J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Sep;36(35):e250. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e250.
SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Persons with Past Natural Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2519870
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e250
Abstract
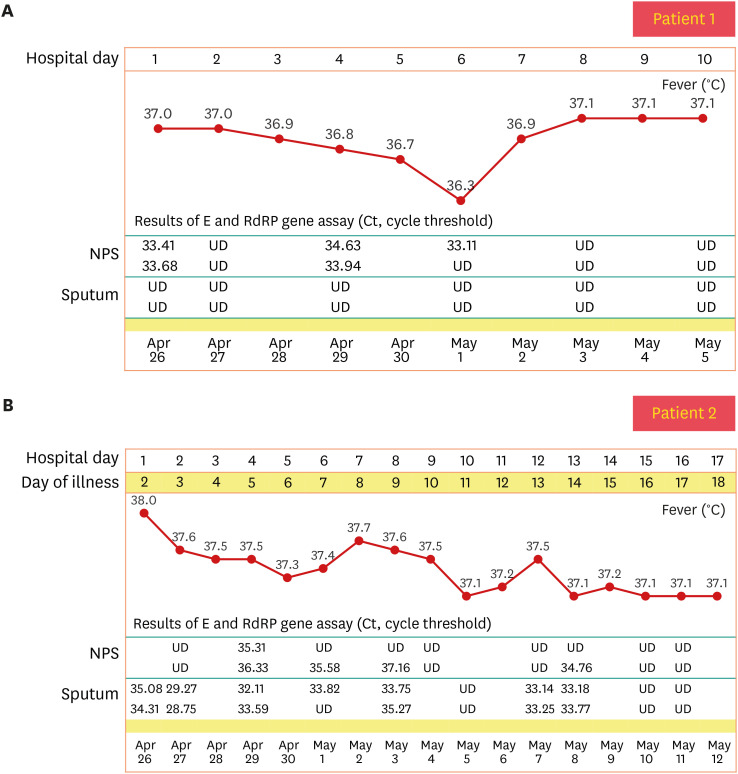
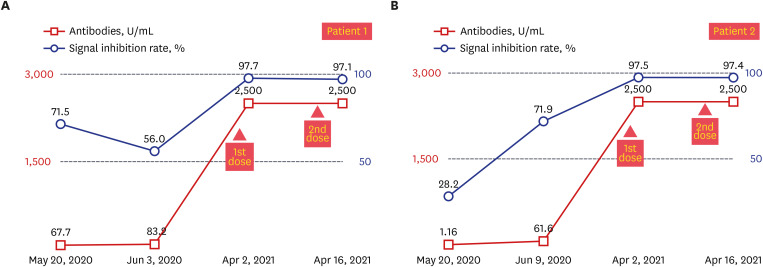
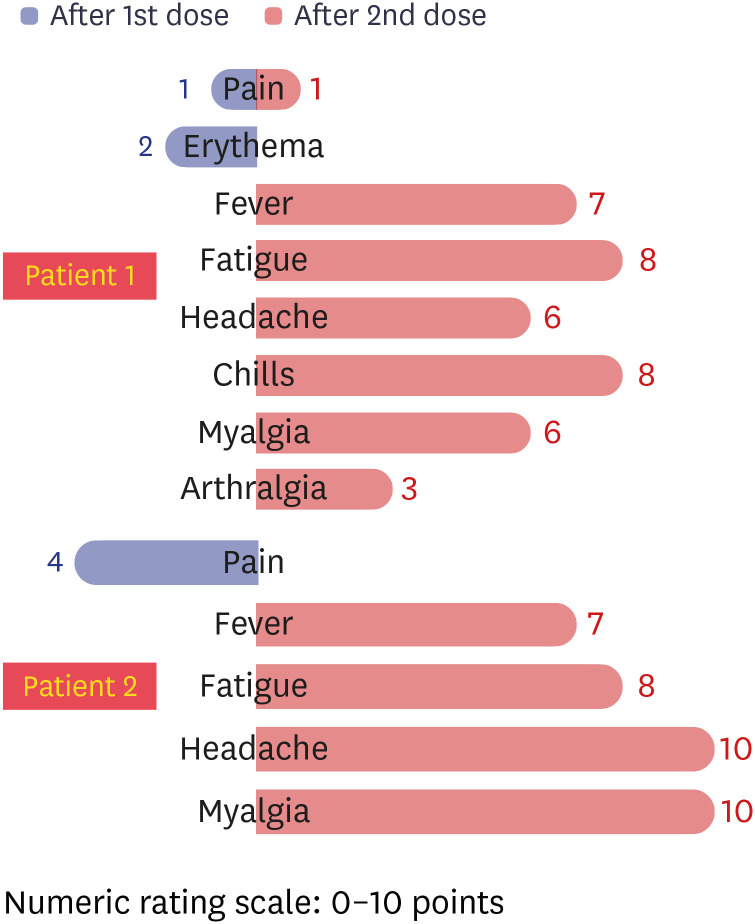
- There are still no agreed guidelines on the vaccination of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) for previously infected patients. Here, we present two seropositive healthcare workers (HCWs) working in an isolation ward who recovered from COVID-19 in April 2020 and got vaccinated with BNT162b2 vaccine in March 2021. We have assessed the clinical course, vaccine-related adverse events, and antibody response after natural infection and after first and second dose vaccination. One of the two HCWs was asymptomatic during quarantine, but the other had mild upper respiratory infection symptoms 1 day before admission, and the symptoms continued for 9 days. There was no pneumonic infiltration in chest X-ray in both patients, and no COVID-19 specific treatment was administered. Total immunoglobulin antibody and neutralizing antibody to anti-spike protein receptorbinding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 were confirmed to be present in both HCWs in blood tests performed at 2 weeks and 4 weeks after discharge. Antibody response to mRNA vaccination showed marked elevation after the first vaccination, which was 30–40 times higher than that of antibody titer after natural infection in each patient (83.2 U/mL vs. > 2,500 U/mL in patient 1; 61.6 U/mL vs. > 2,500 U/mL in patient 2). Signal inhibition rate of neutralizing antibodies was also increased to over 97%. Due to this increased effect, there was little difference in antibody levels after the first and second dose. Both patients 1 and 2 suffered more from adverse vaccine reactions after the second vaccination than from COVID-19 symptoms.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Current COVID-19 vaccination status in Korea. Updated 2021. Assessed June 4, 2021. https://ncv.kdca.go.kr/.2. Our World in Data. COVID-19 dashboard. Updated 2021. Accessed June 4, 2021. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations.3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US). Current COVID-19 vaccination dashboard. Updated 2021. Assessed June 4, 2021. https://korean.cdc.gov.4. Taylor SC, Hurst B, Charlton CL, Bailey A, Kanji JN, McCarthy MK, et al. A new SARS-CoV-2 dual-purpose serology test: highly accurate infection tracing and neutralizing antibody response detection. J Clin Microbiol. 2021; 59(4):e02438-20. PMID: 33500361.
Article5. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Toxicity grading scale for healthy adult and adolescent volunteers enrolled in preventive vaccine clinical trials. Updated 2007. Assessed June 4, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/toxicity-grading-scale-healthy-adult-and-adolescent-volunteers-enrolled-preventive-vaccine-clinical.6. Kim YJ, Bae JY, Bae S, Hwang S, Kwon KT, Chang HH, et al. Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Korean patients who have recovered from COVID-19. Yonsei Med J. 2021; 62(7):584–592. PMID: 34164955.
Article7. Choe PG, Kim KH, Kang CK, Suh HJ, Kang E, Lee SY, et al. Antibody responses one year after mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(21):e157. PMID: 34060263.
Article8. Assis R, Jain A, Nakajima R, Jasinskas A, Kahn S, Palma A, et al. Substantial differences in SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses elicited by natural infection and mRNA vaccination. bioRxiv. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1101/2021.04.15.440089.
Article9. Krammer F, Srivastava K; the PARIS team, Simon V. Robust spike antibody responses and increased reactogenicity in seropositive individuals after a single dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. medRxiv. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1101/2021.01.29.21250653.
Article10. Manisty C, Otter AD, Treibel TA, McKnight Á, Altmann DM, Brooks T, et al. Antibody response to first BNT162b2 dose in previously SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. Lancet. 2021; 397(10279):1057–1058. PMID: 33640038.
Article11. Bradley T, Grundberg E, Selvarangan R, LeMaster C, Fraley E, Banerjee D, et al. Antibody responses after a single dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(20):1959–1961. PMID: 33755375.
Article12. Tré-Hardy M, Cupaiolo R, Papleux E, Wilmet A, Horeanga A, Antoine-Moussiaux T, et al. Reactogenicity, safety and antibody response, after one and two doses of mRNA-1273 in seronegative and seropositive healthcare workers. J Infect. 2021; 83(2):237–279.
Article13. Goldberg Y, Mandel M, Woodbridge Y, Fluss R, Novikov I, Yaari R, et al. Protection of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection is similar to that of BNT162b2 vaccine protection: a three-month nationwide experience from Israel. medRxiv. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1101/2021.04.20.21255670.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes in SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers 6 months after the booster dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine among health care workers
- Anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike antibody response to the third dose of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and associated factors in Japanese hemodialysis patients
- Comparison of antibody responses after the 1st and 2nd doses of COVID-19 vaccine with those of patients with mild or severe COVID-19
- Body Weight is Inversely Associated with Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination in Young and Middle Aged Adults
- Comparison of Antibody and T Cell Responses Induced by Single Doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 Vaccines