J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2021 Aug;47(4):257-268. 10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.4.257.
Comparative evaluation of nasal and alveolar changes in complete unilateral cleft lip and palate patients using intraoral and extraoral nasoalveolar molding techniques: randomized controlled trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry, Government Dental College & Hospital, Nagpur, India
- KMID: 2519823
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.4.257
Abstract
Objectives
Cleft lip and palate is a common congenital anomaly that impairs the aesthetics, speech, hearing, and psychological and social life of an individual. To achieve good aesthetic outcomes, presurgical nasoalveolar molding (NAM) has become important. Currently, the intraoral NAM technique is widely practiced. Numerous modifications have been made to intraoral NAM techniques, but the original problem of compliance leading to discontinuation of treatment remains unsolved. Therefore, the present study compared an extraoral NAM technique with the intraoral NAM technique.
Materials and Methods
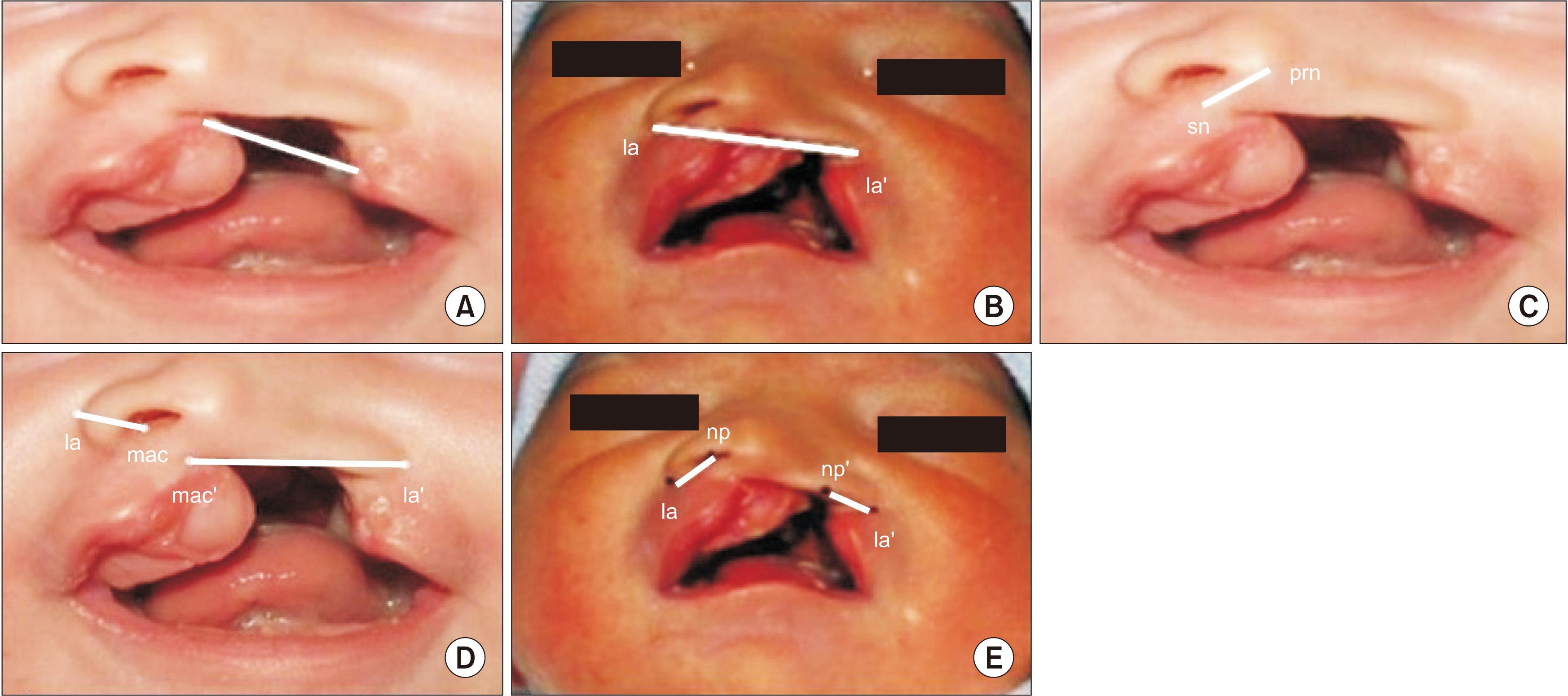
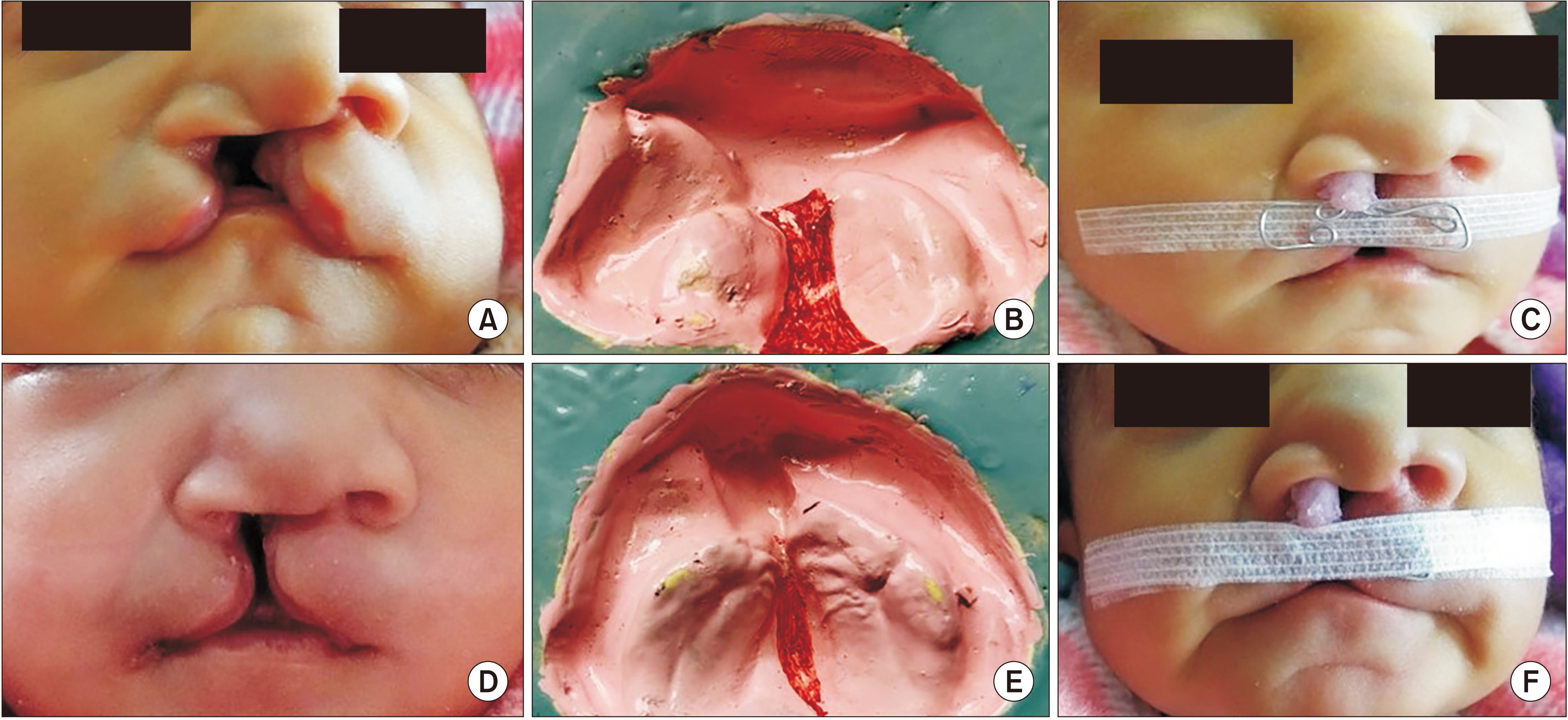
Twenty infants with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate were included and divided into two equal groups. Group A received the intraoral NAM technique, and Group B received the extraoral NAM technique. Pre- and postoperative extraoral and intraoral measurements were recorded.
