44:117–120. PMID: 28505503.12. Chen CT, Lai HY, Jung SM, Lee CY, Wu CT, Lee ST. Neurenteric cyst or neuroendodermal cyst? Immunohistochemical study and pathogenesis. World Neurosurg. 2016; 96:85–90. PMID: 27586176.13. Warf BC. Comparison of endoscopic third ventriculostomy alone and combined with choroid plexus cauterization in infants younger than 1 year of age: a prospective study in 550 African children. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:475–481. PMID: 16383244.14. Savage JJ, Casey JN, McNeill IT, Sherman JH. Neurenteric cysts of the spine. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2010; 1:58–63. PMID: 20890417.15. Breeze RE, Nichols P, Segal H, Apuzzo ML. Intradural epithelial cyst at the craniovertebral junction. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1990; 73:788–791. PMID: 2213172.16. Ergun R, Akdemir G, Gezici AR, Kara C, Ergungor F. Craniocervical neurenteric cyst without associated abnormalities. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2000; 32:95–99. PMID: 10838509.17. Koksel T, Revesz T, Crockard HA. Craniospinal neurenteric cyst. Br J Neurosurg. 1990; 4:425–428. PMID: 2261106.18. Menezes AH, Ryken TC. Craniocervical intradural neurenteric cysts. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1995; 22:88–95. PMID: 7710978.19. Mehdi W, Niaz A, Irfan M, Tasdique S, Majeed S. Far lateral transcondylar approach for anterior foramen magnum lesions. Pak J Neurol Surg. 2020; 24:149–155.20. Liu JK, Couldwell WT. Far-lateral transcondylar approach: surgical technique and its application in neurenteric cysts of the cervicomedullary junction: report of two cases. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 19:1–7.21. Menezes AH, Traynelis VC. Spinal neurenteric cysts in the magnetic resonance imaging era. Neurosurgery. 2006; 58:97–105. PMID: 16385333.22. Menezes AH, Dlouhy BJ. Neurenteric cysts at foramen magnum in children: presentation, imaging characteristics, and surgical management—case series and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020; 36:1379–1384. PMID: 32322975.23. Mazur MD, Couldwell WT, Cutler A, et al. Occipitocervical instability after far-lateral transcondylar surgery: a biomechanical analysis. Neurosurgery. 2017; 80:140–145. PMID: 28362894.24. Gauden AJ, Khurana VG, Tsui AE, Kaye AH. Intracranial neuroenteric cysts: a concise review including an illustrative patient. J Clin Neurosci. 2012; 19:352–359. PMID: 22260959.