Kosin Med J.
2021 Jun;36(1):44-50. 10.7180/kmj.2021.36.1.44.
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension following Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Malfunction in Infant Hydrocephalus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2517225
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2021.36.1.44
Abstract
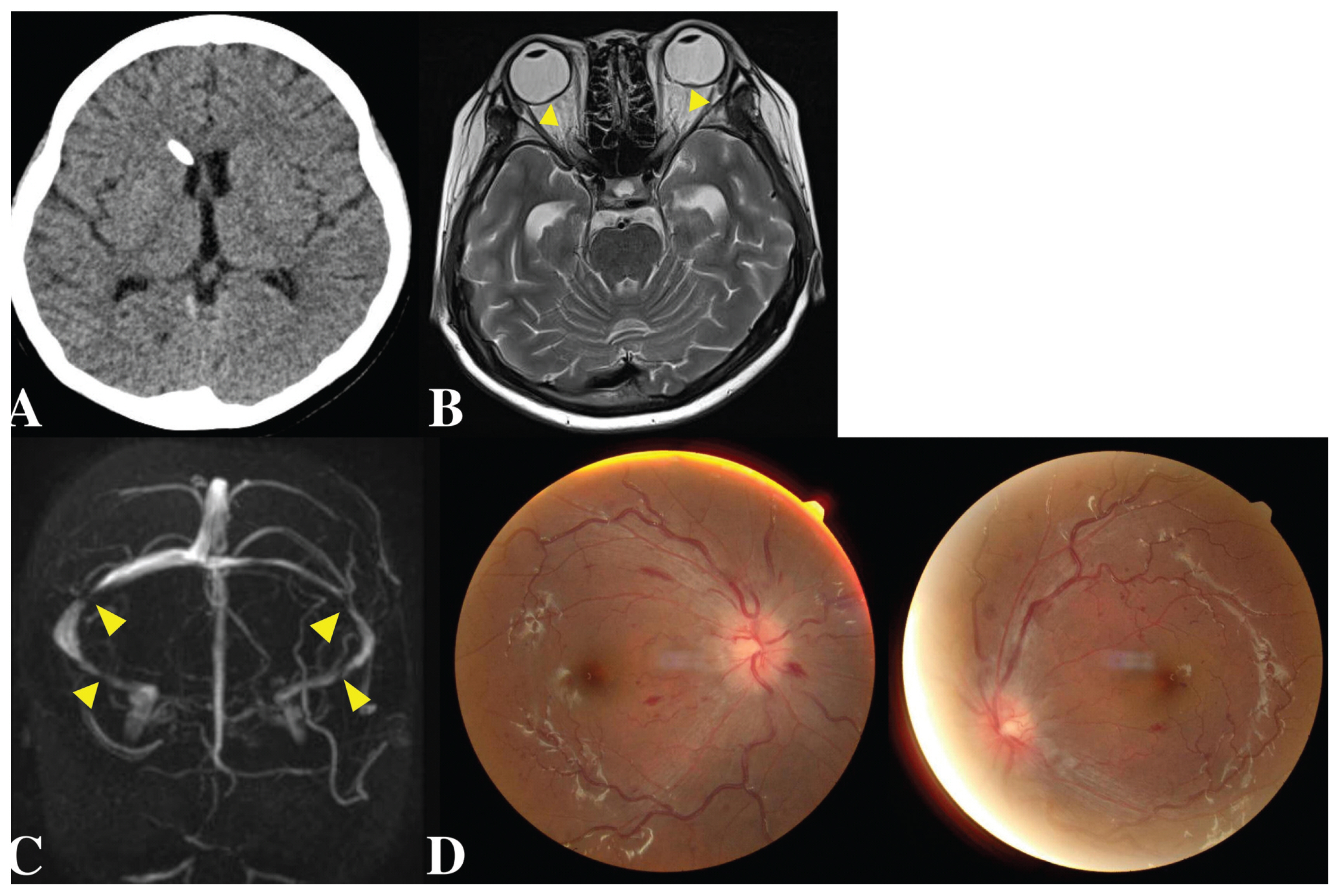
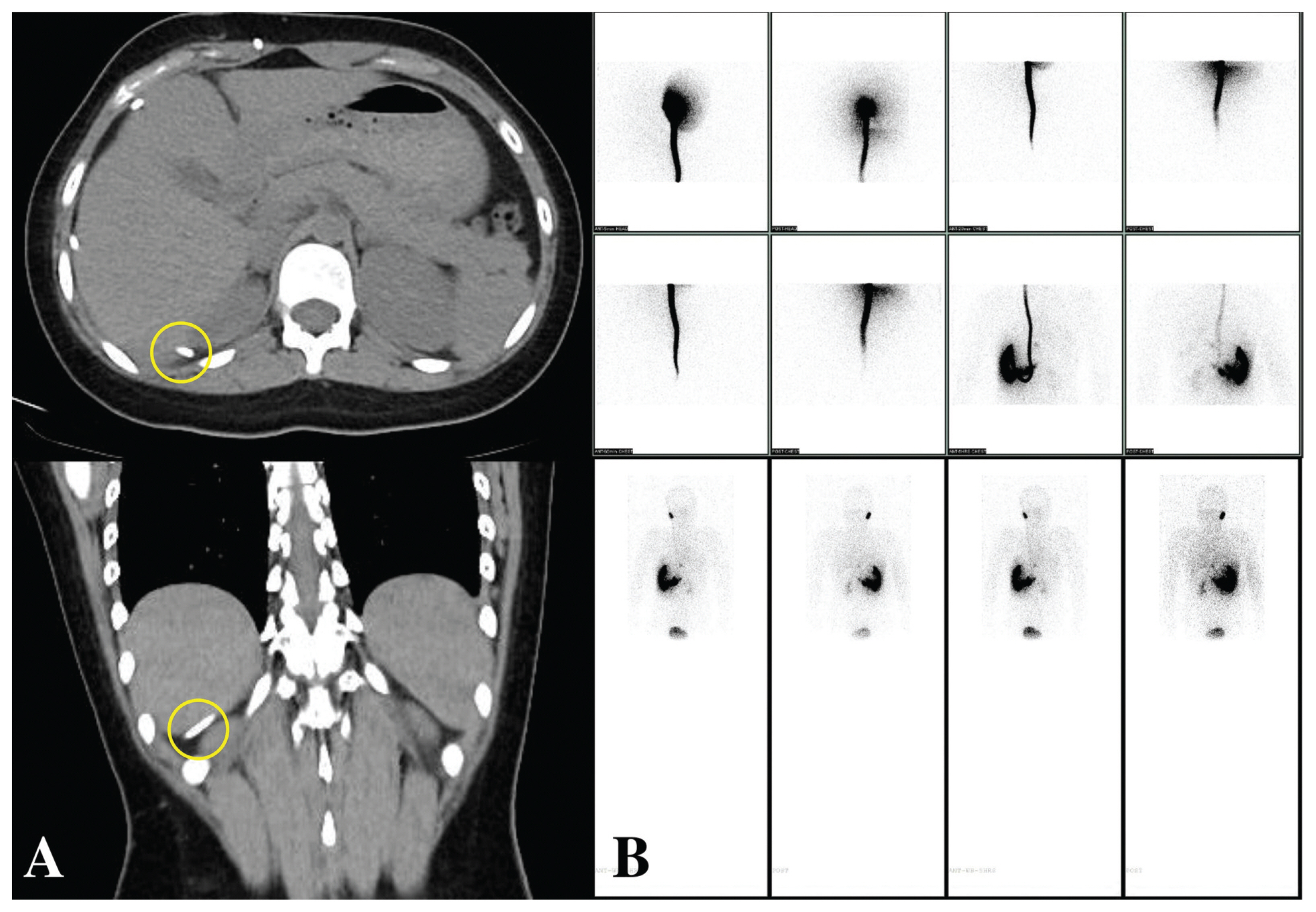
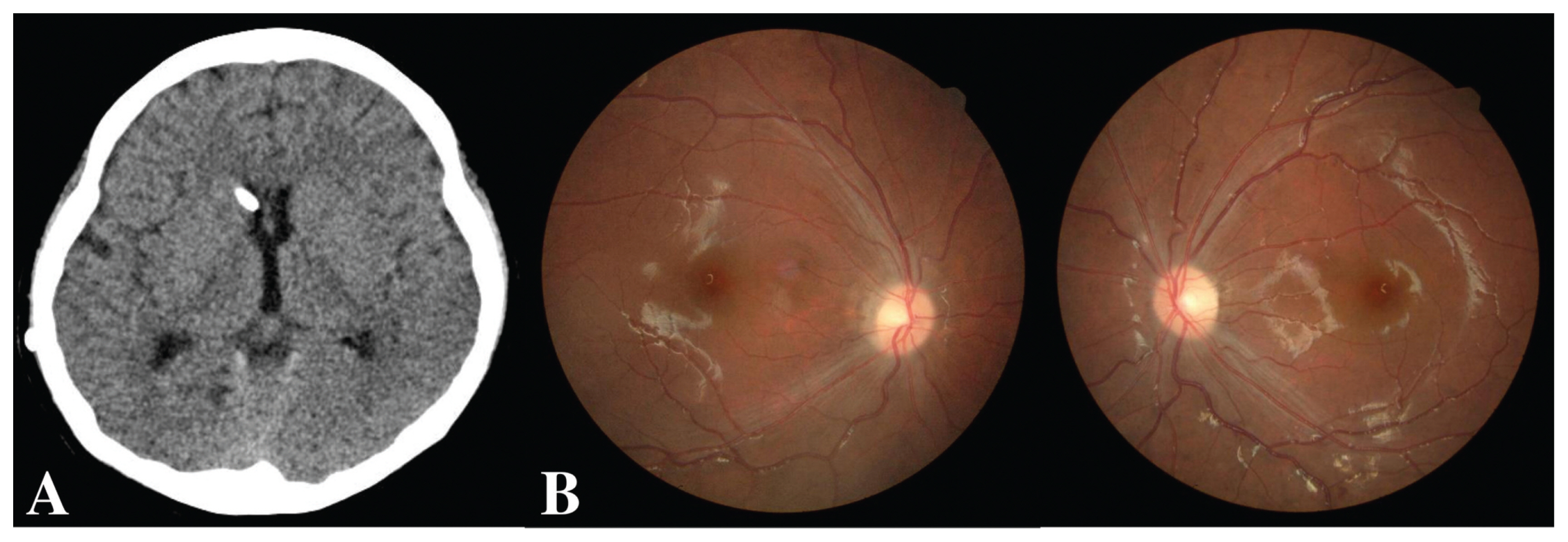
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a syndrome defined by elevated intracranial pressure without any abnormal findings. In the present study, we report a rare case of IIH in a patient after ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) due to infant hydrocephalus. A 13-year-old girl with a history of VPS due to infant hydrocephalus was admitted to emergency room with the complaint of severe headache and visual disturbance. Brain computed tomography showed normal findings. However, based on the measurement by lumbar puncture, her cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure was observed to be very high. The shunt function test revealed a VPS malfunction. Thus, we conducted VPS revision in this patient. All symptoms improved immediately after the revision. Thus, it is proposed that IIH should be considered for patients with visual disturbance and severe headache after VPS due to infant hydrocephalus without ventriculomegaly.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rangwala LM, Liu GT. Pediatric idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Surv Ophthalmol. 2007; 52:597–617.
