Korean J Women Health Nurs.
2021 Sep;27(3):230-242. 10.4069/kjwhn.2021.09.13.
The effects of a maternal nursing competency reinforcement program on nursing students’ problem-solving ability, emotional intelligence, self-directed learning ability, and maternal nursing performance in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Research Institute of Nursing Science, Daegu Catholic University
- KMID: 2521518
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2021.09.13
Abstract
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a maternal nursing competency reinforcement program for nursing students and assess the program’s effectiveness in Korea.
Methods
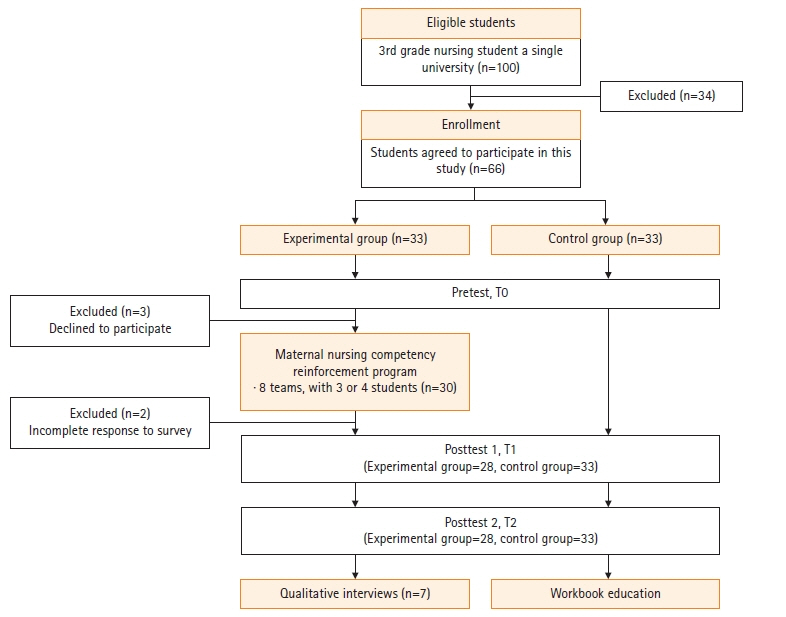
The maternal nursing competency reinforcement program was developed following the ADDIE model. This study employed an explanatory sequential mixed methods design that applied a non-blinded, randomized controlled trial with nursing students (28 experimental, 33 control) followed by open-ended interviews with a subset (n=7). Data were analyzed by both qualitative and quantitative analysis methods.
Results
Repeated measures analysis of variance showed that significant differences according to group and time in maternal nursing performance; assessment of and intervention in postpartum uterine involution and vaginal discharge (F=24.04, p<.001), assessment of and intervention in amniotic membrane rupture (F=36.39, p<.001), assessment of and intervention in delivery process through vaginal examination (F=32.42 p<.001), and nursing care of patients undergoing induced labor (F=48.03 p<.001). Group and time improvements were also noted for problem-solving ability (F=9.73, p<.001) and emotional intelligence (F=4.32 p=.016). There were significant differences between groups in self-directed learning ability (F=13.09 p=.001), but not over time. The three themes derived from content analysis include “learning with a colleague by simulation promotes self-reflection and learning,” “improvement in maternal nursing knowledge and performance by learning various countermeasures,” and “learning of emotionally supportive care, but being insufficient.”
Conclusion
The maternal nursing competency reinforcement program can be effectively utilized to improve maternal nursing performance, problem-solving ability, and emotional intelligence for nursing students.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Choi D. Clinical competence according to experiences on the essential of fundamental nursing skills in nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2014; 20(2):184–191. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2014.20.2.184.
Article2. Lee WS, Kim MO. Effects and adequacy of high-fidelity simulation-based training for obstetrical nursing. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(4):433–443. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.433.
Article3. Yang SH, Hong S. Development and effects of simulation practice program about family centered delivery care. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2017; 23(1):52–61. https://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2017.23.1.52.
Article4. Kim YH, Jang KS. Effect of a simulation-based education on cardio-pulmonary emergency care knowledge, clinical performance ability and problem solving process in new nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(2):245–255. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.245.
Article5. Kim DH, Lee Y, Hwang MS, Park JH, Kim HS, Cha HG. Effects of a simulation-based integrated clinical practice program (SICPP) on the problem solving process, clinical competence and critical thinking in a nursing student. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012; 18(3):499–509. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2012.18.3.499.
Article6. Lee JO. The effects of simulation-based training, underwent before or after the clinical practice for the nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2014; 20(2):203–211. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2014.20.2.203.
Article7. Park HJ, Lee SH. Development and effects of integrated simulation program (maternal-child) for nursing students. Child Health Nurs Res. 2015; 21(4):293–301. https://doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2015.21.4.293.
