Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 Aug;25(3):426-430. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.426.
Portal vein arterialization following a radical left extended hepatectomy for Klatskin tumor: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of General Surgery and Liver Transplantation, San Camillo Hospital, Rome, Italy
- KMID: 2519303
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.426
Abstract
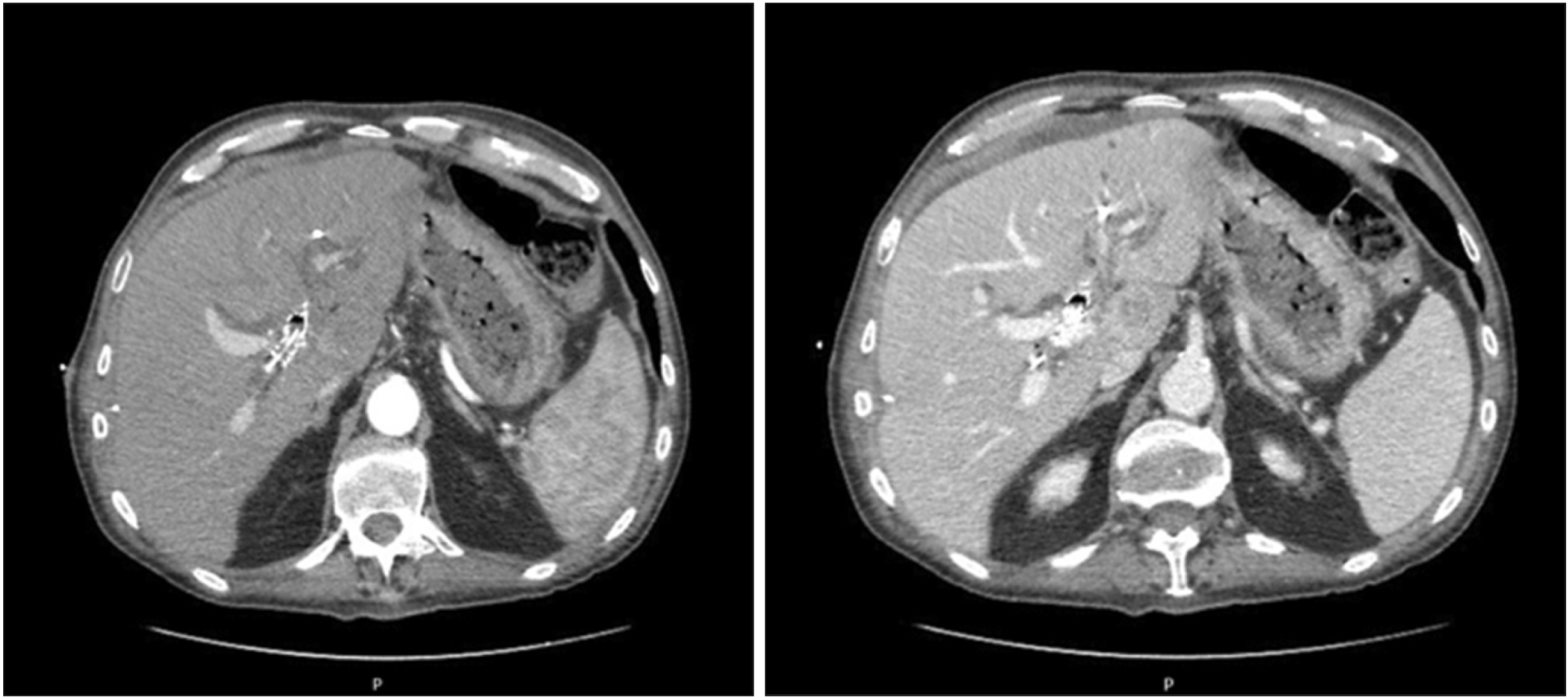
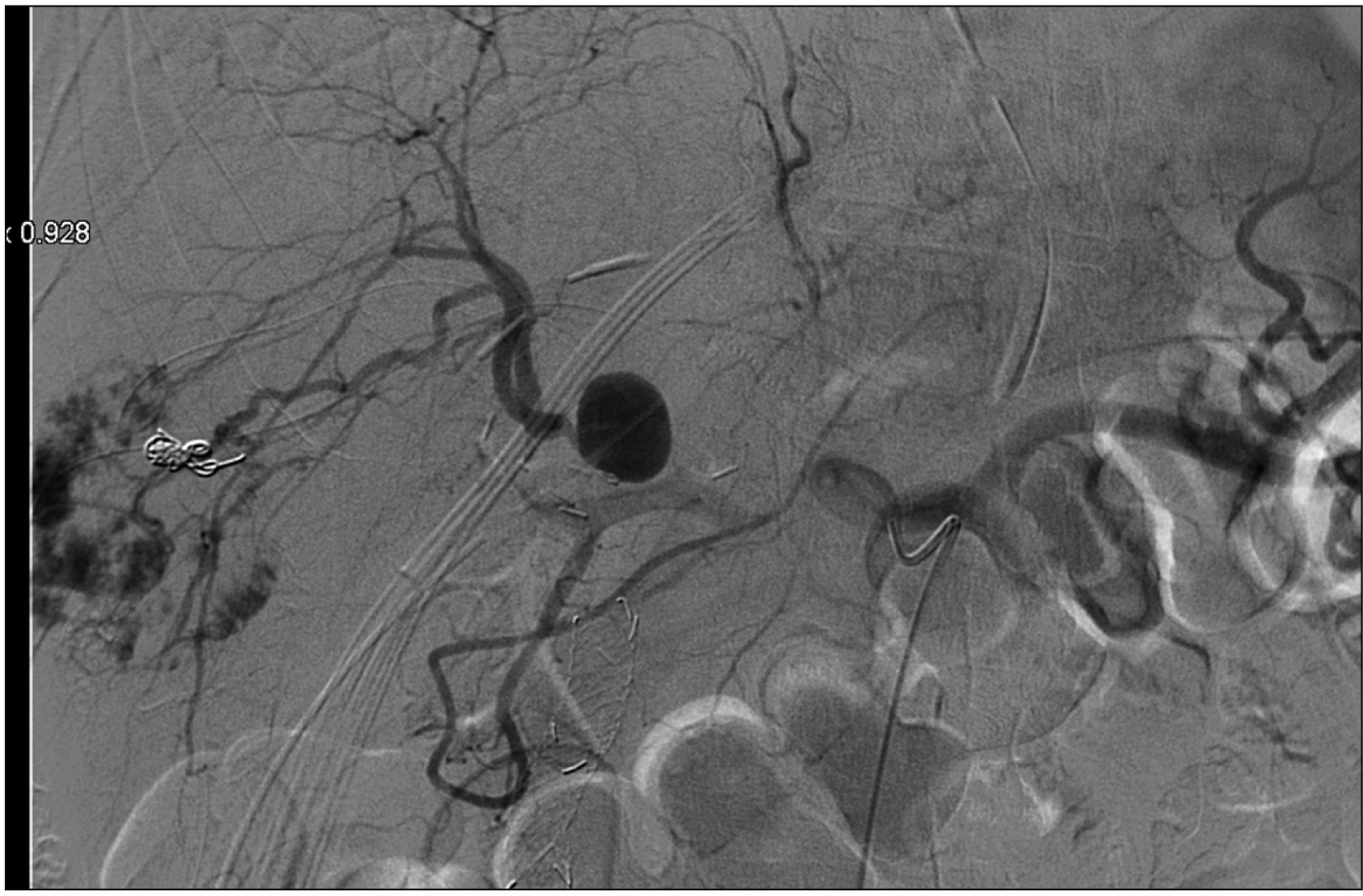
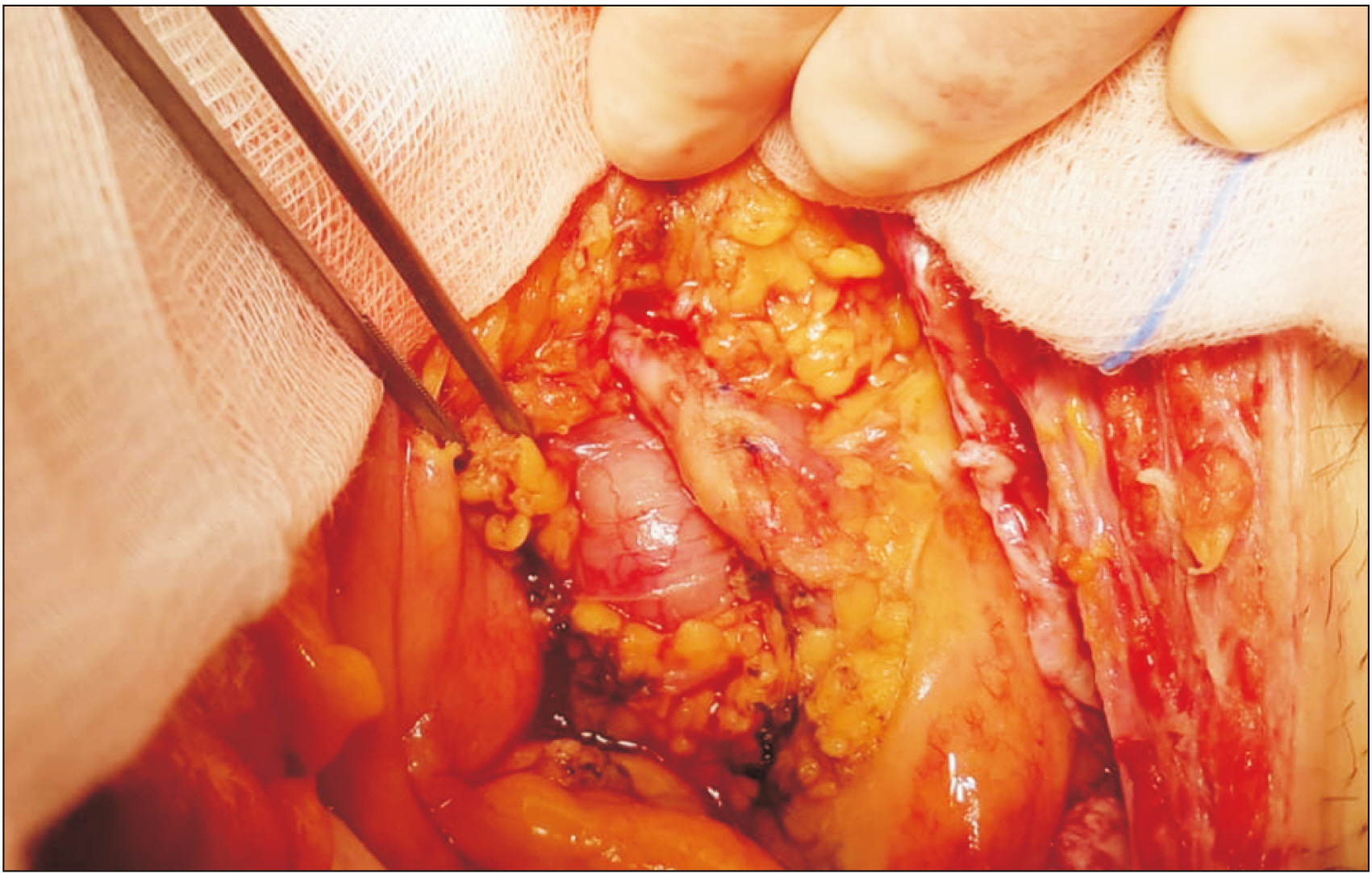
- Portal vein arterialization (PVA) has been attracting attention for its role as a salvage inf low technique in various clinical applications. Initially performed in shunt surgery for portal hypertension, with the aim of preventing a decreased hepatic inf low, it is largely used in case of hepatic artery thrombosis in the transplantation domain or in the enlarged radical operations in case of hilar cancer invading the hepatic artery. A 62-year-old man underwent a left extended hepatectomy with hepatic bile duct resection and right Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Computed tomography scan on postoperative day (POD) 5 revealed right hepatic artery pseudo-aneurysm, which was confirmed by an angiography. Stent placement was infeasible. Coiling of the pseudoaneurysm was associated with a risk of complete occlusion inducing critical liver failure. Since his general conditions were deteriorated, the patient underwent an emergency laparotomy. Hepatic artery reconstruction was impossible. Thus, a PVA was performed by anastomosing the ileocecal artery and vein. The intraoperative ultrasound showed satisfactory patency of the PVA with good portal f low in the absence of arterial f low. Doppler ultrasound on POD 15 showed that the cross-sectional area and blood f low of the portal vein were increased. The patient was discharged on POD 54 in good general condition. Hepatic artery disruption represents potentially lethal complications of hepatic, biliary, and pancreatic surgery. PVA may be a feasible therapeutic strategy to guarantee arterial inf low to the remnant liver. Although PVA is a salvage surgical procedure, increased portal f low should be controlled to avoid portal hypertension and liver fibrosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bhangui P, Salloum C, Lim C, Andreani P, Ariche A, Adam R, et al. 2014; Portal vein arterialization: a salvage procedure for a totally de-arterialized liver. The Paul Brousse Hospital experience. HPB (Oxford). 16:723–738. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12200. PMID: 24329988. PMCID: PMC4113254.2. Iseki J, Touyama K, Noie T, Nakagami K, Takagi M, Hakamada K, et al. 1992; Partial portal arterialization for the prevention of massive liver necrosis following extended pancreatobiliary surgery: experience of two cases. Surg Today. 22:568–571. DOI: 10.1007/BF00308907. PMID: 1472800.
Article3. Tessier DJ, Fowl RJ, Stone WM, McKusick MA, Abbas MA, Sarr MG, et al. 2003; Iatrogenic hepatic artery pseudoaneurysms: an uncommon complication after hepatic, biliary, and pancreatic procedures. Ann Vasc Surg. 17:663–669. DOI: 10.1007/s10016-003-0075-1. PMID: 14564553.
Article4. Jiang J, Wei J, Wu J, Gao W, Li Q, Jiang K, et al. 2016; Partial portal vein arterialization attenuates acute bile duct injury induced by hepatic dearterialization in a rat model. Biomed Res Int. 2016:7427246. DOI: 10.1155/2016/7427246. PMID: 27872855. PMCID: PMC5107218.
Article5. Melandro F, Lai Q, Levi Sandri GB, Guglielmo N, Di Laudo M, Morabito V, et al. 2013; A case of portal vein arterialization after a liver transplant. Exp Clin Transplant. 11:287–289. DOI: 10.6002/ect.2012.0172. PMID: 23767946.
Article6. Sheil AG, Thompson JF, Stephen MS, Eyers AA, Bookallil M, McCaughan GW, et al. 1989; Donor portal vein arterialization during liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 21(1 Pt 2):2343–2344. PMID: 2652760.7. Bonnet S, Sauvanet A, Bruno O, Sommacale D, Francoz C, Dondero F, et al. 2010; Long-term survival after portal vein arterialization for portal vein thrombosis in orthotopic liver transplantation. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 34:23–28. DOI: 10.1016/j.gcb.2009.05.013. PMID: 19643558.
Article8. Paloyo S, Nishida S, Fan J, Tekin A, Selvaggi G, Levi D, et al. 2013; Portal vein arterialization using an accessory right hepatic artery in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 19:773–775. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23653. PMID: 23554089.
Article9. Erhard J, Lange R, Rauen U, Scherer R, Friedrich J, Pietsch M, et al. 1998; Auxiliary liver transplantation with arterialization of the portal vein for acute hepatic failure. Transpl Int. 11:266–271. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.1998.tb00968.x. PMID: 9704389.
Article10. Charco R, Margarit C, López-Talavera JC, Hidalgo E, Castells L, Allende H, et al. 2001; Outcome and hepatic hemodynamics in liver transplant patients with portal vein arterialization. Am J Transplant. 1:146–151. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-6143.2001.10208.x. PMID: 12099362.
Article11. Kondo S, Hirano S, Ambo Y, Tanaka E, Kubota T, Katoh H. 2004; Arterioportal shunting as an alternative to microvascular reconstruction after hepatic artery resection. Br J Surg. 91:248–251. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.4428. PMID: 14760676.
Article12. Young AL, Prasad KR, Adair R, Abu Hilal M, Guthrie JA, Lodge JP. 2008; Portal vein arterialization as a salvage procedure during left hepatic trisectionectomy for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 207:e1–e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2008.07.019. PMID: 18954768.
Article13. Hidalgo E. 2014; Portal vein arterialization: 'enjoy' it responsibly. HPB (Oxford). 16:739. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12219. PMID: 25040489. PMCID: PMC4113255.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of the Preoperative Portal Vein Embolization in Major Hepatectomy
- Successful laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy in a case with challenging portal vein variation
- Two-Stage Hepatectomy for Bilateral Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Tumor Thrombi
- Effect of Partial Portal Arterialization on Graft Survival in Experimental Liver Transplantation
- Portal vein fenestration: a case report of an unusual portal vein developmental anomaly