Results
Groups A and B did not differ significantly in any extraoral or intraoral parameter.
Conclusion
The extraoral NAM technique is as effective as the intraoral NAM technique in achieving significant nasal and alveolar changes in complete unilateral cleft lip and palate patients. Additionally, it reduces the need for frequent hospital visits for activation and the stress associated with the insertion and removal of the intraoral NAM plate, thereby improving compliance.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Grayson BH, Garfinkle JS. 2014; Early cleft management: the case for nasoalveolar molding. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 145:134–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.11.011 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.11.011. PMID: 24485726.
Article2. Mossey PA, Shaw WC, Munger RG, Murray JC, Murthy J, Little J. 2011; Global oral health inequalities: challenges in the prevention and management of orofacial clefts and potential solutions. Adv Dent Res. 23:247–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034511402083 . DOI: 10.1177/0022034511402083. PMID: 21490237. PMCID: PMC6699117.
Article3. Mossey PA, Little J, Munger RG, Dixon MJ, Shaw WC. 2009; Cleft lip and palate. Lancet. 374:1773–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60695-4 . DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60695-4. PMID: 19747722.
Article4. Dixon MJ, Marazita ML, Beaty TH, Murray JC. 2011; Cleft lip and palate: understanding genetic and environmental influences. Nat Rev Genet. 12:167–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2933 . DOI: 10.1038/nrg2933. PMID: 21331089. PMCID: PMC3086810.
Article5. Mossey PA, Little J. Wyskynski DF, editor. 2002. Epidemiology of oral clefts: an international perspective. Cleft lip and palate: from origin to treatment. Oxford University Press;Oxford: p. 127–58.6. Berkowitz S. 2013. Cleft lip and palate: diagnosis and management. 3rd ed. Springer;Berlin:7. Wong FW, King NM. 1998; The oral health of children with clefts--a review. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 35:248–54. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1998_035_0248_tohocw_2.3.co_2 . DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_1998_035_0248_tohocw_2.3.co_2. PMID: 9603560.
Article8. Hunt O, Burden D, Hepper P, Johnston C. 2005; The psychosocial effects of cleft lip and palate: a systematic review. Eur J Orthod. 27:274–85. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cji004 . DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cji004. PMID: 15947228.
Article9. Pfeifer TM, Grayson BH, Cutting CB. 2002; Nasoalveolar molding and gingivoperiosteoplasty versus alveolar bone graft: an outcome analysis of costs in the treatment of unilateral cleft alveolus. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 39:26–9. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_2002_039_0026_nmagva_2.0.co_2 . DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_2002_039_0026_nmagva_2.0.co_2. PMID: 11772166.
Article10. Grayson BH, Santiago PE, Brecht LE, Cutting CB. 1999; Presurgical nasoalveolar molding in infants with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 36:486–98. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1999_036_0486_pnmiiw_2.3.co_2 . DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_1999_036_0486_pnmiiw_2.3.co_2. PMID: 10574667.
Article11. Figueroa AA, Polley JW. Mathes SJ, editor. 2006. Orthodontics in cleft lip and palate management. Plastic surgery: pediatric plastic surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders;Philadelphia: p. 271–310.12. Liou EJ, Subramanian M, Chen PK, Huang CS. 2004; The progressive changes of nasal symmetry and growth after nasoalveolar molding: a three-year follow-up study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 114:858–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000133027.04252.7a . DOI: 10.1097/01.prs.0000133027.04252.7a. PMID: 15468390.
Article13. Matsuo K, Hirose T, Tomono T, Iwasawa M, Katohda S, Takahashi N, et al. 1984; Nonsurgical correction of congenital auricular deformities in the early neonate: a preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg. 73:38–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198401000-00009 . DOI: 10.1097/00006534-198401000-00009. PMID: 6691074.
Article14. Liao YF, Hsieh YJ, Chen IJ, Ko WC, Chen PK. 2012; Comparative outcomes of two nasoalveolar molding techniques for unilateral cleft nose deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 130:1289–95. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31826d16f3 . DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31826d16f3. PMID: 23190811.
