Diabetes Metab J.
2021 Jul;45(4):526-538. 10.4093/dmj.2020.0100.
Study on Risk Factors of Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Establishment of Prediction Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Public Health, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- KMID: 2518895
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0100
Abstract
- Background
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most serious complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). DPN increases the risk of ulcers, foot infections, and noninvasive amputations, ultimately leading to long-term disability.
Methods
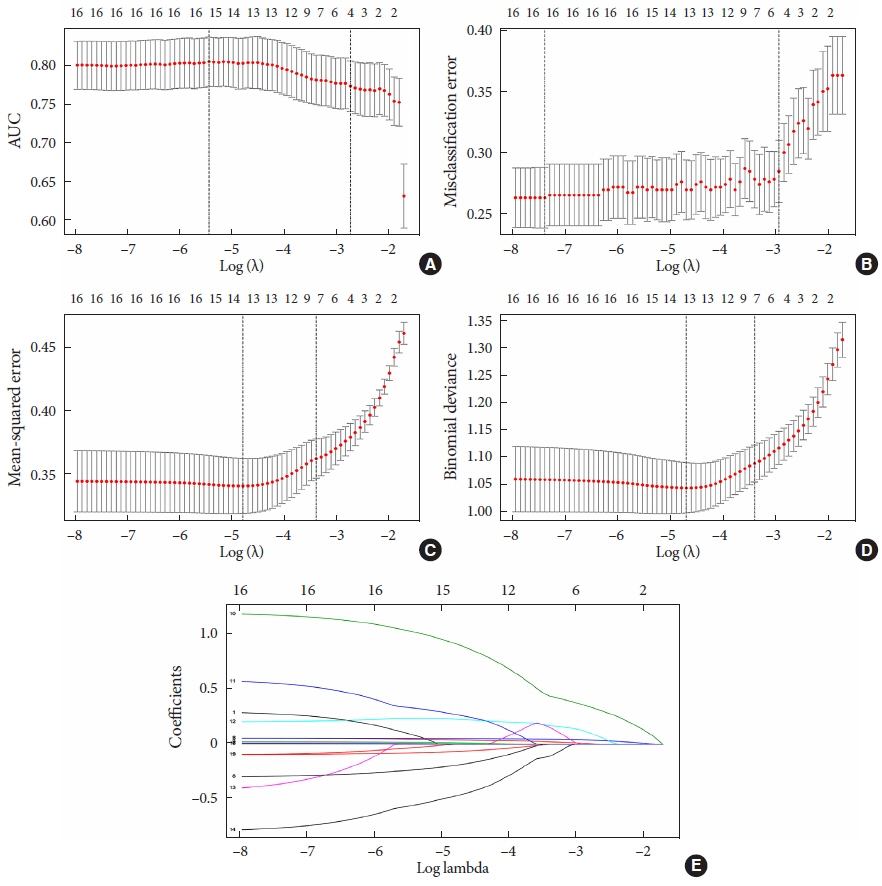
Seven hundred patients with T2DM were investigated from 2013 to 2017 in the Sanlin community by obtaining basic data from the electronic medical record system (EMRS). From September 2018 to July 2019, 681 patients (19 missing) were investigated using a questionnaire, physical examination, biochemical index test, and follow-up Toronto clinical scoring system (TCSS) test. Patients with a TCSS score ≥6 points were diagnosed with DPN. After removing missing values, 612 patients were divided into groups in a 3:1 ratio for external validation. Using different Lasso analyses (misclassification error, mean squared error, –2log-likelihood, and area under curve) and a logistic regression analysis of the training set, models A, B, C, and D were established. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration plot, dynamic component analysis (DCA) measurements, net classification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) were used to validate discrimination and clinical practicality of the model.
Results
Through data analysis, model A (containing four factors), model B (containing five factors), model C (containing seven factors), and model D (containing seven factors) were built. After calibration, ROC curve, DCA, NRI and IDI, models C and D exhibited better accuracy and greater predictive power.
Conclusion
Four prediction models were established to assist with the early screening of DPN in patients with T2DM. The influencing factors in model C and D are more important factors for patients with T2DM diagnosed with DPN.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Khawaja N, Abu-Shennar J, Saleh M, Dahbour SS, Khader YS, Ajlouni KM. The prevalence and risk factors of peripheral neuropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; the case of Jordan. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018; 10:8.
Article2. Agrawal Y, Carey JP, Della Santina CC, Schubert MC, Minor LB. Diabetes, vestibular dysfunction, and falls: analyses from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Otol Neurotol. 2010; 31:1445–50.3. Hou RF, Tang ZY, Zhang W. Comparison of effectiveness among five screening tests for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Chin J Diabetes. 2008; 16:91–4.4. Liu F, Mao JP, Yan X. Toronto clinical scoring system in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008; 33:1137–41.5. Zhang HH, Han X, Wang M, Hu Q, Li S, Wang M, et al. The association between genomic DNA methylation and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2019; 2019:2494057.
Article6. Pai YW, Lin CH, Lee IT, Chang MH. Prevalence and biochemical risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in Taiwanese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018; 12:111–6.
Article7. Sendi RA, Mahrus AM, Saeed RM, Mohammed MA, AlDubai SAR. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy among Saudi diabetic patients: a multicenter cross-sectional study at primary health care setting. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020; 9:197–201.
Article8. Wang DD, Bakhotmah BA, Hu FB, Alzahrani HA. Prevalence and correlates of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a Saudi Arabic population: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e106935.
Article9. Naqvi SS, Imani S, Hosseinifard H, Wen QL, Shahzad MN, Ijaz I, et al. Associations of serum low-density lipoprotein and systolic blood pressure levels with type 2 diabetic patients with and without peripheral neuropathy: systemic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis of observational studies. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019; 19:125.
Article10. Huang L, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Shen X, Yan S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is associated with higher systolic blood pressure in adults with type 2 diabetes with and without hypertension in the Chinese Han population. Can J Diabetes. 2020; 44:615–23.
Article11. Yokoyama H, Yokota Y, Tada J, Kanno S. Diabetic neuropathy is closely associated with arterial stiffening and thickness in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2007; 24:1329–35.12. Sun Q, Tang DD, Yin EG, Wei LL, Chen P, Deng SP, et al. Diagnostic significance of serum levels of nerve growth factor and brain derived neurotrophic factor in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Med Sci Monit. 2018; 24:5943–50.
Article13. Smith AG, Singleton JR. Obesity and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for early diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2013; 27:436–42.
Article14. Tracey TJ, Steyn FJ, Wolvetang EJ, Ngo ST. Neuronal lipid metabolism: multiple pathways driving functional outcomes in health and disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018; 11:10.
Article15. Yang CP, Lin CC, Li CI, Liu CS, Lin WY, Hwang KL, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors increase the risks of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Taiwan Diabetes Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1783.16. Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Shen X, Yan S. Can both normal and mildly abnormal albuminuria and glomerular filtration rate be a danger signal for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus? Neurol Sci. 2017; 38:1381–90.
Article17. Lu B, Hu J, Wen J, Zhang Z, Zhou L, Li Y, et al. Determination of peripheral neuropathy prevalence and associated factors in Chinese subjects with diabetes and pre-diabetes: ShangHai Diabetic neuRopathy Epidemiology and Molecular Genetics Study (SH-DREAMS). PLoS One. 2013; 8:e61053.18. Win MM, Fukai K, Nyunt HH, Hyodo Y, Linn KZ. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and its impact on activities of daily living in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nurs Health Sci. 2019; 21:445–53.
Article19. Kisozi T, Mutebi E, Kisekka M, Lhatoo S, Sajatovic M, Kaddumukasa M, et al. Prevalence, severity and factors associated with peripheral neuropathy among newly diagnosed diabetic patients attending Mulago hospital: a cross-sectional study. Afr Health Sci. 2017; 17:463–73.
Article20. Braffett BH, Gubitosi-Klug RA, Albers JW, Feldman EL, Martin CL, White NH, et al. Risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study. Diabetes. 2020; 69:1000–10.
Article21. Gogia S, Rao CR. Prevalence and risk factors for peripheral neuropathy among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients at a tertiary care hospital in Coastal Karnataka. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 21:665–9.22. Lin X, Xu L, Zhao D, Luo Z, Pan S. Correlation between serum uric acid and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in T2DM patients. J Neurol Sci. 2018; 385:78–82.
Article23. Bacarin TA, Sacco IC, Hennig EM. Plantar pressure distribution patterns during gait in diabetic neuropathy patients with a history of foot ulcers. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2009; 64:113–20.
Article24. Solano MP, Prieto LM, Varon JC, Moreno M, Boulton AJ. Ethnic differences in plantar pressures in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy. Diabet Med. 2008; 25:505–7.
Article25. Birtane M, Tuna H. The evaluation of plantar pressure distribution in obese and non-obese adults. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004; 19:1055–9.
Article26. Gravante G, Russo G, Pomara F, Ridola C. Comparison of ground reaction forces between obese and control young adults during quiet standing on a baropodometric platform. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003; 18:780–2.
Article27. Zhen Q, Yao N, Chen X, Zhang X, Wang Z, Ge Q. Total body adiposity, triglycerides, and leg fat are independent risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract. 2019; 25:270–8.
Article28. Armstrong DG, Peters EJ, Athanasiou KA, Lavery LA. Is there a critical level of plantar foot pressure to identify patients at risk for neuropathic foot ulceration? J Foot Ankle Surg. 1998; 37:303–7.
Article29. Papanas N, Katsiki N, Papatheodorou K, Demetriou M, Papazoglou D, Gioka T, et al. Peripheral neuropathy is associated with increased serum levels of uric acid in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Angiology. 2011; 62:291–5.
Article30. Yu S, Chen Y, Hou X, Xu D, Che K, Li C, et al. Serum uric acid levels and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2016; 53:1045–51.
Article31. Jaiswal M, Lauer A, Martin CL, Bell RA, Divers J, Dabelea D, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in adolescents and young adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth follow-up cohort: a pilot study. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3903–8.
Article32. Andersen ST, Witte DR, Andersen H, Bjerg L, Bruun NH, Jorgensen ME, et al. Risk-factor trajectories preceding diabetic polyneuropathy: ADDITION-Denmark. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1955–62.
Article33. Aubert CE, Michel PL, Gillery P, Jaisson S, Fonfrede M, Morel F, et al. Association of peripheral neuropathy with circulating advanced glycation end products, soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products and other risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014; 30:679–85.
Article34. Wei HC, Ta N, Hu WR, Xiao MX, Tang XJ, Haryadi B, et al. Digital volume pulse measured at the fingertip as an indicator of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the aged and diabetic. Entropy. 2019; 21:1229.
Article35. Oh TJ, Lee JE, Choi SH, Jang HC. Association between body fat and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a preliminary report. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28:112–7.
Article36. Sun JT, Liu Y, Lu L, Liu HJ, Shen WF, Yang K, et al. Diabetes-invoked high-density lipoprotein and its association with coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol. 2016; 118:1674–9.
Article37. Tolle M, Huang T, Schuchardt M, Jankowski V, Prufer N, Jankowski J, et al. High-density lipoprotein loses its anti-inflammatory capacity by accumulation of pro-inflammatoryserum amyloid A. Cardiovasc Res. 2012; 94:154–62.38. Tousoulis D, Papageorgiou N, Androulakis E, Siasos G, Latsios G, Tentolouris K, et al. Diabetes mellitus-associated vascular impairment: novel circulating biomarkers and therapeutic approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62:667–76.39. Cai H, Song C, Endoh I, Goyette J, Jessup W, Freedman SB, et al. Serum amyloid A induces monocyte tissue factor. J Immunol. 2007; 178:1852–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Frequencies and Risk Factors for Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Type II Diabetes Mellitus With or Without Peripheral Neuropathy
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- Review on Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Model in Diabetes Patients
- Computerized Dynamic Posturography and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy