Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Oct;78(4):240-244. 10.4166/kjg.2021.079.
Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Diagnosed Using Neonatal Cholestasis Gene Panel
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2521499
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.079
Abstract
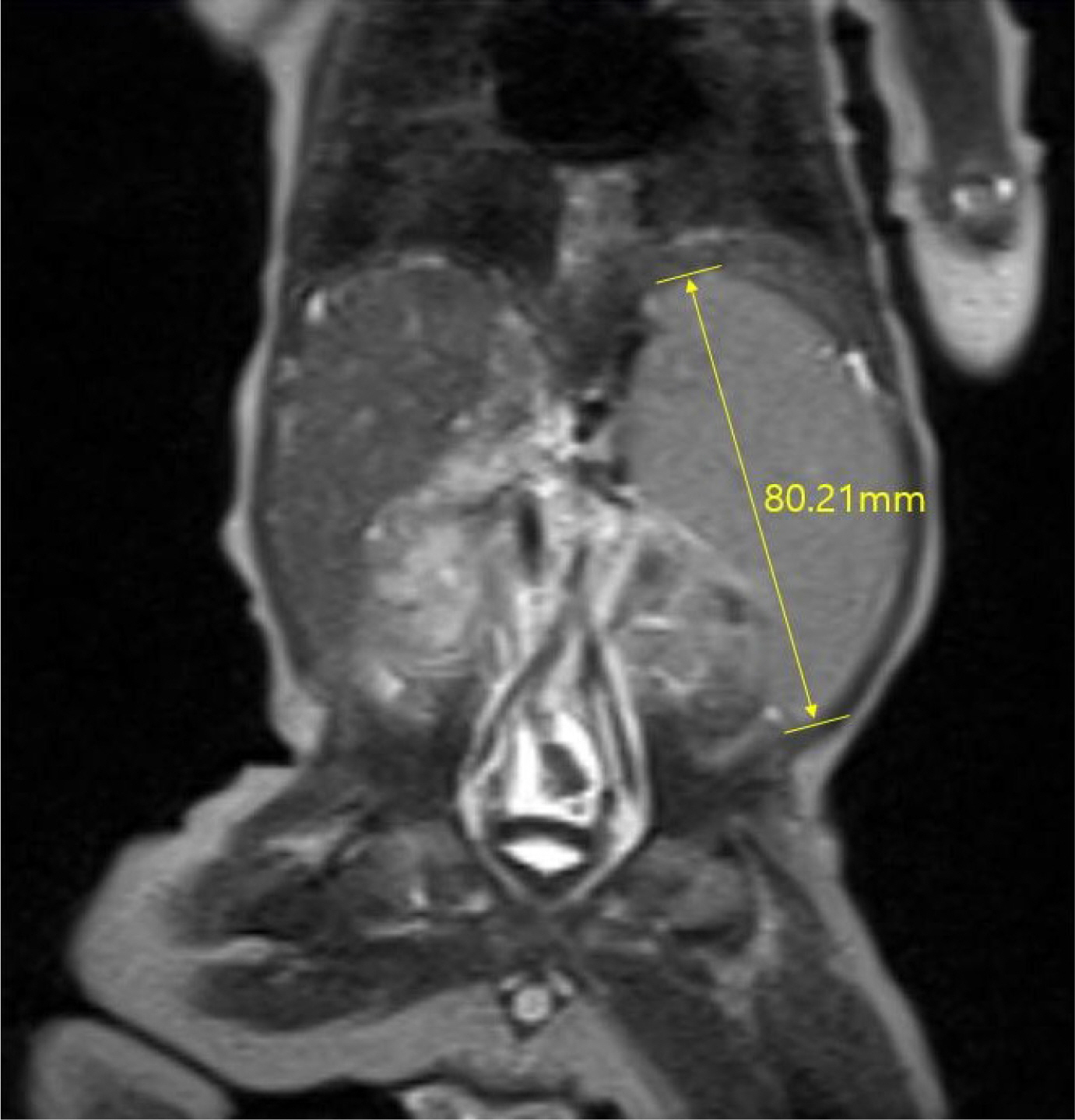
- Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a neurovisceral lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the NPC1 and NPC2 genes. These mutations cause the accumulation of unesterified cholesterol and other lipids in the lysosomes. NPC has a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, depending on the age of onset. A 15-day-old infant presented at the Seoul National University Children's Hospital with neonatal cholestasis and hepatosplenomegaly, with the onset of jaundice at 5 days of age. Despite supportive treatment, the patient was considered for a liver transplant because of progressive liver failure. Unfortunately, the patient died from gastrointestinal bleeding before undergoing the transplant. The neonatal cholestasis gene panel revealed two novel likely pathogenic variants in the NPC1 gene (c.1145C>G [p.Ser382*] and c.2231_2233del [p.Val744del]). The patient was diagnosed with NPC, and both parents were found to be carriers of each variant. In infants presenting with neonatal cholestasis, a gene panel can help diagnose NPC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Patterson M. Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, editors. 2000. Niemann-Pick disease type C. GeneReviews®. University of Washington;Seattle (WA):
Article2. Rosenbaum AI, Maxfield FR. 2011; Niemann-Pick type C disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches. J Neurochem. 116:789–795. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06976.x. PMID: 20807315. PMCID: PMC3008286.
Article3. Vanier MT. 2010; Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 5:16. DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-5-16. PMID: 20525256. PMCID: PMC2902432.
Article4. Geberhiwot T, Moro A, Dardis A, et al. 2018; Consensus clinical management guidelines for Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 13:50. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0785-7. PMID: 29625568. PMCID: PMC5889539.
Article5. Jeong MH, Ko JM, Kim GH, Yoo HW. 2007; Molecular diagnosis of Niemann-Pick type C presenting with neonatal cholestasis and hepatosplenomegaly. J Genet Med. 4:200–203.6. Ko EJ, Sung IY, Yoo HW. 2019; Niemann-Pick disease type C misdiagnosed as cerebral palsy: a case report. Ann Rehabil Med. 43:621–624. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.5.621. PMID: 31693851. PMCID: PMC6835131.
Article7. Spiegel R, Raas-Rothschild A, Reish O, et al. The clinical spectrum of fetal Niemann-Pick type C. Am J Med Genet A. 2009; 149A:446–450. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32642. PMID: 19206179.
Article8. Vanier MT, Millat G. 2003; Niemann-Pick disease type C. Clin Genet. 64:269–281. DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.2003.00147.x. PMID: 12974729.
Article9. Pineda M, Walterfang M, Patterson MC. 2018; Miglustat in Niemann-Pick disease type C patients: a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 13:140. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0844-0. PMID: 30111334. PMCID: PMC6094874.
Article10. Feldman AG, Sokol RJ. 2019; Neonatal cholestasis: emerging molecular diagnostics and potential novel therapeutics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:346–360. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0132-z. PMID: 30903105.
Article11. Yamada N, Inui A, Sanada Y, et al. 2019; Pediatric liver transplantation for neonatal-onset Niemann-Pick disease type C: Japanese multicenter experience. Pediatr Transplant. 23:e13462. DOI: 10.1111/petr.13462.
Article12. Bountouvi E, Papadopoulou A, Vanier MT, et al. 2017; Novel NPC1 mutations with different segregation in two related Greek patients with Niemann-Pick type C disease: molecular study in the extended pedigree and clinical correlations. BMC Med Genet. 18:51. DOI: 10.1186/s12881-017-0409-4. PMID: 28472934. PMCID: PMC5415950.
Article13. Park WD, O'Brien JF, Lundquist PA, et al. 2003; Identification of 58 novel mutations in Niemann-Pick disease type C: correlation with biochemical phenotype and importance of PTC1-like domains in NPC1. Hum Mutat. 22:313–325. DOI: 10.1002/humu.10255. PMID: 12955717.14. Srivastava A. 2014; Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4:25–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.10.005. PMID: 25755532. PMCID: PMC4017198.
Article15. Matte U, Mourya R, Miethke A, et al. 2010; Analysis of gene mutations in children with cholestasis of undefined etiology. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 51:488–493. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181dffe8f. PMID: 20683201. PMCID: PMC4090691.
Article16. Togawa T, Sugiura T, Ito K, et al. 2016; Molecular genetic dissection and neonatal/infantile intrahepatic cholestasis using targeted next-generation sequencing. J Pediatr. 171:171–177.e74. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.01.006. PMID: 26858187.
Article17. Wang NL, Lu YL, Zhang P, et al. 2016; A specially designed multi-gene panel facilitates genetic diagnosis in children with intrahepatic cholestasis: simultaneous test of known large insertions/deletions. PLoS One. 11:e0164058. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164058. PMID: 27706244. PMCID: PMC5051675.
Article