Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Sep;78(3):183-187. 10.4166/kjg.2021.071.
Acute Abdominal Pain due to Accessory Splenic Infarction in an Adult: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 2Departments of Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 3Departments of Pathology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 4Departments of Radiology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 5Departments of Nuclear Medicine , Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- KMID: 2520360
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.071
Abstract
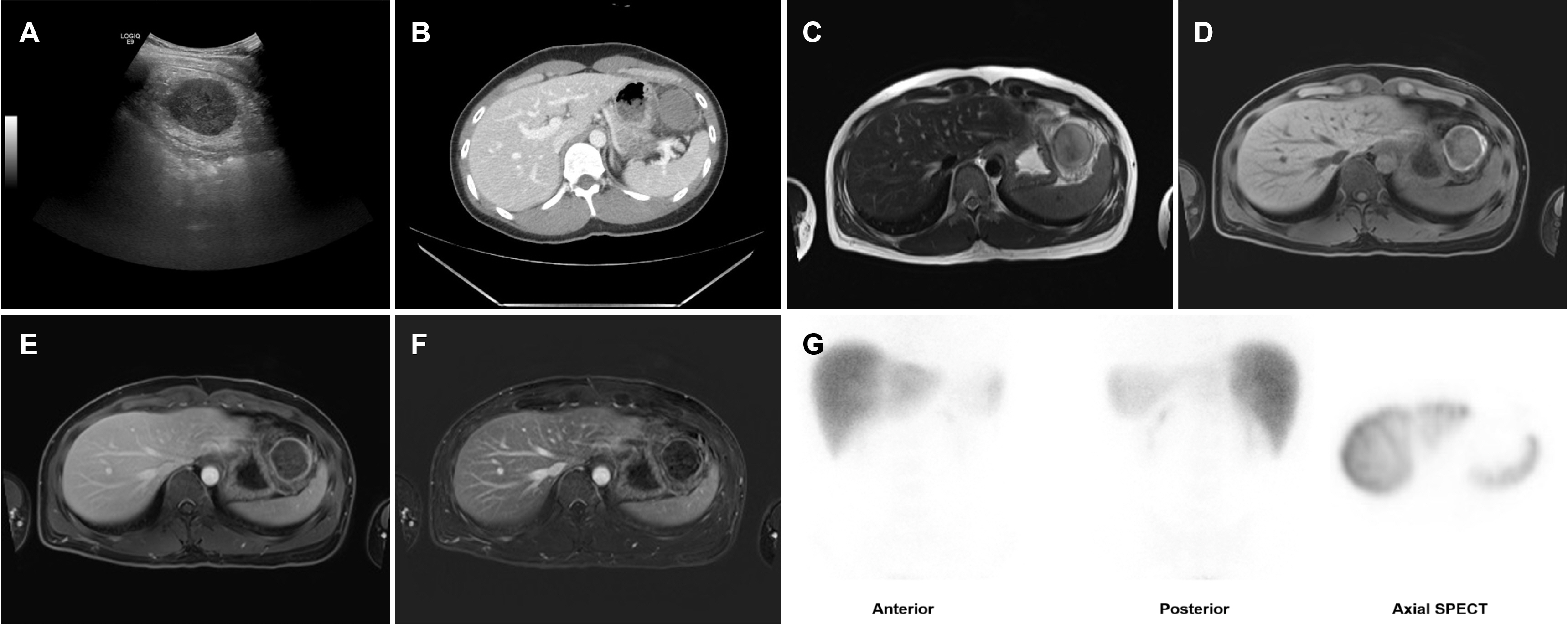
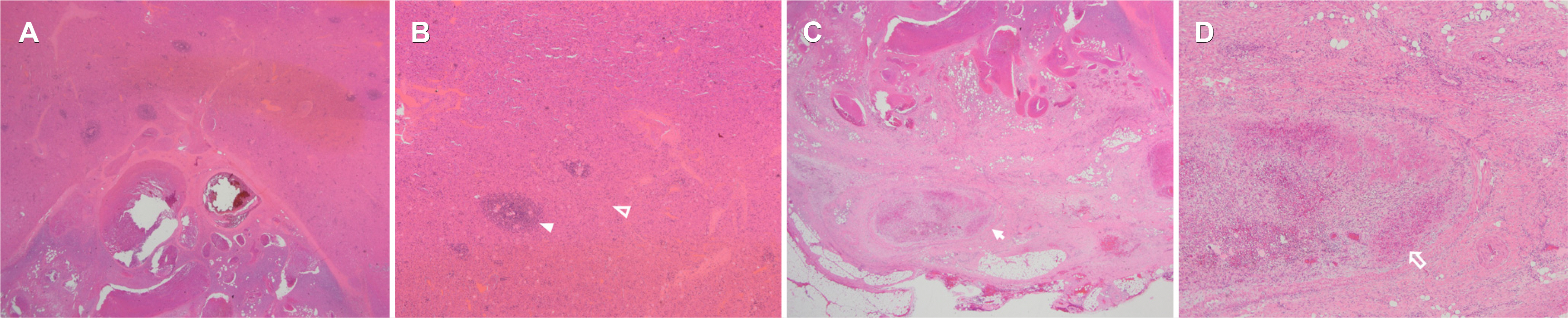
- Accessory spleens are common congenital anatomic variations that are usually asymptomatic. On the other hand, they can be clinically significant if complicated by hemorrhage, torsion, or infarction. This paper describes a case of an infarcted accessory spleen in a 30-year-old male who presented with abdominal pain. Abdominal CT and MRI revealed an isolated mass, 4.5 cm in size, in the perisplenic area. An infarcted accessory spleen was suspected. The patient underwent laparoscopic accessory splenectomy. Histopathology identified the mass as splenic tissue that had undergone ischemic necrosis. A definitive diagnosis of an infarcted accessory spleen was made, and the patient was discharged on day 5 after surgery symptom-free.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morgenstern L, Skandalakis JE. Hiatt JR, Phillips EH, Morgenstern L, editors. 1997. Anatomy and embryology of the spleen. Surgical diseases of the spleen. Springer;Berlin, Heidelberg: p. 15–24. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-60574-1_2. PMID: 8996481.
