Arch Hand Microsurg.
2021 Sep;26(3):184-192. 10.12790/ahm.21.0092.
Outcomes after Arterial Reconstruction with Autogenous Vein Graft for Limb Salvage in Traumatized Extremity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2519472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.21.0092
Abstract
- Purpose
The patients with major vascular injuries in the traumatized extremity and underwent arterial reconstruction using autogenous vein grafts for limb salvage. This study aims to report the outcomes of arterial reconstruction with autogenous vein graft in patients.
Methods
From February 2015 to April 2017, a study was retrospectively analyzed 13 patients with limb injuries caused by significant arterial damage and underwent arterial reconstruction using vascular autografts for limb salvage. Such as cause, Mangled Extremity Severity Scores (MESS), ischemic time, length of the grafted vein, reconstructed arterial status, and survival status were analyzed.
Results
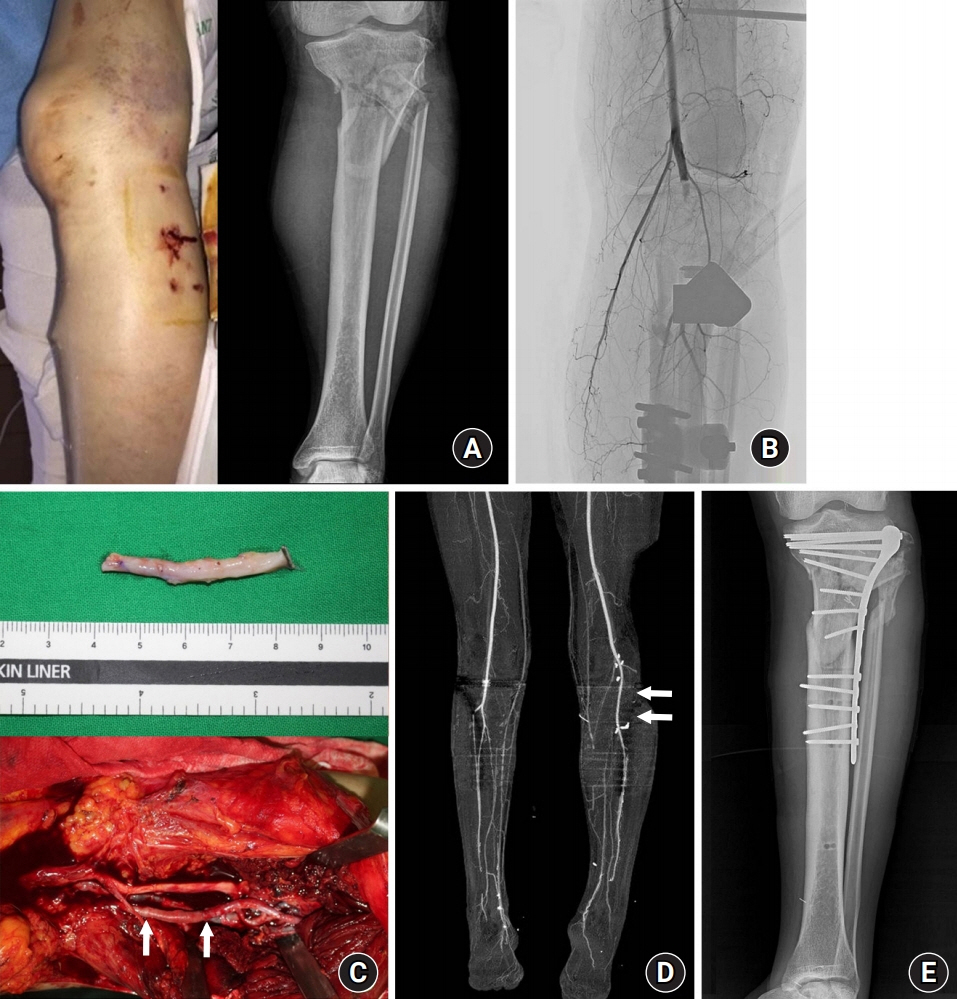
Among the patients analyzed, nine patients’ injuries were caused by traffic accidents and three industrial accidents, one fall down. Mean MESS was 6.2 (range, 5–8) and mean ischemic time was 12.3 hours (range, 5–25 hours). As arterial reconstruction, seven patients underwent posterior tibial artery reconstruction, three underwent popliteal artery reconstruction, two underwent anterior tibial artery reconstruction, and one underwent radial artery reconstruction; the greater saphenous vein was grafted in 12 reconstruction cases. Mean length of the grafted vein was 4.9 cm (range, 3–10 cm). All patients have salvaged injured limbs.