Article2. Wall M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol Clin. 2010; 28:593–617.
Article3. Bateman GA, Smith RL, Siddique SH. Idiopathic hydrocephalus in children and idiopathic intracranial hypertension in adults: two manifestations of the same pathophysiological process? J Neurosurg. 2007; 107:439–44.
Article4. Tully HM, Dobyns WB. Infantile hydrocephalus: a review of epidemiology, classification and causes. Eur J Med Genet. 2014; 57:359–68.
Article5. Rekate HL. Hydrocephalus in infants: the unique biomechanics and why they matter. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020; 36:1713–28.
Article6. Chumas PD, Kulkarni AV, Drake JM, Hoffman HJ, Humphreys RP, Rutka JT. Lumboperitoneal shunting: a retrospective study in the pediatric population. Neurosurgery. 1993; 32:376–83.7. Hermann EJ, Polemikos M, Heissler HE, Krauss JK. Shunt Surgery in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Aided by Electromagnetic Navigation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2017; 95:26–33.
Article8. Epstein F, Lapras C, Wisoff JH. ‘Slit-ventricle syndrome’: etiology and treatment. Pediatr Neurosci. 1988; 14:5–10.
Article9. Freimann FB, Sprung C. Shunting with gravitational valves--can adjustments end the era of revisions for overdrainage-related events?: clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2012; 117:1197–204.10. Sainte-Rose C, Piatt JH, Renier D, Pierre-Kahn A, Hirsch JF, Hoffman HJ, et al. Mechanical complications in shunts. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1991; 17:2–9.
Article11. Blount JP, Campbell JA, Haines SJ. Complications in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid shunting. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1993; 4:633–56.