Article2. Yildiz AE, Ariyurek MO, Karcaaltincaba M. 2013; Splenic anomalies of shape, size, and location: pictorial essay. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013:321810. DOI: 10.1155/2013/321810. PMID: 23710135. PMCID: PMC3654276.
Article3. Varga I, Babala J, Kachlik D. 2018; Anatomic variations of the spleen: current state of terminology, classification, and embryological background. Surg Radiol Anat. 40:21–29. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-017-1893-0. PMID: 28631052.
Article4. Mohammadi S, Hedjazi A, Sajjadian M, Ghrobi N, Moghadam MD, Mohammadi M. 2016; Accessory spleen in the splenic hilum: a cadaveric study with clinical significance. Med Arch. 70:389–391. DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2016.70.389-391. PMID: 27994303. PMCID: PMC5136441.
Article5. Varga I, Galfiova P, Adamkov M, et al. 2009; Congenital anomalies of the spleen from an embryological point of view. Med Sci Monit. 15:RA269–RA276.6. Rashid SA. 2014; Accessory spleen: prevalence and multidetector CT appearance. Malays J Med Sci. 21:18–23.7. Ko HS, Goo HW, Yoon CH. 2004; Unusual infarction of the accessory spleen or polysplenia in two children: case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 51:555–558. DOI: 10.3348/jkrs.2004.51.5.555.
Article8. Babcock TL, Coker DD, Haynes JL, Conklin HB. 1974; Infarction of an accessory spleen causing an acute abdomen. Am J Surg. 127:336–337. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90044-0.
Article9. Onuigbo WI, Ojukwu JO, Eze WC. 1978; Infarction of accessory spleen. J Pediatr Surg. 13:129–130. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3468(78)80004-9.
Article10. Hems TE, Bellringer JF. 1990; Torsion of an accessory spleen in an elderly patient. Postgrad Med J. 66:838–839. DOI: 10.1136/pgmj.66.780.838. PMID: 2099424. PMCID: PMC2429706.
