Healthc Inform Res.
2021 Jul;27(3):200-213. 10.4258/hir.2021.27.3.200.
Concerns of Thalassemia Patients, Carriers, and their Caregivers in Malaysia: Text Mining Information Shared on Social Media
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Computer Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
- 2Regenerative Medicine Cluster, Advanced Medical and Dental Institute, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
- KMID: 2519036
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2021.27.3.200
Abstract
Objectives
The main aim of this study was to use text mining on social media to analyze information and gain insight into the health-related concerns of thalassemia patients, thalassemia carriers, and their caregivers.
Methods
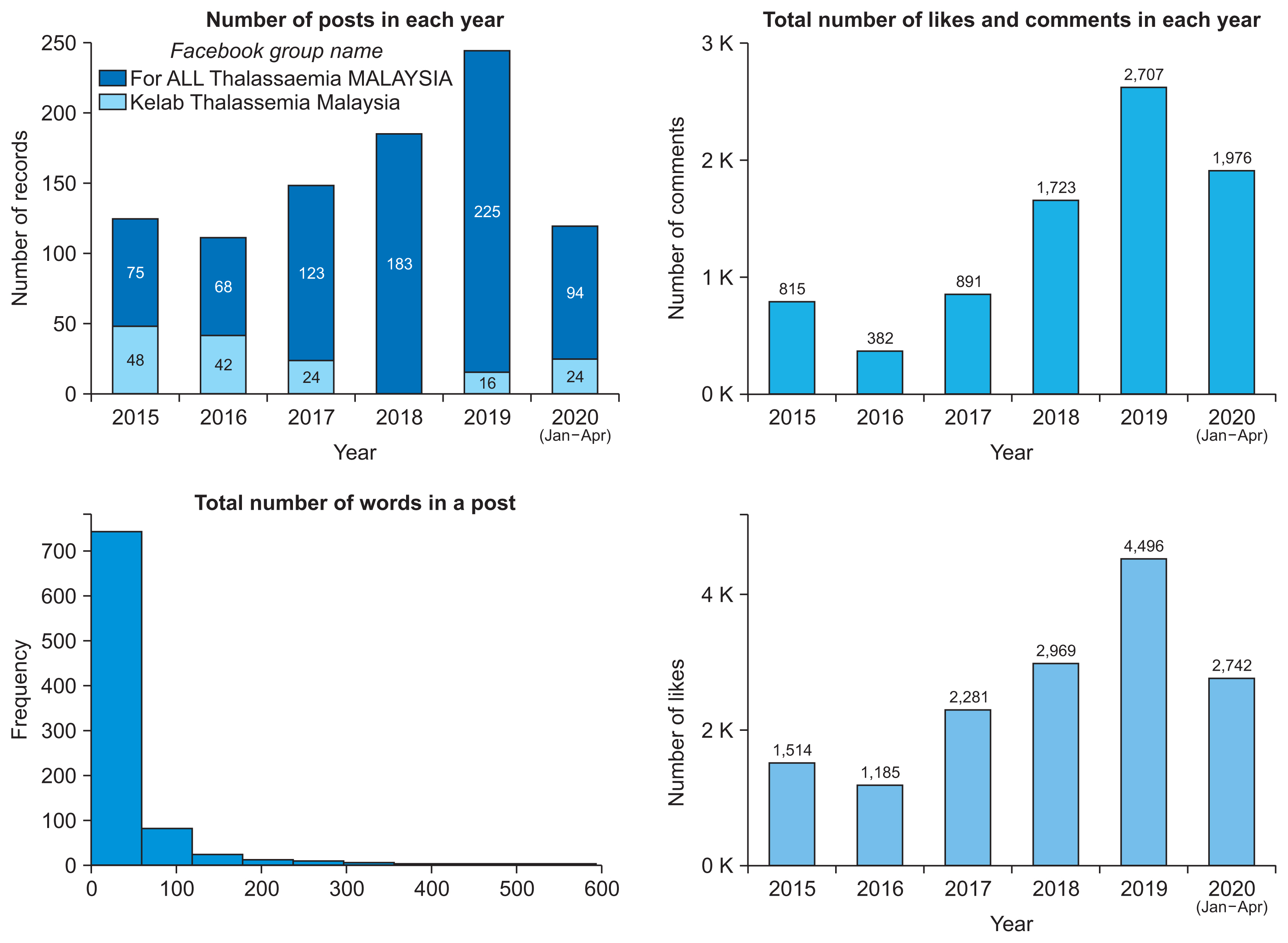
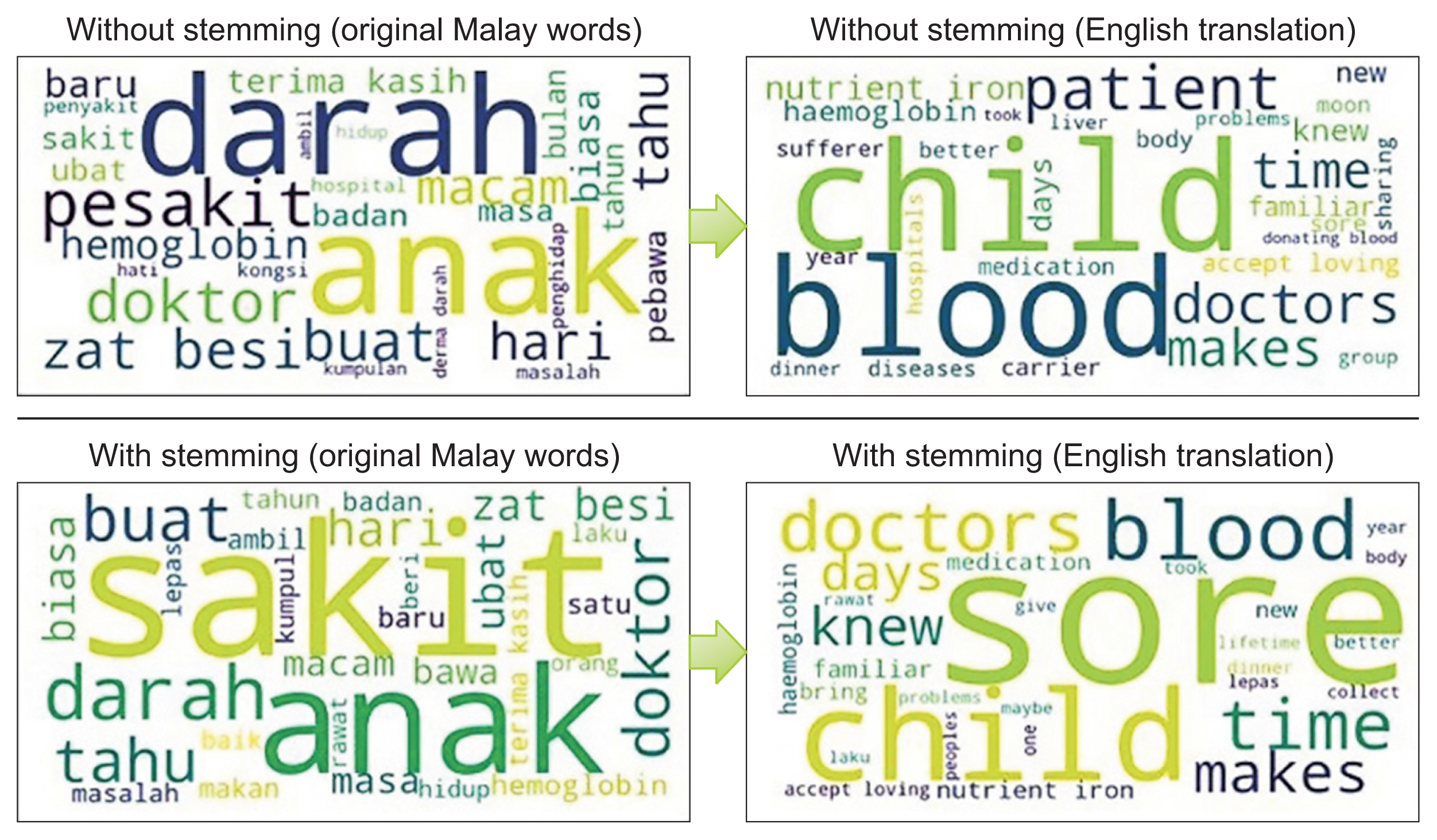
Posts from two Facebook groups whose members consisted of thalassemia patients, thalassemia carriers, and caregivers in Malaysia were extracted using the Data Miner tool. In this study, a new framework known as Malay-English social media text pre-processing was proposed for performing the steps of pre-processing the noisy mixed language (Malay-English language) of social media posts. Topic modeling was used to identify hidden topics within posts shared among members. Three different topic models—latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) in GenSim, LDA in MALLET, and latent semantic analysis—were applied to the dataset with and without stemming using Python.
Results
LDA in MALLET without stemming was found to be the best topic model for this dataset. Eight topics were identified within the posts shared by members. Of those eight topics, four were newly discovered by this study, and four others corresponded to the findings of previous studies that used an interview approach.
Conclusions
Topic 2 (the challenges faced by thalassemia patients) was found to be the topic with the highest attention and engagement. Healthcare practitioners and other concerned parties should make an effort to build a stronger support system related to this issue for those affected by thalassemia.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Alnaami A, Wazqar D. Disease knowledge and treatment adherence among adult patients with thalassemia: a cross-sectional correlational study. Pielegniarstwo XXI wieku/Nurs 21st Century. 2019; 18(2):95–101.
Article2. Modell B, Darlison M. Global epidemiology of haemoglobin disorders and derived service indicators. Bull World Health Organ. 2008; 86(6):480–7.
Article3. Mohd Ibrahim H. Malaysian thalassaemia registry report 2018. Putrajaya, Malaysia: Medical Development Division, Ministry of Health;2019.4. Wahab IA, Naznin M, Nora MZ, Suzanah AR, Zulaiho M, Faszrul AR, et al. Thalassaemia: a study on the perception of patients and family members. Med J Malaysia. 2011; 66(4):326–34.5. Ismail WI, Hassali MA, Farooqui M, Saleem F, Aljadhey H. Perceptions of thalassemia and its treatment among Malaysian thalassemia patients: a qualitative study. Australas Med J (Online). 2016; 9(5):103–10.6. Shafie AA, Chhabra IK, Wong JH, Mohammed NS, Ibrahim HM, Alias H. Health-related quality of life among children with transfusion-dependent thalassemia: a cross-sectional study in Malaysia. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020; 18(1):141.
Article7. Mashayekhi F, Jozdani RH, Chamak MN, Mehni S. Caregiver burden and social support in mothers with β-thalassemia children. Glob J Health Sci. 2016; 8(12):206–12.
Article8. Platania S, Gruttadauria S, Citelli G, Giambrone L, Di Nuovo S. Associations of thalassemia major and satisfaction with quality of life: the mediating effect of social support. Health Psychol Open. 2017; 4(2):2055102917742054.
Article9. Paramore C, Levine L, Bagshaw E, Ouyang C, Kudlac A, Larkin M. Patient- and caregiver-reported burden of transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia measured using a digital application. Patient. 2021; 14:197–208.
Article10. Rocha HM, Savatt JM, Riggs ER, Wagner JK, Faucett WA, Martin CL. Incorporating social media into your support tool box: points to consider from genetics-based communities. J Genet Couns. 2018; 27(2):470–80.
Article11. Maheri A, Sadeghi R, Shojaeizadeh D, Tol A, Yaseri M, Rohban A. Depression, anxiety, and perceived social support among adults with beta-thalassemia major: cross-sectional study. Korean J Fam Med. 2018; 39(2):101–7.
Article12. Tapi Nzali MD, Bringay S, Lavergne C, Mollevi C, Opitz T. What patients can tell us: topic analysis for social media on breast cancer. JMIR Med Inform. 2017; 5(3):e23.
Article13. Curiskis SA, Drake B, Osborn TR, Kennedy PJ. An evaluation of document clustering and topic modelling in two online social networks: Twitter and Reddit. Inf Process Manag. 2020; 57(2):102034.
Article14. Tessore JP, Esnaola LM, Russo CC, Baldassarri S. Comparative analysis of preprocessing tasks over social media texts in Spanish. In : Proceedings of the XX International Conference on Human Computer Interaction; 2019 Jun 25–28; Donostia, Spain. p. 1–8.
Article15. Omar N, Hamsani AF, Abdullah NA, Abidin SZ. Construction of Malay abbreviation corpus based on social media data. J Eng Appl Sci. 2017; 12(3):468–74.16. Husein Z. Malaya: Natural Language Toolkit for bahasa Malaysia [Internet]. GitHub Repository. 2018. [cited at 2021 Jun 29]. Available from: https://github.com/huseinzol05/malaya .17. Kwee AT, Tsai FS, Tang W. Sentence-level novelty detection in English and Malay. Theeramunkong T, Kijsirikul B, Cercone N, Ho TB, editors. Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer;20009. p. 40–51.
Article18. Blei DM, Ng AY, Jordan MI. Latent Dirichlet allocation. J Mach Learn Res. 2003; 3:993–1022.19. Landauer TK, Foltz PW, Laham D. An introduction to latent semantic analysis. Discourse Process. 1998; 25(2–3):259–284.
Article20. Pouraboli B, Abedi HA, Abbaszadeh A, Kazemi M. The burden of care: experiences of parents of children with thalassemia. J Nurs Care. 2017; 6(2):389.
Article21. Dadipoor S, Haghighi H, Madani A, Ghanbarnejad A, Shojaei F, Hesam A, et al. Investigating the mental health and coping strategies of parents with major thalassemic children in Bandar Abbas. J Educ Health Promot. 2015; 4:59.22. Mufti GE, Towell T, Cartwright T. Pakistani children’s experiences of growing up with beta-thalassemia major. Qual Health Res. 2015; 25(3):386–96.
Article23. Ishfaq K, Hashmi M, Naeem SB. Mothers’ awareness and experiences of having a thalassemic child: a qualitative approach. Pak J Appl Soc Sci. 2015; 2(1):35–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Text Mining in Biomedical Domain with Emphasis on Document Clustering
- Social Media Mining Toolkit (SMMT)
- Analysis of Adverse Drug Reaction Reports using Text Mining
- Role for Social Media in Pediatric Liver Disease: Caregiver and Provider Perspectives
- PubMiner: Machine Learning-based Text Mining for Biomedical Information Analysis