Article15. Sischo L, Clouston SA, Phillips C, Broder HL. 2016; Caregiver responses to early cleft palate care: a mixed method approach. Health Psychol. 35:474–82. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0000262 . DOI: 10.1037/hea0000262. PMID: 26280177. PMCID: PMC4757521.
Article16. Wang Q, Zhou L, Zhao JZ, Ko EW. 2013; An extraoral nasoalveolar molding technique in complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 1:e26. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0b013e31829e0d4b . DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0b013e31829e0d4b. PMID: 25289220. PMCID: PMC4173837.
Article17. Koya S, Husain A, Khader M. 2018; Complete bilateral cleft lip and palate with protruding premaxilla: a multidisciplinary approach. Arch Med Health Sci. 6:298–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/amhs.amhs_136_18 .
Article18. Murthy PS, Deshmukh S, Bhagyalakshmi A, Srilatha K. 2013; Pre surgical nasoalveolar molding: changing paradigms in early cleft lip and palate rehabilitation. J Int Oral Health. 5:70–80. PMID: 24155594. PMCID: PMC3768063.19. Yang S, Stelnicki EJ, Lee MN. 2003; Use of nasoalveolar molding appliance to direct growth in newborn patient with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Pediatr Dent. 25:253–6. PMID: 12889702.20. Grayson BH, Maull D. 2005; Nasoalveolar molding for infants born with clefts of the lip, alveolus, and palate. Semin Plast Surg. 19:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-925902 . DOI: 10.1016/S0094-1298(03)00140-8. PMID: 15145660.
Article21. McNeil CK. 1950; Orthodontic procedures in the treatment of congenital cleft palate. Dent Rec (London). 70:126–32. PMID: 24537837.22. Dogliotti PL, Bennún RD, Losoviz EA, Ganiewich E. 1991; [Non-surgical treatment of nasal deformity in the cleft patient]. Rev. Ateneo Argent Odontol. 27:31–5. Spanish.23. Chen YF, Liao YF. 2015; A modified nasoalveolar molding technique for correction of unilateral cleft nose deformity. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43:2100–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.10.003 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.10.003. PMID: 26541749.
Article24. Shetty V, Vyas HJ, Sharma SM, Sailer HF. 2012; A comparison of results using nasoalveolar moulding in cleft infants treated within 1 month of life versus those treated after this period: development of a new protocol. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 41:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2011.09.002 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.09.002. PMID: 22018821.
Article25. Shapira Y, Lubit E, Kuftinec MM, Borell G. 1999; The distribution of clefts of the primary and secondary palates by sex, type, and location. Angle Orthod. 69:523–8. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(1999)069<0523:TDOCOT>2.3.CO;2 . DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1999)069<0523:TDOCOT>2.3.CO;2. PMID: 10593442.
Article26. Tabaie S. 2017; Stopping female feticide in India: the failure and unintended consequence of ultrasound restriction. J Glob Health. 7:010304. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.07.010304 . DOI: 10.7189/jogh.07.010304. PMID: 28567276. PMCID: PMC5441446.
Article27. Jurkiewicz MJ, Bryant DL. 1968; Cleft lip and palate in dogs: a progress report. Cleft Palate J. 5:30–6. PMID: 4383842.
Article28. Monasterio L, Ford A, Gutiérrez C, Tastets ME, García J. 2013; Comparative study of nasoalveolar molding methods: nasal elevator plus DynaCleft® versus NAM-Grayson in patients with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 50:548–54. https://doi.org/10.1597/11-245 . DOI: 10.1597/11-245. PMID: 22906392.
Article29. Zuhaib M, Bonanthaya K, Parmar R, Shetty PN, Sharma P. 2016; Presurgical nasoalveolar moulding in unilateral cleft lip and palate. Indian J Plast Surg. 49:42–52. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-0358.182235 . DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.182235. PMID: 27274121. PMCID: PMC4878243.
