Blood Res.
2021 Jun;56(2):79-85. 10.5045/br.2021.2021024.
Investigating the expression pattern of the angiopoietin-Tie system in ALL and its correlation with baseline characteristics
- Affiliations
-
- 1Immunology Research Center, Department of Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
- 2Division of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine, Department of Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
- 3Student Research Committee, Department of Medical Genetics, School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 4HSCT Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 5Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
- KMID: 2517004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2021.2021024
Abstract
- Background
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common type of leukemia in children. Several environmental and genetic factors are known to be involved in its development and progression. The angiopoietin-Tie system is one of the most critical factors in angiogenesis, and its possible role in solid tumors and leukemia has been previously investigated. In this study, we examined the expression of these genes in ALL patients (early pre-B-ALL and pre-B-ALL) and compared them with normal samples.
Methods
Bone marrow samples were collected from 40 patients (aged 0‒19 yr) newly diagnosed with early pre-B-ALL or pre-B-ALL using molecular and flow cytometric tests and from 15 control individuals. For molecular tests, RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were performed, and Ang1, Ang2, Ang4, Tie1, and Tie2 gene expression was examined by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results
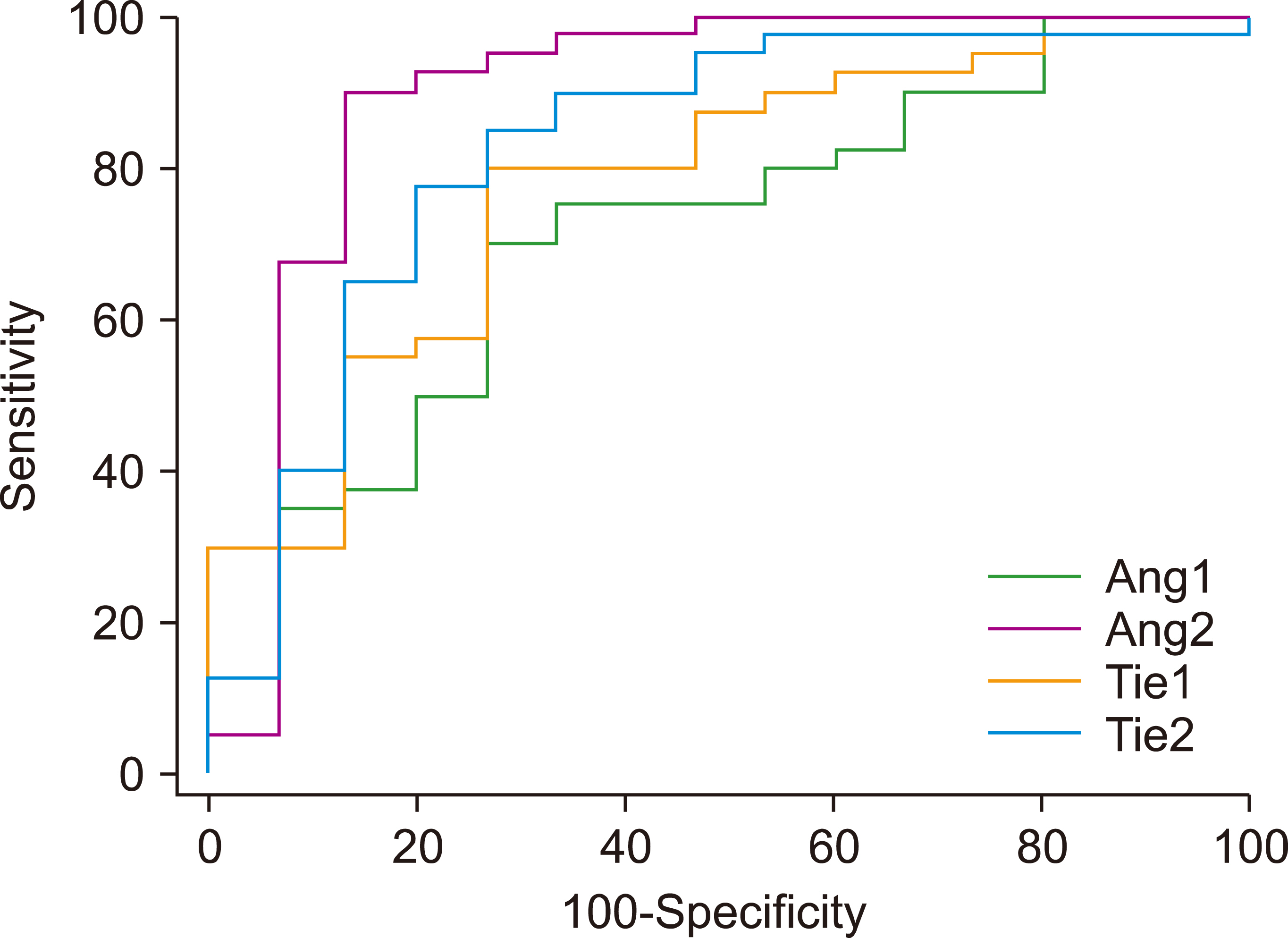
Ang2, Tie1, and Tie2 gene expression were significantly increased in patients with ALL, whereas Ang1 gene expression was decreased. The Ang4 gene did not show significant expression changes between the two groups.
Conclusion
Changes in the expression of the Ang-Tie system indicate a possible role of angiogenesis in ALL prognosis. Moreover, such changes can be considered as potential diagnostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. 2020; Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21590. PMID: 31912902.
Article2. Hunger SP, Mullighan CG. 2015; Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N Engl J Med. 373:1541–52. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1400972. PMID: 26465987.
Article3. Terwilliger T, Abdul-Hay M. 2017; Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 7:e577. DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2017.53. PMID: 28665419. PMCID: PMC5520400.
Article4. Han Y, Wang X, Wang B, Jiang G. 2016; The progress of angiogenic factors in the development of leukemias. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 5:6–16. DOI: 10.5582/irdr.2015.01048. PMID: 26989643. PMCID: PMC4761589.
Article5. Aguayo A, Giles F, Albitar M. 2003; Vascularity, angiogenesis and angiogenic factors in leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma. 44:213–22. DOI: 10.1080/1042819021000029777. PMID: 12688336.
Article6. Allahbakhshian Farsani M, Kamel M, Mehrpouri M, et al. 2020; The expression of interferon gamma (IFN-g) and interleukin 6 (IL6) in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Pathol Oncol Res. 26:461–6. DOI: 10.1007/s12253-018-0536-z. PMID: 30443842.7. Jabari M, Allahbakhshian Farsani M, Salari S, Hamidpour M, Amiri V, Mohammadi MH. 2019; Hypoxia-inducible factor1-A (HIF1a) and vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) expression in de novo AML patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 20:705–10. DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.3.705. PMID: 30909668. PMCID: PMC6825791.8. Eklund L, Kangas J, Saharinen P. 2017; Angiopoietin-Tie signalling in the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Clin Sci (Lond). 131:87–103. DOI: 10.1042/CS20160129. PMID: 27941161. PMCID: PMC5146956.
Article9. Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, et al. 1996; Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 87:1161–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81812-7. PMID: 8980223.
Article10. Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, et al. 1997; Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science. 277:55–60. DOI: 10.1126/science.277.5322.55. PMID: 9204896.
Article11. Harfouche R, Hasséssian HM, Guo Y, et al. 2002; Mechanisms which mediate the antiapoptotic effects of angiopoietin-1 on endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 64:135–47. DOI: 10.1006/mvre.2002.2421. PMID: 12074640.
Article12. Khan AA, Sandhya VK, Singh P, et al. 2014; Signaling network map of endothelial TEK tyrosine kinase. J Signal Transduct. 2014:173026. DOI: 10.1155/2014/173026. PMID: 25371820. PMCID: PMC4211299.
Article13. Amani F, Allahbakhshian Farsani M, Gholami M, Aghamiri SMR, Bakhshandeh M, Hossein Mohammadi M. 2021; The protective effect of oleuropein against radiation-induced cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and genetic damage in cultured human lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Biol. 97:179–93. DOI: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1793014. PMID: 32970517.
Article14. Kim I, Kim JH, Moon SO, Kwak HJ, Kim NG, Koh GY. 2000; Angiopoietin-2 at high concentration can enhance endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Oncogene. 19:4549–52. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203800. PMID: 11002428.
Article15. Lee HJ, Cho CH, Hwang SJ, et al. 2004; Biological characterization of angiopoietin‐3 and angiopoietin‐4. FASEB J. 18:1200–8. DOI: 10.1096/fj.03-1466com. PMID: 15284220.
Article16. Koenecke C, Kümpers P, Lukasz A, et al. 2010; Shedding of the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2 correlates with leukemic blast burden and outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for AML. Ann Hematol. 89:459–67. DOI: 10.1007/s00277-009-0869-5. PMID: 20054548.
Article17. Seegar TC, Eller B, Tzvetkova-Robev D, et al. 2010; Tie1-Tie2 interactions mediate functional differences between angiopoietin ligands. Mol Cell. 37:643–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.02.007. PMID: 20227369. PMCID: PMC2841065.
Article18. Huang H, Bhat A, Woodnutt G, Lappe R. 2010; Targeting the ANGPT-TIE2 pathway in malignancy. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:575–85. DOI: 10.1038/nrc2894. PMID: 20651738.
Article19. Mazzieri R, Pucci F, Moi D, et al. 2011; Targeting the ANG2/TIE2 axis inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by impairing angiogenesis and disabling rebounds of proangiogenic myeloid cells. Cancer Cell. 19:512–26. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.005. PMID: 21481792.
Article20. Karakurt N, Aksu T, Koksal Y, et al. 2016; Angiopoietins in the bone marrow microenvironment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology. 21:325–31. DOI: 10.1080/10245332.2015.1125078. PMID: 26901808.
Article21. Hatfield KJ, Hovland R, Øyan AM, et al. 2008; Release of angiopoietin-1 by primary human acute myelogenous leukemia cells is associated with mutations of nucleophosmin, increased by bone marrow stromal cells and possibly antagonized by high systemic angiopoietin-2 levels. Leukemia. 22:287–93. DOI: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404985. PMID: 17943167.
Article22. Ghaffari S, Torabi-Rahvar M, Omidkhoda A, Ahmadbeigi N. 2019; Impact of various culture conditions on ex vivo expansion of polyclonal T cells for adoptive immunotherapy. APMIS. 127:737–45. DOI: 10.1111/apm.12981. PMID: 31273832.23. Schliemann C, Bieker R, Padro T, et al. 2006; Expression of angiopoietins and their receptor Tie2 in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 91:1203–11. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V108.11.1894.1894. PMID: 16956819.
Article24. Müller A, Lange K, Gaiser T, et al. 2002; Expression of angiopoietin-1 and its receptor TEK in hematopoietic cells from patients with myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 26:163–8. DOI: 10.1016/S0145-2126(01)00110-2. PMID: 11755466.
Article25. Loges S, Heil G, Bruweleit M, et al. 2005; Analysis of concerted expression of angiogenic growth factors in acute myeloid leukemia: expression of angiopoietin-2 represents an independent prognostic factor for overall survival. J Clin Oncol. 23:1109–17. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.058. PMID: 15718307.
Article26. Hou HA, Chou WC, Lin LI, et al. 2008; Expression of angiopoietins and vascular endothelial growth factors and their clinical significance in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 32:904–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2007.08.010. PMID: 17904634.
Article27. Handschuh L, Kaźmierczak M, Milewski MC, et al. 2018; Gene expression profiling of acute myeloid leukemia samples from adult patients with AML-M1 and-M2 through boutique microarrays, real-time PCR and droplet digital PCR. Int J Oncol. 52:656–78. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4233. PMID: 29286103. PMCID: PMC5807040.28. Cheng CL, Hou HA, Jhuang JY, et al. 2011; High bone marrow angiopoietin-1 expression is an independent poor prognostic factor for survival in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Cancer. 105:975–82. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.340. PMID: 21878936. PMCID: PMC3185953.
Article29. Mahvi A, Mardani G, Ghasemi-Dehkordi P, et al. 2015; Effects of phenanthrene and pyrene on cytogenetic stability of human dermal fibroblasts using alkaline comet assay technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci. 85:1055–63. DOI: 10.1007/s40011-015-0514-0.
Article30. Atesoglu EB, Tarkun P, Mehtap O, et al. 2016; Serum angiopoietin levels are different in acute and chronic myeloid neoplasms: angiopoietins do not only regulate tumor angiogenesis. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 32:162–7. DOI: 10.1007/s12288-015-0548-8. PMID: 27065577. PMCID: PMC4789009.
Article31. Aref S, El Menshawy N, Azmy E, El-Refaie M. 2009; Soluble angiopoietin-2/sTie2 receptor ratio is an independent prognostic marker in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 25:17–22. DOI: 10.1007/s12288-009-0004-8. PMID: 23100966. PMCID: PMC3453480.
Article32. Schliemann C, Bieker R, Thoennissen N, et al. 2007; Circulating angiopoietin-2 is a strong prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 21:1901–6. DOI: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404820. PMID: 17597808.
Article33. Kivivuori SM, Siitonen S, Porkka K, Vettenranta K, Alitalo R, Saarinen-Pihkala U. 2007; Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 and Tie1 tyrosine kinase receptor on acute leukemia cells. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 48:387–92. DOI: 10.1002/pbc.20857. PMID: 16685739.
Article34. Aguayo A, Manshouri T, O'Brien S, et al. 2001; Clinical relevance of Flt1 and Tie1 angiogenesis receptors expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leuk Res. 25:279–85. DOI: 10.1016/S0145-2126(00)00139-9. PMID: 11248324.
Article35. Verstovsek S, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T, et al. 2002; Prognostic significance of Tie‐1 protein expression in patients with early chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 94:1517–21. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.10363. PMID: 11920509.
Article36. Verstovsek S, Estey E, Manshouri T, et al. 2001; High expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase Tie-1 in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma. 42:511–6. DOI: 10.3109/10428190109064609. PMID: 11699417.
Article37. Lee CY, Tien HF, Hu CY, Chou WC, Lin LI. 2007; Marrow angiogenesis-associated factors as prognostic biomarkers in patients with acute myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 97:877–82. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603966. PMID: 17848952. PMCID: PMC2360422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Angiopoietins in Diabetic Nephropathy
- The expression of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, Tie-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA in normal ovary, benign ovarian cyst, and epithelial ovarian cancer
- Expressions and Clinical Significances of Angiopoietin-1, Angiopoietin-2, and Tie-2 Receptor in Patients With Colorectal Cancer
- Expression of Angiopoietin-1 and -2 and Tie-2 mRNA in Uterine Endometrial Cancer
- Expression and Clinical Significance of Angiopoietin-2 and its Receptor Tie-2 in Invasive Breast Cancer