Conclusion
Artery reconstruction using autogenous vein graft is an efficient treatment method when vascular damage cannot be directly repaired during limb salvage.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah DM, Leather RP, Corson JD, Karmody AM. Polytetrafluoroethylene grafts in the rapid reconstruction of acute contaminated peripheral vascular injuries. Am J Surg. 1984; 14:229–33.
Article2. Peck JJ, Eastman AB, Bergan JJ, Sedwitz MM, Hoyt DB, McReynolds DG. Popliteal vascular trauma. A community experience. Arch Surg. 1990; 125:1339–43.3. Sciarretta JD, Macedo FI, Otero CA, Figueroa JN, Pizano LR, Namias N. Management of traumatic popliteal vascular injuries in a level I trauma center: a 6-year experience. Int J Surg. 2015; 18:136–41.
Article4. Hiatt MD, Fleischmann D, Hellinger JC, Rubin GD. Angiographic imaging of the lower extremities with multidetector CT. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005; 43:1119–27.
Article5. Doody O, Given MF, Lyon SM. Extremities--indications and techniques for treatment of extremity vascular injuries. Injury. 2008; 39:1295–303.
Article6. Kim YW, Park HY, Sur YJ. Soft tissue reconstruction for open tibia fractures. Arch Hand Microsurg. 2020; 25:207–18.
Article7. Siddique MK, Bhatti AM. A two-year experience of treating vascular trauma in the extremities in a military hospital. J Pak Med Assoc. 2013; 63:327–30.8. McCready RA, Logan NM, Daugherty ME, Mattingly SS, Crocker C, Hyde GL. Long- term results with autogenous tissue repair of traumatic extremity vascular injuries. Ann Surg. 1987; 206:804–8.9. Dorigo W, Di Carlo F, Troisi N, et al. Lower limb revascularization with a new bioactive prosthetic graft: early and late results. Ann Vasc Surg. 2008; 22:79–87.
Article10. Dorigo W, Pulli R, Castelli P, et al. A multicenter comparison between autologous saphenous vein and heparin-bonded expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) graft in the treatment of critical limb ischemia in diabetics. J Vasc Surg. 2011; 54:1332–8.
Article11. Halvorson JJ, Anz A, Langfitt M, et al. Vascular injury associated with extremity trauma: initial diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011; 19:495–504.
Article12. Huynh TT, Pham M, Griffin LW, et al. Management of distal femoral and popliteal arterial injuries: an update. Am J Surg. 2006; 192:773–8.
Article13. Lin CH, Wei FC, Levin LS, Su JI, Yeh WL. The functional outcome of lower- extremity fractures with vascular injury. J Trauma. 1997; 43:480–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Outcomes after Arterial or Venous Reconstructions in Limb Salvage Surgery for Extremity Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Comparative Analysis of Graft Patency and Limb Salvage Rate in DM & Non-DM after Infrainguinal Arterial Reconstruction
- Outcomes of Vascular Resection and Reconstruction in Extremity Soft Tissue Sarcoma and Bone Tumors
- Results of Infrainguinal Bypass with a Composite Graft Combining Polytetrafluoroethylene and Vein Graft in Absence of Appropriate Saphenous Vein Graft
- Outcomes of Infrainguinal Arterial Bypasses for the Patients with Atherosclerotic Lower Extremity Arterial Occlusive Disease