J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Sep;36(35):e216. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e216.
Development and Verification of an Internet Game Literacy Scale
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Psychiatry, Chung-Ang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3School of Social Welfare, Soongsil University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2519865
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e216
Abstract
- Background
Education on internet games for parents and internet game literacy are needed to prevent problematic internet game playing in Korea. We created an 18-item Internet Game Literacy Scale (IGLS). It is a valuable tool for assessing the positive and negative aspects of internet game play. We aimed to determine the validity of the IGLS and the cut-off for the tendency for internet gameplay.
Methods
An online research company gathered data from 300 participants. Factor analysis, including Cronbach's α and consistency coefficient, exploratory factor analysis, and confirmatory factor analysis were conducted to verify the 18 items of the IGLS. Additionally, a K-means cluster analysis was performed to determine the cut-off values for positive and negative IGLS scores.
Results
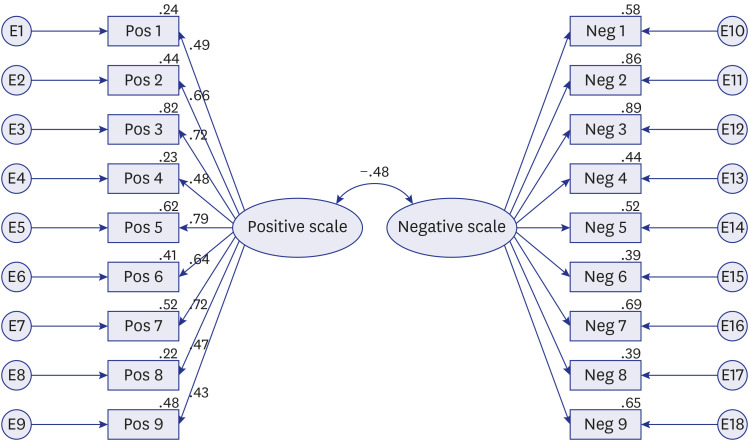
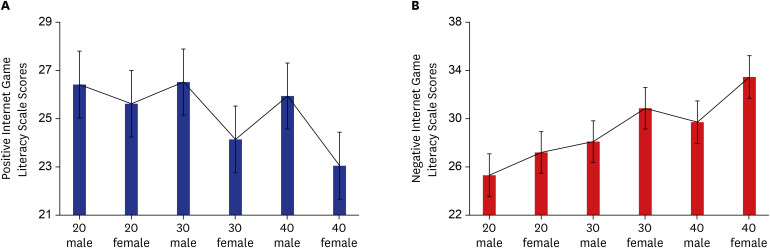
The 18 items of the IGLS were proven to be reliable, as evidenced by a high Cronbach's alpha (α = 0.892). The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin measure of sampling adequacy was 0.903, and Bartlett's test of sphericity was good (χ2 = 1,623.314, P < 0.001). All 18 items were segregated into two factors, with nine items each. The eigenvalue of all 18 items was significant at > 0.4. In the analysis of the validity of the 18-item IGLS with confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) (maximum likelihood estimation, with an oblique method), the fit indices of the standard three-factor model reached acceptable standards. The cut-off point of the total score between the low positive and average positive groups was 23, and the cut-off point of the total score between the average positive and high positive groups was 30. The cut-off point of the total score between the low negative and the average negative groups was 24. The cut-off point of the total score between the average negative group and the high negative group was 32.
Conclusion
The study assessed the reliability and validity of the IGLS and suggested a cut-off for low, average, and high Internet game literacy degree with 300 Korean adults aged 21–49 years. The current results suggest that the IGLS has good internal consistency and a proper cut-off for positive and negative internet game literacy degrees.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arakji RY, Lang KR. Avatar business value analysis: a method for the evaluation of business value creation in virtual commerce. J Econ Commer Res. 2008; 9(3):207–218.2. Lu HP, Wang SM. The role of internet addiction in online game loyalty: an exploratory study. Internet Res. 2008; 18(5):499–519.
Article3. Yoon HM, editor. “70% of Korean are gamers...” Increased playing time of internet game. Chosun Daily Newspaper;2020 Aug 7: Sect. IT.4. Li W, O'Brien JE, Snyder SM, Howard MO. Characteristics of internet addiction/pathological internet use in U.S. university students: a qualitative-method investigation. PLoS One. 2015; 10(2):e0117372. PMID: 25647224.
Article5. Kang SK, Kim GJ. An comparative study on the self-regulation of the digital game. J Korea Game Soc. 2012; 12(6):107–120.
Article6. Sung W. A study on the effect of the policy of online game shutdown on the game time of youth. Soc Sci Res Rev. 2014; 30(2):233–256.7. Kim MY. A study on the problem and its improvement in game shutdown policy. Legis Polic. 2012; 6:61–88.8. Eklund L, Bergmark KH. Parental mediation of digital gaming and internet use. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games (FDG 2013). 2013 May 14-17; Chania, Greece. Santa Cruz, CA, USA: Society for the Advancement of the Science of Digital Games;2013. p. 63–70.9. Kutner LA, Olson CK, Warner DE, Hertzog SM. Parents' and sons' perspectives on video game play: a qualitative study. J Adolesc Res. 2008; 23(1):76–96.10. Beck J, Wade M, editors. Got Game: How the Gamer Generation is Reshaping Business Forever. Boston, MA, USA: Harvard Business School Press;2004.11. Han DH, Jung EJ, Park SO, Kim MC, Bae SJ, editors. A Study on the Difference between the Professional Approach Methodology and Coping Strategies in Internet Gaming Disorder. Naju, Korea: Korea Creative Content Agency;2018.12. Kim JY, Kim D, Lee J, Mo SH, Chang G. A study on the perception types of online games and their characteristics. J Korea Game Soc. 2013; 13(4):91–104.
Article13. Byrne BM, editor. Structural Equation Modeling with EQS and EQS/Windows. Thousand Oaks, CA, USA: Sage Publications;1994.14. Anderson JC, Gerbing DW. The effect of sampling error on convergence, improper solutions, and goodness-of-fit indices for maximum likelihood confirmatory factor analysis. Psychometrika. 1984; 49:155–173.
Article15. Lee C, Bae S, Nam JJ, Jin JC, Han DH. Development and verification of a web board game scale. Psychiatry Investig. 2020; 17(2):106–113.
Article16. Cole DA. Utility of confirmatory factor analysis in test validation research. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1987; 55(4):584–594. PMID: 3624616.
Article17. Marsh HW, Balla JR, Mcdonald RP. Goodness-of-fit indexes in confirmatory factor analysis: the effect of sample size. Psychol Bull. 1988; 103(3):391–410.
Article18. Steiger JH. Structural model evaluation and modification - an interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behav Res. 1990; 25(2):173–180. PMID: 26794479.19. Hu LT, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct Equ Modeling. 1999; 6(1):1–55.
Article20. Carlson SA, Fulton JE, Lee SM, Foley JT, Heitzler C, Huhman M. Influence of limit-setting and participation in physical activity on youth screen time. Pediatrics. 2010; 126(1):e89–96. PMID: 20547642.
Article21. Gentile DA, Reimer RA, Nathanson AI, Walsh DA, Eisenmann JC. Protective effects of parental monitoring of children's media use: a prospective study. JAMA Pediatr. 2014; 168(5):479–484. PMID: 24686493.22. Su B, Yu C, Zhang W, Su Q, Zhu J, Jiang Y. Father-child longitudinal relationship: parental monitoring and internet gaming disorder in Chinese adolescents. Front Psychol. 2018; 9:95. PMID: 29467704.
Article23. Krossbakken E, Torsheim T, Mentzoni RA, King DL, Bjorvatn B, Lorvik IM, et al. The effectiveness of a parental guide for prevention of problematic video gaming in children: a public health randomized controlled intervention study. J Behav Addict. 2018; 7(1):52–61. PMID: 29313731.
Article24. Aarseth E, Bean AM, Boonen H, Colder Carras M, Coulson M, Das D, et al. Scholars' open debate paper on the World Health Organization ICD-11 Gaming Disorder proposal. J Behav Addict. 2017; 6(3):267–270. PMID: 28033714.
Article25. van Rooij AJ, Ferguson CJ, Colder Carras M, Kardefelt-Winther D, Shi J, Aarseth E, et al. A weak scientific basis for gaming disorder: let us err on the side of caution. J Behav Addict. 2018; 7(1):1–9. PMID: 29529886.
Article26. Hong JS, Kim SM, Jung JW, Kim SY, Chung US, Han DH. A comparison of risk and protective factors for excessive internet game play between Koreans in Korea and immigrant Koreans in the United States. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34(23):e162. PMID: 31197982.
Article27. Griffiths MD, Király O, Pontes HM, Demetrovics Z, editors. An Overview of Problematic Gaming. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press;2015.28. King DL, Delfabbro PH, Doh YY, Wu AM, Kuss DJ, Pallesen S, et al. Policy and prevention approaches for disordered and hazardous gaming and internet use: an international perspective. Prev Sci. 2018; 19(2):233–249. PMID: 28677089.
Article29. Vondráčková P, Gabrhelík R. Prevention of internet addiction: a systematic review. J Behav Addict. 2016; 5(4):568–579. PMID: 27998173.
Article30. Holtz P, Appel M. Internet use and video gaming predict problem behavior in early adolescence. J Adolesc. 2011; 34(1):49–58. PMID: 20303580.
Article31. Király O, Griffiths MD, King DL, Lee HK, Lee SY, Bányai F, et al. Policy responses to problematic video game use: a systematic review of current measures and future possibilities. J Behav Addict. 2018; 7(3):503–517. PMID: 28859487.
Article32. Zhu JJ, Zhang W, Yu CF, Bao ZZ. Early adolescent internet game addiction in context: how parents, school, and peers impact youth. Comput Human Behav. 2015; 50:159–168.
Article33. Choung HM, Lee DS. A study on difference of internet game addiction tendency according to the game with use. J Korea Soc Comput Inf. 2008; 13(2):159–166.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effectiveness of Game Coding Education on Problematic Internet Gaming
- The Effect of Stress on Internet Game Addiction Trends in Adults: Mindfulness and Conscientiousness as Mediators
- Effect of Parental Perception on the Prevalence of Adolescent Internet Gaming Disorder During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Internet Game Addiction and Emotional and Behavioral Characteristics in Upper Grade Elementary School Students and Middle School Students
- Effects of School Adjustment on Higher Grade Elementary School Students' Internet Game Addiction: Focused on Gender Difference