Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2021 Oct;23(2):121-125. 10.14253/acn.2021.23.2.121.
Refractory Bell’s palsy responding to late treatment with high-dose intravenous steroids
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2521890
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2021.23.2.121
Abstract
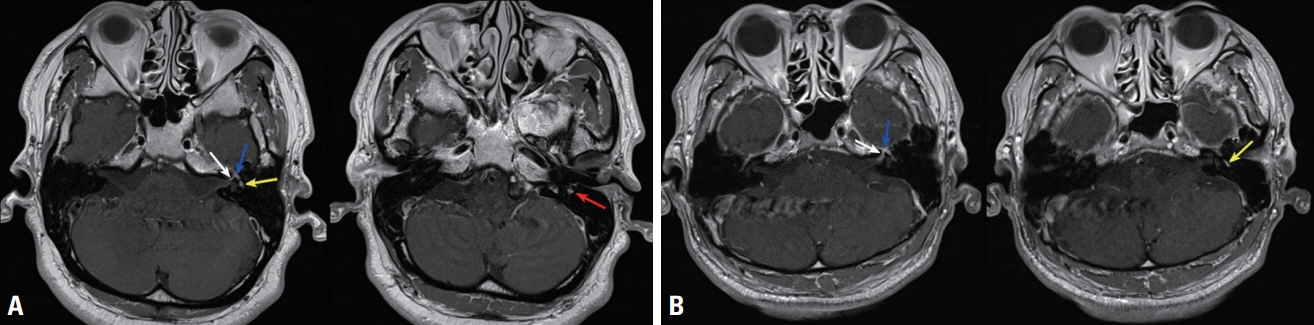
- Bell’s palsy is an acute peripheral facial paralysis with no detectable cause. Although the prognosis of Bell’s palsy is generally good, some patients experience poor recoveries and there is no established treatment for those that do not recover even after receiving the conventional treatment. Here we present two cases of refractory Bell’s palsy with facial nerve enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging who showed symptomatic improvement after the late administration of high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holland NJ, Weiner GM. Recent developments in Bell’s palsy. BMJ. 2004; 329:553–557.
Article2. Peitersen E. Bell’s palsy: the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 2002; (549):4–30.
Article3. Kress B, Griesbeck F, Stippich C, Bähren W, Sartor K. Bell palsy: quantitative analysis of MR imaging data as a method of predicting outcome. Radiology. 2004; 230:504–509.
Article4. Yoo MC, Soh Y, Chon J, Lee JH, Jung J, Kim SS, et al. Evaluation of factors associated with favorable outcomes in adults with Bell palsy. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020; 146:256–263.
Article5. Fisch U. Prognostic value of electrical tests in acute facial paralysis. Am J Otol. 1984; 5:494–498.6. Donati D, De Santi L, Ginanneschi F, Cerase A, Annunziata P. Successful response of non-recovering Ramsay Hunt syndrome to intravenous high dose methylprednisolone. J Neurol Sci. 2012; 318:160–162.
Article7. May M, Blumenthal F, Klein SR. Acute Bell’s palsy: prognostic value of evoked electromyography, maximal stimulation, and other electrical tests. Am J Otol. 1983; 5:1–7.8. Tien RD, Dillon WP. Herpes trigeminal neuritis and rhombencephalitis on Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990; 11:413–414.9. Kim IS, Shin SH, Kim J, Lee WS, Lee HK. Correlation between MRI and operative findings in Bell’s palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Yonsei Med J. 2007; 48:963–968.
Article10. Coutinho AE, Chapman KE. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011; 335:2–13.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Central Serous Chorioretinopathy Associated with Systemic Corticosteroid Treatment of Bell's Palsy
- A Case of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescent Presenting with Bell's Palsy
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Bell’s Palsy
- Update on Medical Management of Acute Peripheral Facial Palsy
- Association Between High Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Delayed Recovery From Bell's Palsy