Korean J Transplant.
2021 Jun;35(2):71-76. 10.4285/kjt.21.0004.
Organ donation after controlled circulatory death (Maastricht classification III) following the withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment in Korea: a suggested guideline
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Korea University Medical Center, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Transplantation Center, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Korea Organ Donation Agency, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Acute Care Surgery, Department of Surgery, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2517288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.21.0004
Abstract
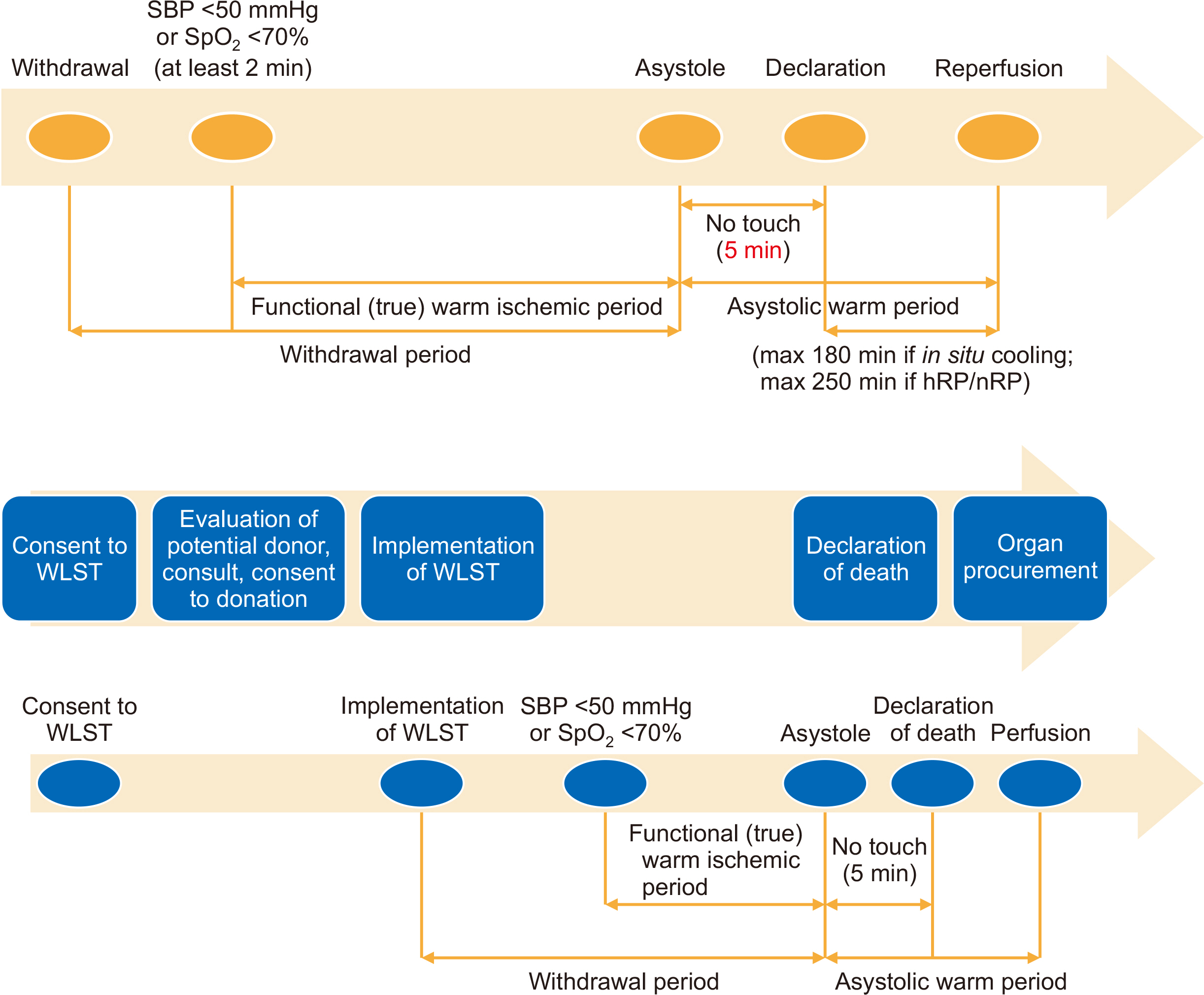
- The “Act on hospice and palliative care and decisions on life-sustaining treatment for patients at the end of life” was enacted in February 2018 in Korea. Therefore, we suggest a Korean guideline for organ donation after circulatory death (DCD) category III after the withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment (WLST). Implementation of WLST includes stopping ventilation, extubation, discontinuation of inotropics and vasoconstrictors, cessation of continuous renal replacement therapy, and cessation of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Medical staff involved in organ procurement or transplantation surgery cannot participate in the WLST process. Following cardiac arrest, 5 minutes of “no touch time” should pass, after which circulatory death can be declared. The procurement team can enter the room after the declaration of death. The final procurement decision is made after the surgeon visually checks the organ condition. DCD category III activation in Korea will help increase organ donation and reduce the demand-supply mismatch of organ transplantation.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Predicted Impact of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease 3.0 in a Region Suffering Severe Organ Shortage
Deok-Gie Kim, Seung Hyuk Yim, Eun-Ki Min, Mun Chae Choi, Jae Geun Lee, Myoung Soo Kim, Dong Jin Joo
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(35):e274. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e274.Recent Trends in the Withdrawal of Life-Sustaining Treatment in Patients with Acute Cerebrovascular Disease : 2017–2021
Seung Hwan Kim, Ji Hwan Jang, Young Zoon Kim, Kyu Hong Kim, Taek Min Nam
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2024;67(1):73-83. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2023.0074.
Reference
-
1. Manara AR, Murphy PG, O'Callaghan G. 2012; Donation after circulatory death. Br J Anaesth. 108 Suppl 1:i108–21. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aer357. PMID: 22194426.
Article2. Truog RD, Miller FG, Halpern SD. 2013; The dead-donor rule and the future of organ donation. N Engl J Med. 369:1287–9. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMp1307220. PMID: 24088088.
Article3. Lomero M, Gardiner D, Coll E, Haase-Kromwijk B, Procaccio F, Immer F, et al. 2020; Donation after circulatory death today: an updated overview of the European landscape. Transpl Int. 33:76–88. DOI: 10.1111/tri.13506. PMID: 31482628.
Article4. International Registry in Organ Donation and Transplantation. 2019. International Registry in Organ Donation and Transplantation (IRODaT) newsletter 2019 [Internet]. IRODaT-DTI Foundation;Barcelona: Available from: https://www.irodat.org/img/database/pdf/NEWSLETTER2019-June.pdf. cited 2021 May 7.5. Korean Network for Organ Sharing. 2020. Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS) quarterly statistics data [Internet]. Korean Network for Organ Sharing; 2020;Seoul: Available from: https://www.konos.go.kr/konosis/common/bizlogic.jsp. cited 2021 May 7.6. Kim JM, Kim SJ. 2010; The use of non-heart beating donors to expand the donor pool. J Korean Soc Transplant. 24:165–72. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.3.165.
Article7. Morrissey PE, Monaco AP. 2014; Donation after circulatory death: current practices, ongoing challenges, and potential improvements. Transplantation. 97:258–64. DOI: 10.1097/01.TP.0000437178.48174.db. PMID: 24492420.8. American Society of Anesthesiologists. 2017. Statement on controlled organ donation after circulatory death. Committees of origin: critical care medicine, ethics and transplant anesthesia [Internet]. American Society of Anesthesiologists;Schaumburg (IL): Available from: https://www.asahq.org/standards-and-guidelines/statement-on-controlled-organ-donation-after-circulatory-death. cited 2021 May 7.9. Korea National Institute For Bioethics Policy. 2019. 1st Annual report of decisions on life-sustaining treatment [Internet]. Korea National Institute for Bioethics Policy;Seoul: Available from: https://www.lst.go.kr/comm/referenceDetail.do?pgNo=1&cate=&searchOption=0&searchText=&bno=946. cited 2021 May 7.10. World Health Organization. 2012. International guidelines for the determination of death: phase I. May 30-31, 2012 Montreal forum report [Internet]. World Health Organization;Geneva: Available from: https://www.who.int/patientsafety/montreal-forum-report.pdf. cited 2021 May 7.11. Thuong M, Ruiz A, Evrard P, Kuiper M, Boffa C, Akhtar MZ, et al. 2016; New classification of donation after circulatory death donors definitions and terminology. Transpl Int. 29:749–59. DOI: 10.1111/tri.12776. PMID: 26991858.
Article12. Shemie SD, Baker AJ, Knoll G, Wall W, Rocker G, Howes D, et al. 2006; National recommendations for donation after cardiocirculatory death in Canada: donation after cardiocirculatory death in Canada. CMAJ. 175:S1. DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.060895. PMID: 17124739. PMCID: PMC1635157.13. Korea National Institute for Bioethics Policy. Registration status of medical institution ethics committee [Internet]. Korea National Institute for Bioethics Policy; 2021;Seoul: Available from: https://www.lst.go.kr/comm/monthlyStatistics.do. cited 2021 May 7.14. Korea Organ Donation Agency. 2019. Korea Organ Donation Agency (KODA) 2019 annual report [Internet]. Korea Organ Donation Agency;Seoul: Available from: https://www.koda1458.kr/newPr/eBook.do?num=24&idx=13. cited 2021 May 7.15. Intensive Care Society; NHS Blood and Transplant; British Transplantation Society. 2010. Organ donation after circulatory death: report of a consensus meeting, 2010 London [Internet]. Available from: https://nhsbtdbe.blob.core.windows.net/umbraco-assets-corp/1360/donation-after-circulatory-death-dcd_consensus_2010.pdf. cited 2021 May 7.16. Gift of Life Donor Program. 2009. Operating room donation after cardiac death flow sheet translated and revised by KONOS. Gift of Life Donor Program;Philadelphia (PA):17. Australian Organ and Tissue Donation and Transplantation Authority. 2010. National protocol for donation after cardiac death [Internet]. Australian Organ and Tissue Donation and Transplantation Authority;Canberra: Available from: https://donatelife.gov.au/resources/clinical-guidelines-and-protocols/national-protocol-donation-after-cardiac-death-2010. cited 2021 May 7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- First Organ Donation after Circulatory Death Following Withdrawal of Life-sustaining Treatment in Korea: a Case Report
- Factors Influencing Withdrawal of Life-Sustaining Treatment in Tertiary General Hospital Workers -Knowledge and Attitude of Organ Donation and Transplantation, Awareness of Death, Knowledge and Perception of Hospice Palliative Care-
- The first donation after circulatory death following withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment in Korea
- Withdraw life sustaining treatment and organ donation
- The Relationship among Attitudes toward the Withdrawal of Life-sustaining Treatment, Death Anxiety, and Death Acceptance among Hospitalized Elderly Cancer Patients