Article30. Gomez DF, Donohue ST, Figueroa AA, Polley JW. 2012; Nasal changes after presurgical nasoalveolar molding (PNAM) in the unilateral cleft lip nose. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 49:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1597/11-007 . DOI: 10.1597/11-007. PMID: 21846257.
Article31. Pai BC, Ko EW, Huang CS, Liou EJ. 2005; Symmetry of the nose after presurgical nasoalveolar molding in infants with unilateral cleft lip and palate: a preliminary study. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 42:658–63. https://doi.org/10.1597/04-126.1 . DOI: 10.1597/04-126.1. PMID: 16241178.
Article32. Singh GD, Levy-Bercowski D, Santiago PE. 2005; Three-dimensional nasal changes following nasoalveolar molding in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate: geometric morphometrics. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 42:403–9. https://doi.org/10.1597/04-063.1 . DOI: 10.1597/04-063.1. PMID: 16001922.
Article33. Patel D, Goyal R. 2012; Pre-surgical nasoalveolar moulding in patient with unilateral cleft of lip, alveolus and palate: case report. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 65:122–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2011.06.011 . DOI: 10.1016/j.bjps.2011.06.011. PMID: 21768006.
Article34. Prahl C, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, van't Hof MA, Prahl-Andersen B. 2001; A randomised prospective clinical trial into the effect of infant orthopaedics on maxillary arch dimensions in unilateral cleft lip and palate (Dutchcleft). Eur J Oral Sci. 109:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0722.2001.00056.x . DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0722.2001.00056.x. PMID: 11695749.
Article35. Mishima K, Mori Y, Sugahara T, Minami K, Sakuda M. 2000; Comparison between palatal configurations in UCLP infants with and without a Hotz plate until four years of age. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 37:185–90. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_2000_037_0185_cbpciu_2.3.co_2 . DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_2000_037_0185_cbpciu_2.3.co_2. PMID: 10749060.
Article36. Sabarinath VP, Thombare P, Hazarey PV, Radhakrishnan V, Agrekar S. 2010; Changes in maxillary alveolar morphology with nasoalveolar molding. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 35:207–12. https://doi.org/10.17796/jcpd.35.2.f80u21362566qr34 . DOI: 10.17796/jcpd.35.2.f80u21362566qr34. PMID: 21417127.
Article37. Doruk C, Kiliç B. 2005; Extraoral nasal molding in a newborn with unilateral cleft lip and palate: a case report. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 42:699–702. https://doi.org/10.1597/04-134r.1 . DOI: 10.1597/04-134r.1. PMID: 16241184.
Article38. Larson M, Sällström KO, Larson O, McWilliam J, Ideberg M. 1993; Morphologic effect of preoperative maxillofacial orthopedics (T-traction) on the maxilla in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 30:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1993_030_0029_meopmo_2.3.co_2 . DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_1993_030_0029_meopmo_2.3.co_2. PMID: 8418869.
Article39. Da Silveira AC, Oliveira N, Gonzalez S, Shahani M, Reisberg D, Daw JL Jr, et al. 2003; Modified nasal alveolar molding appliance for management of cleft lip defect. J Craniofac Surg. 14:700–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001665-200309000-00018 . DOI: 10.1097/00001665-200309000-00018. PMID: 14501332.
Article40. Nordin KE, Larson O, Nylén B, Eklund G. 1983; Early bone grafting in complete cleft lip and palate cases following maxillofacial orthopedics. I. The method and the skeletal development from seven to thirteen years of age. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 17:33–50. https://doi.org/10.3109/02844318309007177 . DOI: 10.3109/02844318309007177. PMID: 6622984.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The nasoalveolar molding technique versus DynaCleft nasal elevator application in infants with unilateral cleft lip and palate
- Correction of Unilateral Cleft Lip Using Surgeon-Made Nasoalveolar Molding Device
- Effect of presurgical nasoalveolar molding (PNAM) appliance and cheiloplasty on alveolar molding of complete unilateral cleft lip and palate patients
- Biocreative Alveolar Molding Plate Treatment (BioAMP) for neonatal unilateral cleft lip and palate with excessively wide alveolar cleft and maxillary arch width
- Cleft Treatment Protocol in Korea