Diabetes Metab J.
2021 Sep;45(5):795-795. 10.4093/dmj.2021.0256.
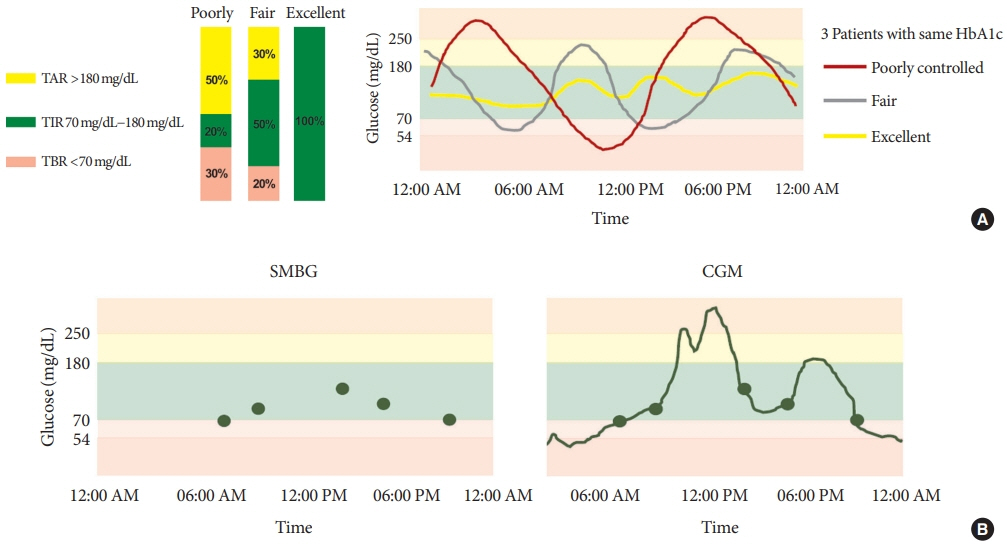
Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2520864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0256
Figure
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Changes in metrics of continuous glucose monitoring during COVID-19 in Korean children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Application of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGMS) and Patient Education
- Importance of continuous glucose monitoring in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
- Use of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Patients on Intensive Insulin Treatment