Article8. Lee SK. The effect of simulation practice education on the clinical judgment, self-confidence and clinical performance ability in nursing student. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2017; 17(11):577–587. https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2017.17.11.577.
Article9. Gatewood E. Use of simulation to increase self-directed learning for nurse practitioner students. J Nurs Educ. 2019; 58(2):102–106. https://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20190122-07.
Article10. World Ecomomic Forum. New vision for education: fostering social and emotional learning through technology [Internet]. Geneva: World Economic Forum;2016. [cited 2020 Oct 12]. Available from: http://hdl.voced.edu.au/10707/443447.11. Al-Hamdan Z, Oweidat IA, Al-Faouri I, Codier E. Correlating emotional intelligence and job performance among jordanian hospitals’ registered nurses. Nurs Forum. 2017; 52(1):12–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/nuf.12160.
Article12. Han SH. Factors affecting problem solving ability among nursing students. AJMAHS. 2017; 7(5):245–254. https://doi.org/10.35873/ajmahs.2017.7.5.023.
Article13. Brown AH, Green TD. The essentials of instructional design: connecting fundamental principles with process and practice. 4th ed. New York, NY: Routledge;2019. p. 292.14. Creswell JW, Clark VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications;2017. p. 190–123.15. Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Trials. 2010; 11:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-11-32.
Article16. Song YA, Son YJ. Effects of simulation-based practice education for core skill of maternity nursing. Korean Parent-Child Health J. 2013; 16(1):37–44.17. Lee J, Son HK. Comparison of learning transfer using simulation problem-based learning and demonstration: an application of papanicolaou smear nursing education. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041765.
Article18. Lee WS, Park SH, Choi EY. Development of a Korean problem solving process inventory for adults. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2008; 15(4):548–557.19. Wong CS, Law KS. The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude: an exploratory study. Leadersh Q. 2002; 13(3):243–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1048-9843(02)00099-1.
Article20. Jung HW, Jung DS. A study on the effect of emotional intelligence on organizational commitment in the Korean firm organization. Soc Sci Res. 2007; 23(2):325–348.21. Lee S, Chang Y, Lee H, Park K. A study on the development of life-skills: communication. problem solving, and self-directed learning. Seoul: Korean Educational Development Institute;2003.22. Hsieh HF, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005; 15(9):1277–1288. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732305276687.
Article23. Hall SW. High-fidelity simulation for senior maternity nursing students. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2015; 36(2):124–127. https://doi.org/10.5480/12-996.1.
Article24. Song YA. Effect of simulation-based practice by applying problem based learning on problem solving process, self-confidence in clinical performance and nursing competence. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2014; 20(4):246–254. https://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2014.20.4.246.
Article25. Oh PJ, Jeon KD, Koh MS. The effects of simulation-based learning using standardized patients in nursing students: a meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2015; 35(5):e6–e15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2015.01.019.
Article26. Carragher J, Gormley K. Leadership and emotional intelligence in nursing and midwifery education and practice: a discussion paper. J Adv Nurs. 2017; 73(1):85–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.13141.
Article27. Foster K, McCloughen A, Delgado C, Kefalas C, Harkness E. Emotional intelligence education in pre-registration nursing programmes: an integrative review. Nurse Educ Today. 2015; 35(3):510–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2014.11.009.
Article28. Aghajani Inche Kikanloo A, Jalali K, Asadi Z, Shokrpour N, Amiri M, Bazrafkan L. Emotional intelligence skills: is nurses' stress and professional competence related to their emotional intelligence training? A quasi experimental study. J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2019; 7(3):138–143. https://doi.org/10.30476/JAMP.2019.74922.
Article29. Sandars J, Walsh K. Self-directed learning. Educ Prim Care. 2016; 27(2):151–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/14739879.2016.1149956.
Article30. Noh GO, Kim DH. Effectiveness of a self-directed learning program using blended coaching among nursing students in clinical practice: a quasi-experimental research design. BMC Med Educ. 2019; 19(1):225. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1672-1.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Jigsaw Cooperation Learning on Communication Ability, Problem Solving Ability, Critical Thinking Disposition, Self-directed Learning Ability and Cooperation of Nursing Students
- Effects of Task Performance Style in Nursing Management Practicum on Problem-Solving and Nursing Competency according to Communication Ability of Nursing Students
- The Effects of Learning Styles and Nursing Professional Attitude on Problem-Solving Ability among Nursing Students
- Metacognition, Learning Flow and Problem Solving Ability in Nursing Simulation Learning
- The Effect of Case-based Learning (CBL) on Critical Thinking Disposition, Communication Ability, Problem Solving Ability and Self-directed Learning Ability of Nursing Students in Pathophysiology Course