Article11. Sheth H, Chaudhari S, Sinha Y, Prajapati R. 2018; Infarcted accessory spleen masquerading as a mesenteric cyst. BMJ Case Rep. 2018:bcr2018226130. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-226130. PMID: 30115724. PMCID: PMC6101306.
Article12. Yousef Y, Cameron BH, Maizlin ZV, Boutross-Tadross O. 2010; Laparoscopic excision of infarcted accessory spleen. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 20:301–303. DOI: 10.1089/lap.2009.0286. PMID: 20059391.
Article13. Ishibashi H, Oshio T, Sogami T, Nii A, Mori H, Shimada M. 2012; Torsion of an accessory spleen with situs inversus in a child. J Med Invest. 59:220–223. DOI: 10.2152/jmi.59.220. PMID: 22450011.
Article14. Simon DA, Fleishman NR, Choi P, Fraser JD, Fischer RT. 2020; Torsion of an accessory spleen in a child with biliary atresia splenic malformation syndrome. Front Pediatr. 8:220. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.00220. PMID: 32432066. PMCID: PMC7212802.
Article15. Ozeki M, Asakuma M, Go N, et al. 2015; Torsion of an accessory spleen: a rare case preoperatively diagnosed and cured by single-port surgery. Surg Case Rep. 1:100. DOI: 10.1186/s40792-015-0101-x. PMID: 26943424. PMCID: PMC4596154.
Article16. Sadro CT, Lehnert BE. 2015; Torsion of an accessory spleen: case report and review of the literature. Radiol Case Rep. 8:802. DOI: 10.2484/rcr.v8i1.802. PMID: 27330618. PMCID: PMC4900206.
Article17. Nishiguchi S, Habu D, Ishizu H, et al. 2001; Accessory spleen in the pelvis diagnosed by Tc-99m phytate scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med. 15:263–265. DOI: 10.1007/BF02987843. PMID: 11545199.
Article18. Kim SH, Lee JM, Han JK, et al. 2008; Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: findings on MR Imaging, CT, US and scintigraphy, and the pathologic analysis. Korean J Radiol. 9:162–174. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.2.162. PMID: 18385564. PMCID: PMC2627219.
Article19. Chung YH, Park HJ, Park IS, et al. 2009; An epidermoid cyst in an intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Korean J Med. 76:742–745.20. Im CJ, Kweon JH, Hwang ET, et al. 2009; An intrapancreatic accessory spleen mimicking a tumor of the pancreas. Korean J Med. 77:S326–S331.21. Kim JH, Chung KH, Oh SY, et al. 2014; Two cases of epidermoid cysts in the intrapancreatic accessory spleen mimicking pancreatic cystic neoplasm. Korean J Pancreas Biliary Tract. 19:52–58. DOI: 10.15279/kpba.2014.19.1.52.
Article22. Ko HJ, Shim JR, Lee TB, et al. 2020; Epidermoid cyst in an intrapancreatic accessory spleen in the pancreas head: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 20:392. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01540-4. PMID: 33218300. PMCID: PMC7678289.
Article23. Barawi M, Bekal P, Gress F. 2000; Accessory spleen: a potential cause of misdiagnosis at EUS. Gastrointest Endosc. 52:769–772. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2000.108666. PMID: 11115915.
Article24. Renno A, Hill M, Abdel-Aziz Y, Meawad H, Lenhard A, Nawras A. 2020; Diagnosis of intrapancreatic accessory spleen by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration mimicking a pancreatic neoplasm: a case report and review of literature. Clin J Gastroenterol. 13:287–297. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-019-01045-y. PMID: 31549337.
Article25. Fritscher-Ravens A, Mylonaki M, Pantes A, Topalidis T, Thonke F, Swain P. 2003; Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy for the diagnosis of focal lesions of the spleen. Am J Gastroenterol. 98:1022–1027. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07399.x. PMID: 12809823.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unusual Infarction of the Accessory Spleen or Polysplenia in Two Children: Case Report
- A Case of Acute Pancreatitis and Splenic Infarction Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- Accessory Splenic Infarction Presenting as a Hemorrhagic Tumor in the Pancreas
- Splenic infarction as a complication of celiac artery thromboembolism: an unusual cause of abdominal pain
- Spontaneous Rupture of Accessory Spleen Detected during Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy