Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Oct;78(4):205-212. 10.4166/kjg.2021.121.
Recent Updates on Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiography-guided Intraductal Radiofrequency Ablation for Malignant Biliary Stricture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2521494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.121
Abstract
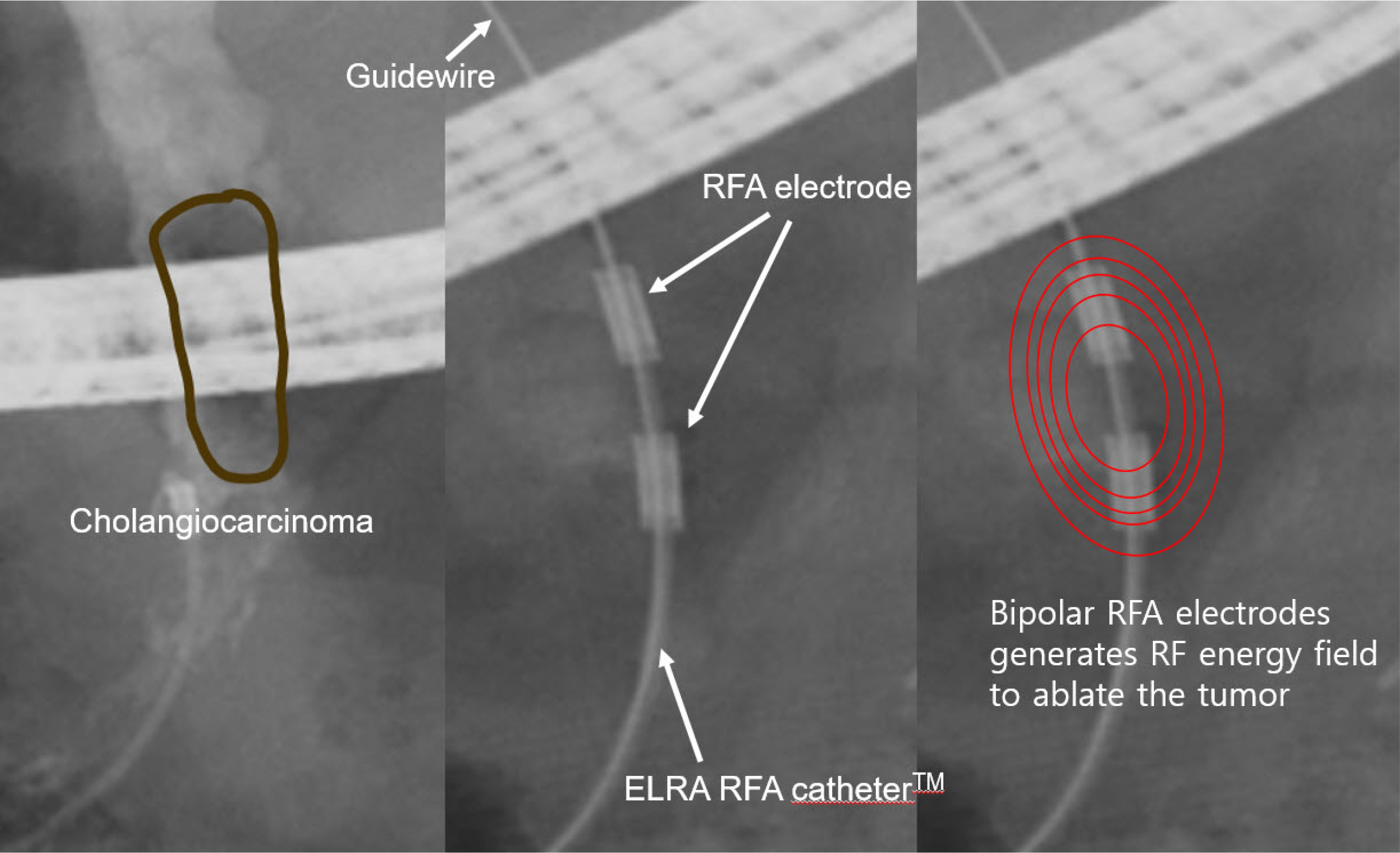
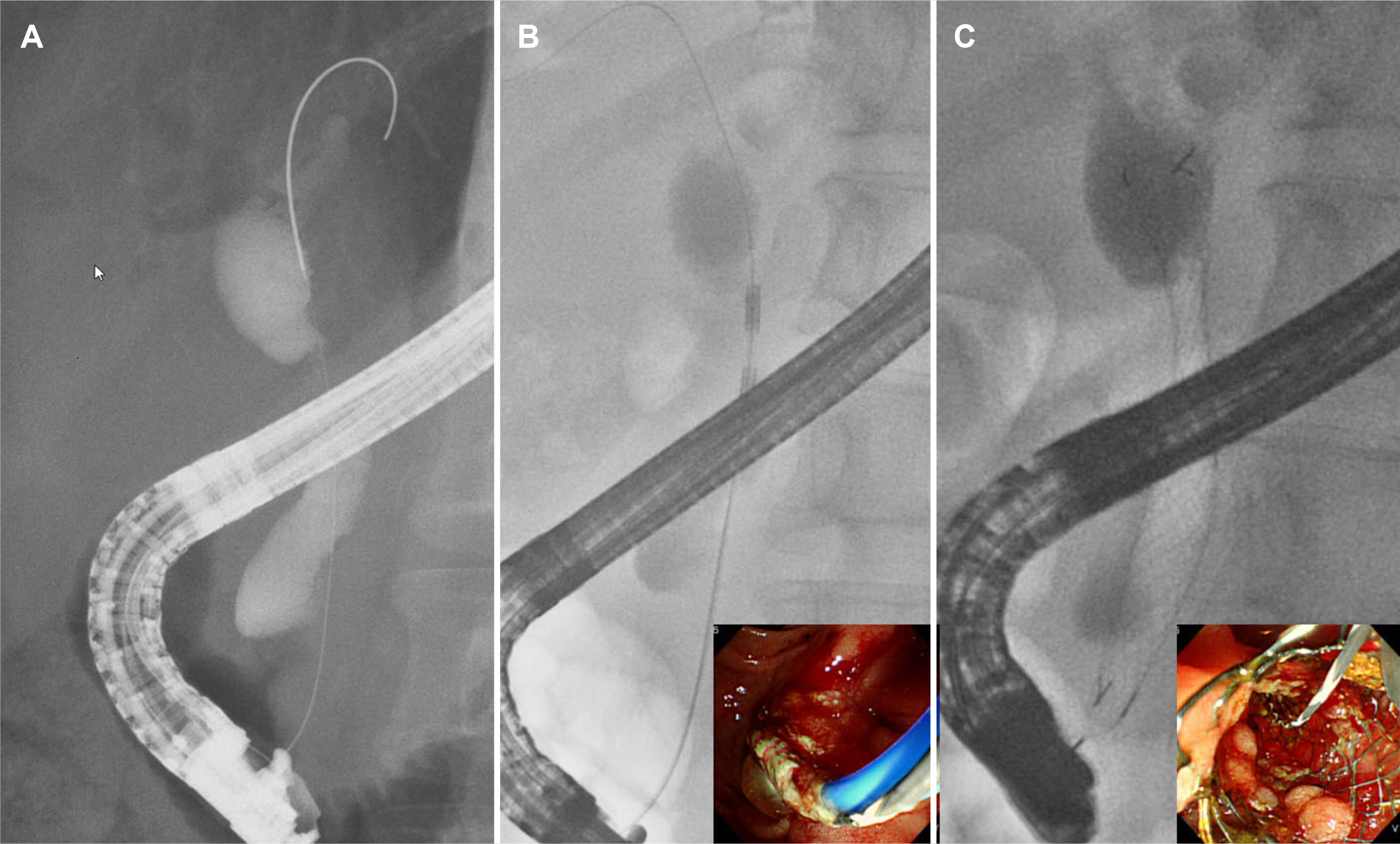
- Malignant biliary strictures are caused by pancreatobiliary cancer and other metastatic malignancies. Most of them are unresectable at diagnosis with a dismal prognosis. Various new ablation methods have been introduced. Of them, ERCP-guided intraductal radiofrequency ablation (ID-RFA) appears to be the most promising minimally invasive endoscopic treatment by delivering a high-frequency alternating current to the target tissue, leading to coagulative necrosis. Thus far, many studies have provided evidence that ERCP-guided ID-RFA is a safe, feasible, and effective treatment modality for stent patency and overall survival. Compared to other ablation treatments, ERCP-guided ID-RFA has several advantages, including ease of delivery, controlled application of thermal energy, low cost, and fewer systemic side effects with an acceptable safety profile. Therefore, ERCP-guided ID-RFA can be considered an adjunctive treatment for the palliation of unresectable malignant biliary strictures. On the other hand, the decision of local ablation treatment should be individualized by multidisciplinary team support due to the lack of comparative studies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah DR, Green S, Elliot A, McGahan JP, Khatri VP. 2013; Current oncologic applications of radiofrequency ablation therapies. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 5:71–80. DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i4.71. PMID: 23671734. PMCID: PMC3648666.
Article2. Yousaf MN, Ehsan H, Muneeb A, et al. 2021; Role of radiofrequency ablation in the management of unresectable pancreatic cancer. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:624997. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.624997. PMID: 33644089. PMCID: PMC7904870.
Article3. Testoni SGG, Healey AJ, Dietrich CF, Arcidiacono PG. 2020; Systematic review of endoscopy ultrasound-guided thermal ablation treatment for pancreatic cancer. Endosc Ultrasound. 9:83–100. DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_74_19. PMID: 32295966. PMCID: PMC7279078.
Article4. Cho JH, Jang SI, Lee DK. 2020; Recent developments in endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation for pancreatic lesions. Int J Gastrointest Interv. 9:170–176. DOI: 10.18528/ijgii200030.
Article5. Brace C. 2011; Thermal tumor ablation in clinical use. IEEE Pulse. 2:28–38. DOI: 10.1109/MPUL.2011.942603. PMID: 25372967. PMCID: PMC4226271.
Article6. Friedman M, Mikityansky I, Kam A, et al. 2004; Radiofrequency ablation of cancer. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 27:427–434. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-004-0062-0. PMID: 15383844. PMCID: PMC2408956.
Article7. Zacharoulis D, Lazoura O, Sioka E, et al. 2013; Habib EndoHPB: a novel endobiliary radiofrequency ablation device. An experimental study. J Invest Surg. 26:6–10. DOI: 10.3109/08941939.2012.681832. PMID: 23273142.
Article8. Itoi T, Isayama H, Sofuni A, et al. 2012; Evaluation of effects of a novel endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation biliary catheter using an ex-vivo pig liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 19:543–547. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-011-0465-7. PMID: 22038500.
Article9. Cho JH, Lee KH, Kim JM, Kim YS, Lee DH, Jeong S. 2017; Safety and effectiveness of endobiliary radiofrequency ablation according to the different power and target temperature in a swine model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 32:521–526. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13472. PMID: 27300312.
Article10. Cho JH, Jeong S, Kim EJ, Kim JM, Kim YS, Lee DH. 2018; Long-term results of temperature-controlled endobiliary radiofrequency ablation in a normal swine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 87:1147–1150. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.09.013. PMID: 28958907.
Article11. Kim EJ, Cho JH, Kim YJ, et al. 2019; Intraductal temperature-controlled radiofrequency ablation in malignant hilar obstruction: a preliminary study in animals and initial human experience. Endosc Int Open. 7:E1293–E1300. DOI: 10.1055/a-0970-9005. PMID: 31595223. PMCID: PMC6779589.
Article12. Kasugai H, Osaki Y, Oka H, Kudo M, Seki T. Osaka Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007; Severe complications of radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: an analysis of 3,891 ablations in 2,614 patients. Oncology. 72(Suppl 1):72–75. DOI: 10.1159/000111710. PMID: 18087185.
Article13. Lao OB, Farjah F, Flum DR, Yeung RS. 2009; Adverse events after radio-frequency ablation of unresectable liver tumors: a single-center experience. Am J Surg. 198:76–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.09.025. PMID: 19285299.
Article14. Tal AO, Vermehren J, Friedrich-Rust M, et al. 2014; Intraductal endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hilar non-resectable malignant bile duct obstruction. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 6:13–19. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i1.13. PMID: 24527176. PMCID: PMC3921441.
Article15. Dolak W, Schreiber F, Schwaighofer H, et al. 2014; Endoscopic radio-frequency ablation for malignant biliary obstruction: a nationwide retrospective study of 84 consecutive applications. Surg Endosc. 28:854–860. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-013-3232-9. PMID: 24196547.
Article16. Sharaiha RZ, Sethi A, Weaver KR, et al. 2015; Impact of radiofrequency ablation on malignant biliary strictures: results of a collaborative registry. Dig Dis Sci. 60:2164–2169. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-015-3558-3. PMID: 25701319.
Article17. Laleman W, van der Merwe S, Verbeke L, et al. 2017; A new intraductal radiofrequency ablation device for inoperable biliopancreatic tumors complicated by obstructive jaundice: the IGNITE-1 study. Endoscopy. 49:977–982. DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-113559. PMID: 28732391.
Article18. Yang J, Wang J, Zhou H, et al. 2018; Efficacy and safety of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a randomized trial. Endoscopy. 50:751–760. DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-124870. PMID: 29342492.
Article19. Lee YN, Jeong S, Choi HJ, et al. 2019; The safety of newly developed automatic temperature-controlled endobiliary radiofrequency ablation system for malignant biliary strictures: a prospective multi-center study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 34:1454–1459. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14657. PMID: 30861593.
Article20. Kim EJ, Chung DH, Kim YJ, et al. 2018; Endobiliary radiofrequency ablation for distal extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a clinicopathological study. PLoS One. 13:e0206694. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206694. PMID: 30439965. PMCID: PMC6237299.
Article21. Steel AW, Postgate AJ, Khorsandi S, et al. 2011; Endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation appears to be safe in the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 73:149–153. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.09.031. PMID: 21184881.
Article22. Figueroa-Barojas P, Bakhru MR, Habib NA, et al. 2013; Safety and efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in the management of unresectable bile duct and pancreatic cancer: a novel palliation technique. J Oncol. 2013:910897. DOI: 10.1155/2013/910897. PMID: 23690775. PMCID: PMC3649248.
Article23. Alis H, Sengoz C, Gonenc M, Kalayci MU, Kocatas A. 2013; Endobiliary radiofrequency ablation for malignant biliary obstruction. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 12:423–427. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(13)60066-1.
Article24. Kallis Y, Phillips N, Steel A, et al. 2015; Analysis of endoscopic radio-frequency ablation of biliary malignant strictures in pancreatic cancer suggests potential survival benefit. Dig Dis Sci. 60:3449–3455. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-015-3731-8. PMID: 26038094.
Article25. Laquière A, Boustière C, Leblanc S, Penaranda G, Désilets E, Prat F. 2016; Safety and feasibility of endoscopic biliary radiofrequency ablation treatment of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Endosc. 30:1242–1248. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-015-4322-7. PMID: 26162420.
Article26. Wang F, Li Q, Zhang X, et al. 2016; Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for malignant biliary strictures. Exp Ther Med. 11:2484–2488. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3235. PMID: 27284336. PMCID: PMC4888002.
Article27. Schmidt A, Bloechinger M, Weber A, et al. 2016; Short-term effects and adverse events of endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation appear to be comparable with photodynamic therapy in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. United European Gastroenterol J. 4:570–579. DOI: 10.1177/2050640615621235. PMID: 27536367. PMCID: PMC4971790.
Article28. Sharaiha RZ, Natov N, Glockenberg KS, Widmer J, Gaidhane M, Kahaleh M. 2014; Comparison of metal stenting with radio-frequency ablation versus stenting alone for treating malignant biliary strictures: is there an added benefit? Dig Dis Sci. 59:3099–3102. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-014-3264-6. PMID: 25033929.
Article29. Kong YL, Zhang HY, Liu CL, et al. Improving biliary stent patency for malignant obstructive jaundice using endobiliary radio-frequency ablation: experience in 150 patients. Surg Endosc. 2021; Mar. 31. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-021-08457-3.
Article30. Xia MX, Wang SP, Yuan JG, et al. Effect of endoscopic radio-frequency ablation on the survival of patients with inoperable malignant biliary strictures: a large cohort study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021; Apr. 8. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.960. PMID: 33829657.
Article31. Sofi AA, Khan MA, Das A, et al. 2018; Radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement versus stent placement alone for malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 87:944–951.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.10.029. PMID: 29108980.32. Kang H, Chung MJ, Cho IR, et al. 2021; Efficacy and safety of palliative endobiliary radiofrequency ablation using a novel temperature-controlled catheter for malignant biliary stricture: a single-center prospective randomized phase II TRIAL. Surg Endosc. 35:63–73. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-020-07689-z. PMID: 32488654.
Article33. Gao DJ, Yang JF, Ma SR, et al. 2021; Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation plus plastic stent placement versus stent placement alone for unresectable extrahepatic biliary cancer: a multi-center randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 94:91–100.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.12.016. PMID: 33359435.
Article34. Hu B, Sun B, Gao DJ, et al. 2020; Initial experience of ERCP-guided radio-frequency ablation as the primary therapy for inoperable ampullary carcinomas. Dig Dis Sci. 65:1453–1459. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-019-05849-3. PMID: 31562610.
Article35. Yang J, Wang J, Zhou H, et al. 2020; Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation plus a novel oral 5-fluorouracil compound versus radiofrequency ablation alone for unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 92:1204–1212.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.04.075. PMID: 32437711.36. Bokemeyer A, Matern P, Bettenworth D, et al. 2019; Endoscopic radio-frequency ablation prolongs survival of patients with unresectable hilar cholangiocellular carcinoma - a case-control study. Sci Rep. 9:13685. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-50132-0. PMID: 31548703. PMCID: PMC6757045.
Article37. Rustagi T, Irani S, Reddy DN, et al. 2017; Radiofrequency ablation for intraductal extension of ampullary neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 86:170–176. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.11.002. PMID: 27866907.38. Camus M, Napol?on B, Vienne A, et al. 2018; Efficacy and safety of endobiliary radiofrequency ablation for the eradication of residual neoplasia after endoscopic papillectomy: a multicenter prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 88:511–518. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2018.04.2332. PMID: 29660322.
Article39. Cho JH. 2021; Intraductal radiofrequency ablation for residual adenoma after endoscopic papillectomy: an additional treatment modality expected to be safe and effective. Gut Liver. 15:151–152. DOI: 10.5009/gnl210080. PMID: 33716222. PMCID: PMC7960971.
Article40. Choi YH, Yoon SB, Chang JH, Lee IS. 2021; The safety of radio-frequency ablation using a novel temperature-controlled probe for the treatment of residual intraductal lesions after endoscopic papillectomy. Gut Liver. 15:307–314. DOI: 10.5009/gnl20043. PMID: 32616684. PMCID: PMC7960966.
Article41. So H, Oh CH, Song TJ, et al. 2021; Feasibility and safety of endoluminal radiofrequency ablation as a rescue treatment for bilateral metal stent obstruction due to tumor ingrowth in the hilum: a pilot study. J Clin Med. 10:952. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10050952. PMID: 33804429. PMCID: PMC7957686.
Article42. Nayar MK, Oppong KW, Bekkali NLH, Leeds JS. 2018; Novel temperature-controlled RFA probe for treatment of blocked metal biliary stents in patients with pancreaticobiliary cancers: initial experience. Endosc Int Open. 6:E513–E517. DOI: 10.1055/s-0044-102097. PMID: 29713676. PMCID: PMC5906122.
Article43. Strand DS, Cosgrove ND, Patrie JT, et al. 2014; ERCP-directed radio-frequency ablation and photodynamic therapy are associated with comparable survival in the treatment of unresectable cholangiocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 80:794–804. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.02.1030. PMID: 24836747.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A review of the recent advances in endoscopic retrograde cholangiography-guided intraductal radiofrequency ablation for malignant biliary strictures
- Intraductal Radiofrequency Ablation as a Palliative Treatment for Advanced Malignant Hilar Biliary Obstruction
- A Case of Direct Peroral Cholangioscopy-Guided Intraductal Radiofrequency Ablation for Malignancy Biliary Obstruction via Choledochoduodenostomy Orifice
- Recent Update of Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation for Pancreatobiliary Disease
- Recent advances of diagnostic approaches for indeterminate biliary tract obstruction