Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Oct;78(4):249-251. 10.4166/kjg.2021.088.
Esophageal Involvement of Bullous Pemphigoid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2521501
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.088
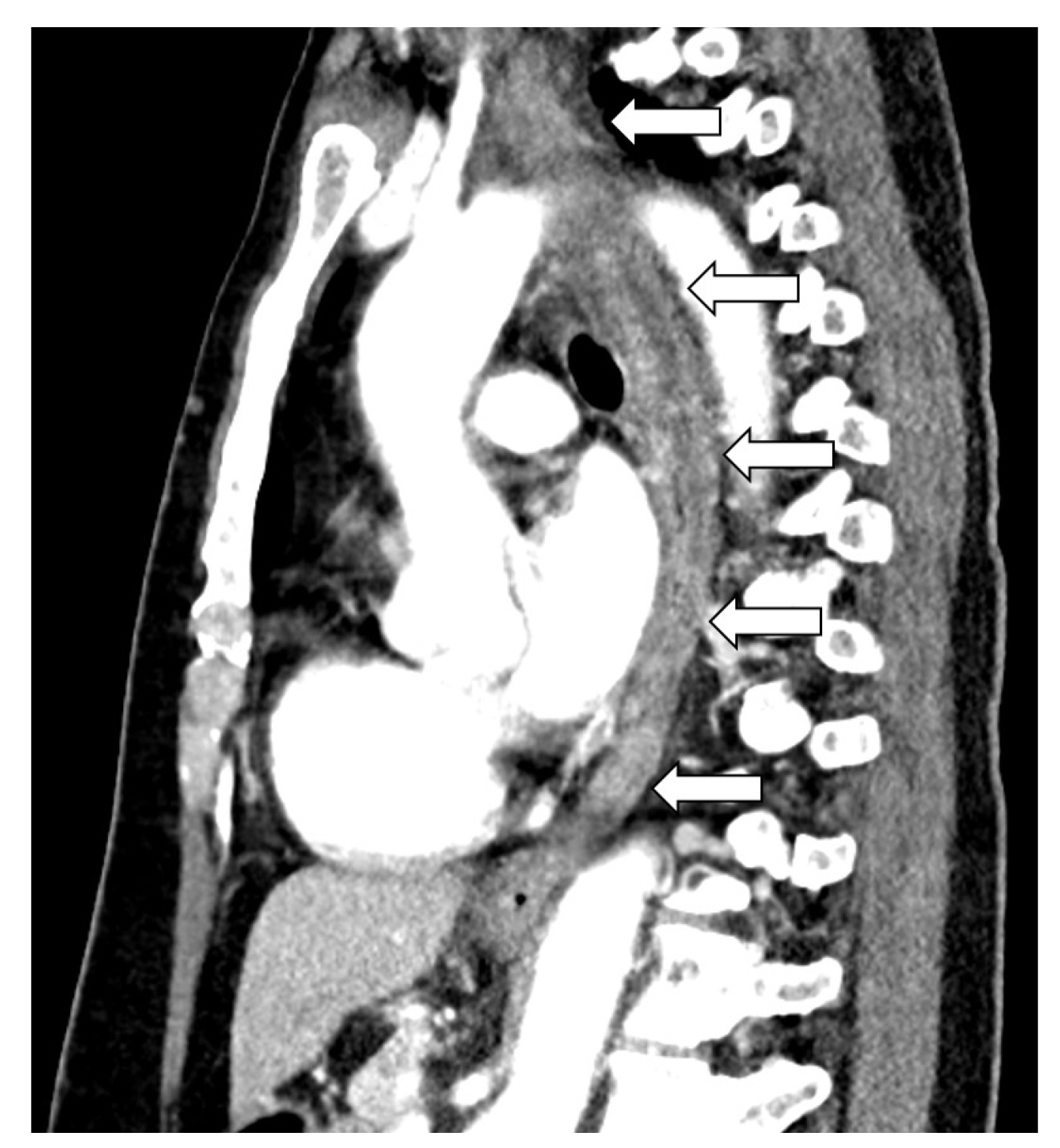
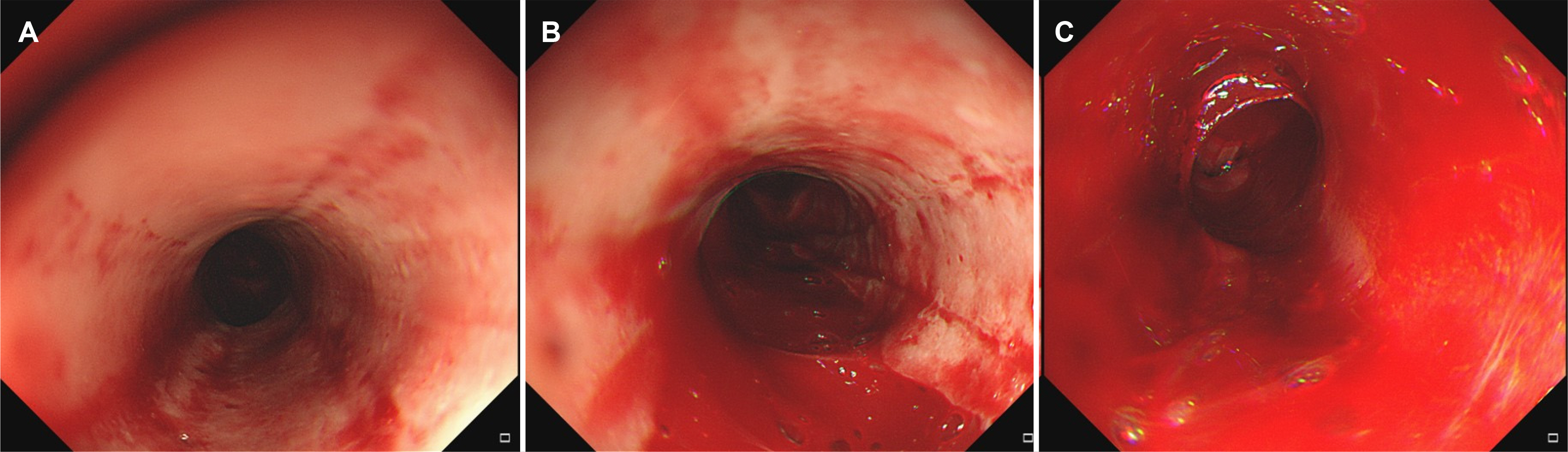
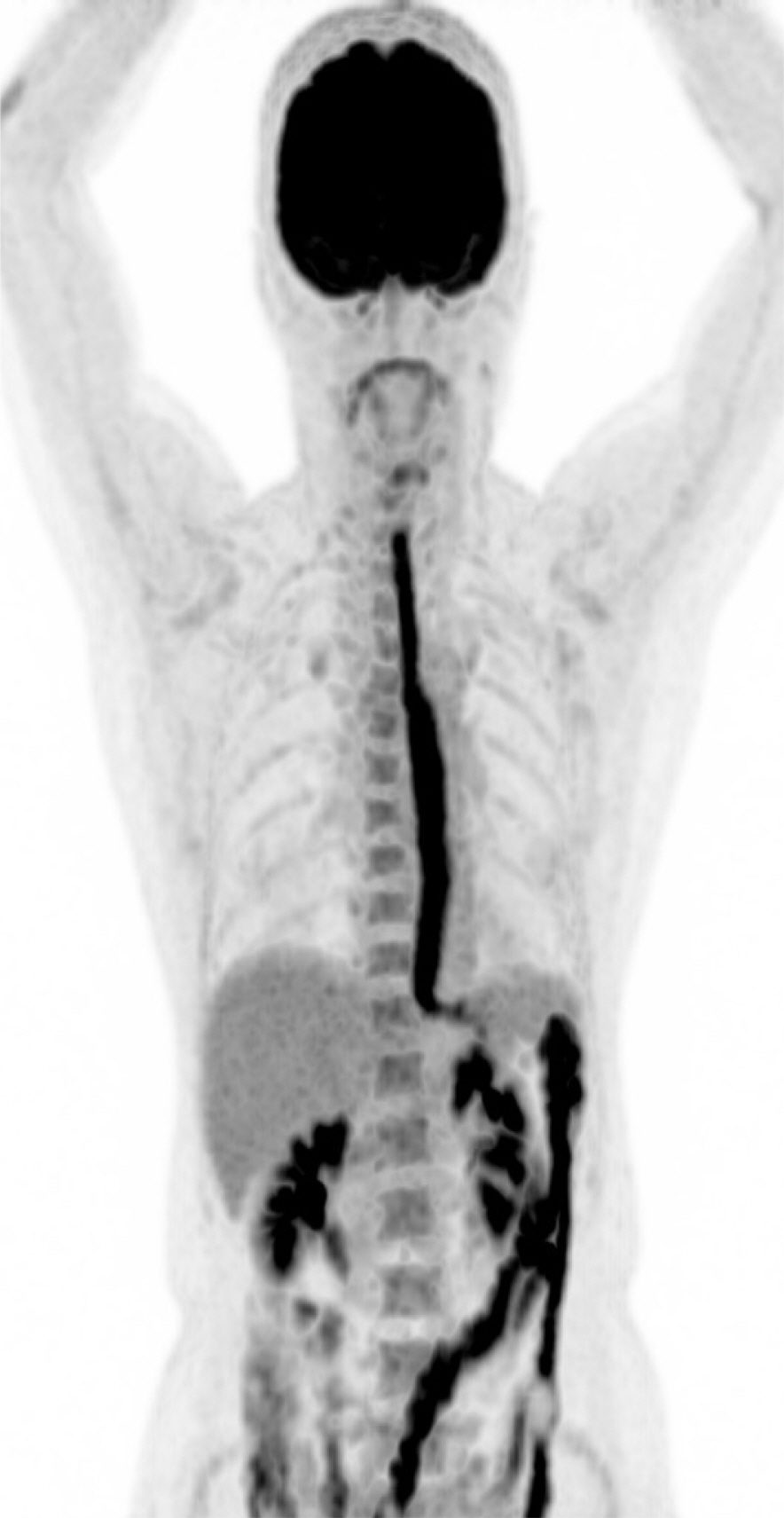
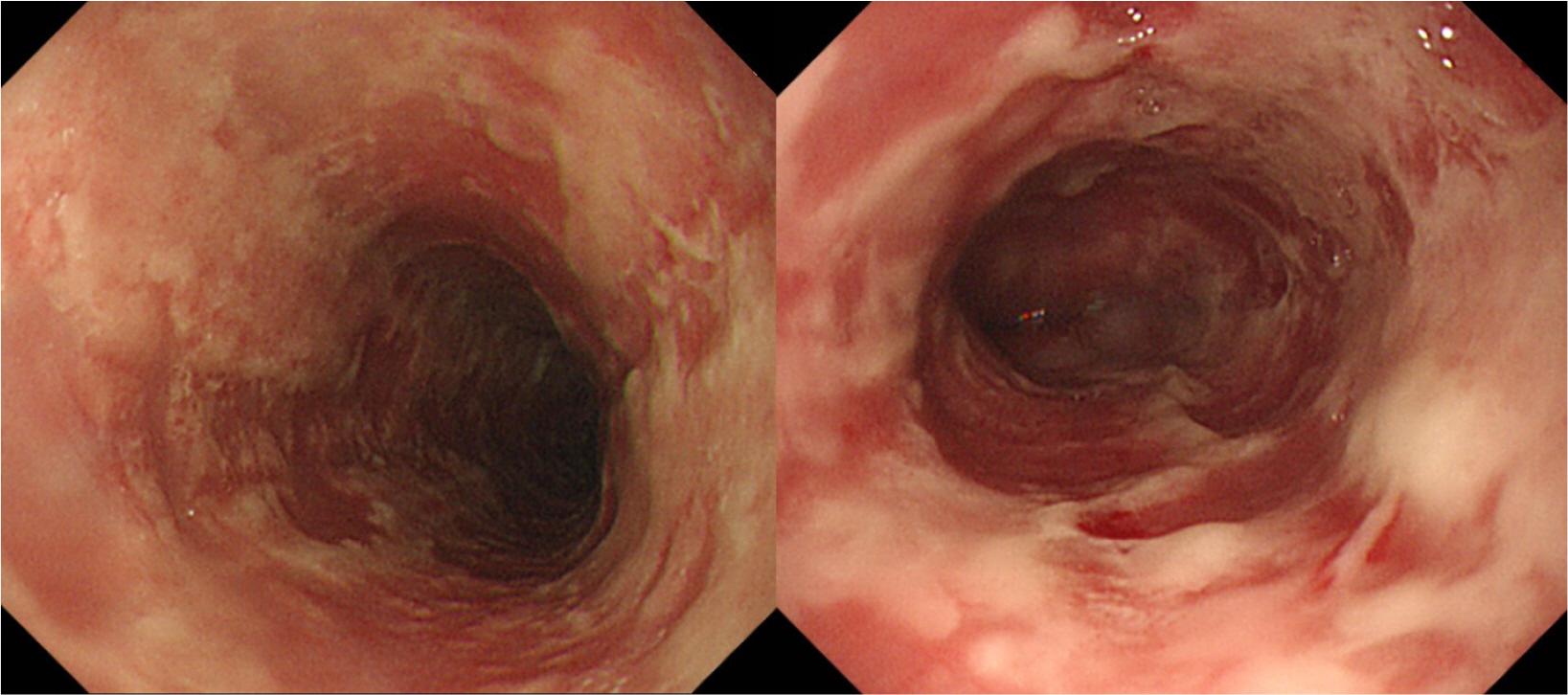
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clapé A, Muller C, Gatouillat G, et al. 2018; Mucosal involvement in bullous pemphigoid is mostly associated with disease severity and to absence of anti-BP230 autoantibody. Front Immunol. 9:479. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00479. PMID: 29662486. PMCID: PMC5890137.
Article2. Kim BD, Kim SC. 2005; Clinical study of Korean patients with pemphigus. Korean J Dermatol. 43:1077–1084.3. Miyamoto D, Santi CG, Aoki V, Maruta CW. 2019; Bullous pemphigoid. An Bras Dermatol. 94:133–146. DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20199007. PMID: 31090818. PMCID: PMC6486083.
Article4. Ghoneim S, Shah A, Calderon A. 2019; Esophageal Nikolsky's sign: a rare finding in a patient with bullous pemphigoid. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 13:445–449. DOI: 10.1159/000503898. PMID: 31762733. PMCID: PMC6873001.
Article5. Kim KO, Jang BI, Eun JR, Kim TN. 2007; A case of esophageal bullous pemphigoid manifestated by upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 24(Suppl 2):S671–S675. DOI: 10.12701/yujm.2007.24.2S.S671.
Article6. Hwang JY, Park KS, Cho KB, Hwang JS, Ahn SH. 2004; Esophageal mucosal desquamation with hemorrhage in bullous pemphigoid: a case report. Korean J Gastroenterol. 43:264–267.7. Kim YC, Chung WC, Kang SJ, et al. 2007; A case of esophageal involvement in pemphigus vulgaris. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 35:159–164.8. Kneisel A, Hertl M. 2011; Autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Part 1: clinical manifestations. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 9:844–857. DOI: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2011.07793.x. PMID: 21955378.
Article9. Zehou O, Raynaud JJ, Le Roux-Villet C, et al. 2017; Oesophageal involvement in 26 consecutive patients with mucous membrane pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 177:1074–1085. DOI: 10.1111/bjd.15592. PMID: 28417469.
Article10. McFarlane M, Azam A, Snead D, Disney B. 2019; Oesophageal pemphigoid: a rare cause of dysphagia. Clin J Gastroenterol. 12:25–28. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-018-0897-6. PMID: 30141184.
Article11. Nagashima R, Tsuge K, Harada M, Katagiri Y, Shinzawa H, Takahashi T. 2000; Endoscopic hemostasis of hemorrhage from esophageal bullous pemphigoid. Gastrointest Endosc. 52:433–434. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2000.108297. PMID: 10968870.
Article12. Gaspar R, Moutinho-Ribeiro P, Macedo G. 2017; Bullous pemphigoid: extensive esophageal involvement. Gastrointest Endosc. 86:400–402. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.02.015. PMID: 28238716.
Article13. Seo PG, Choi WW, Chung JH. 2003; Pemphigus in Korea: clinical manifestations and treatment protocol. J Dermatol. 30:782–788. DOI: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2003.tb00478.x. PMID: 14684934.
Article14. Brick KE, Weaver CH, Lohse CM, et al. 2014; Incidence of bullous pemphigoid and mortality of patients with bullous pemphigoid in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1960 through 2009. J Am Acad Dermatol. 71:92–99. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.02.030. PMID: 24704091. PMCID: PMC4324601.
Article15. Lee JH, Kim SC. 2014; Mortality of patients with bullous pemphigoid in Korea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 71:676–683. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.05.006. PMID: 24930586.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coexistence of Bullous Pemphigoid and Psoriasis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Bullous Pemphigoid Associated with Prostate Adenocarcinoma
- Esophageal Mucosal Desquamation with Hemorrhage in Bullous Pemphigoid: A Case Report
- A Case of Dyshidrosiform Pemphigoid
- Atypical Variant of Bullous Pemphigoid: Prolonged Eruptions of Papulourticarial Lesions