Article12. Tsai SY, Wang SY, Shiau YC, Yang LH, Wu YW. Clinical value of radionuclide shuntography by qualitative methods in hydrocephalic adult patients with suspected ventriculoperitoneal shunt malfunction. Medicine(Baltimore). 2017; 96:e6767.
Article13. Riva-Cambrin J, Kestle JR, Holubkov R, Butler J, Kulkarni AV, Drake J, et al. Risk factors for shunt malfunction in pediatric hydrocephalus: a multicenter prospective cohort study. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016; 17:382–90.
Article14. Engel M, Carmel PW, Chutorian AM. Increased intraventricular pressure without ventriculomegaly in children with shunts: “normal volume” hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 1979; 5:549–52.15. Shapiro K, Fried A. Pressure-volume relationships in shunt-dependent childhood hydrocephalus. The zone of pressure instability in children with acute deterioration. J Neurosurg. 1986; 64:390–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Malfunction during Pregnancy
- Acute Shunt Malfunction Caused by Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy without Shunt Infection
- Asymptomatic Fracture of a Distal Shunt Catheter after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt for Post-traumatic Hydrocephalus
- Laparoscopic Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Placement in Hydrocephalus
- Comparison of Clinical Usefulness of Lumboperitoneal Shunt with Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt for Treating Chronic Hydrocephalus in Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm