J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Jun;36(25):e169. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e169.
Peer Reviewers in Central Asia: Publons Based Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Kalinga Institute of Medical Sciences, KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, India
- 2Department of Biology and Biochemistry, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Shymkent, Kazakhstan
- KMID: 2516987
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e169
Abstract
- Background
The five Central Asian republics comprise of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. Their research and publication activities are gradually improving but there is limited data on how good their peer reviewing practices are.
Methods
We have use the Publons database to extract information on the reviewers registered including the number of verified review, Publons award winners, and top universities in the domain of peer reviewing. This has been analysed overall and country wise.
Results
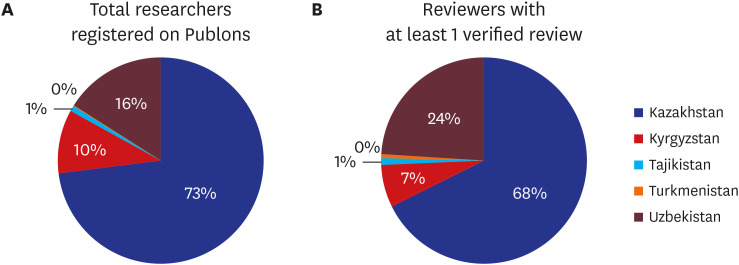
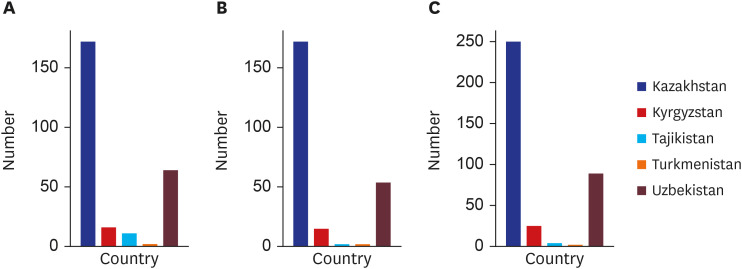
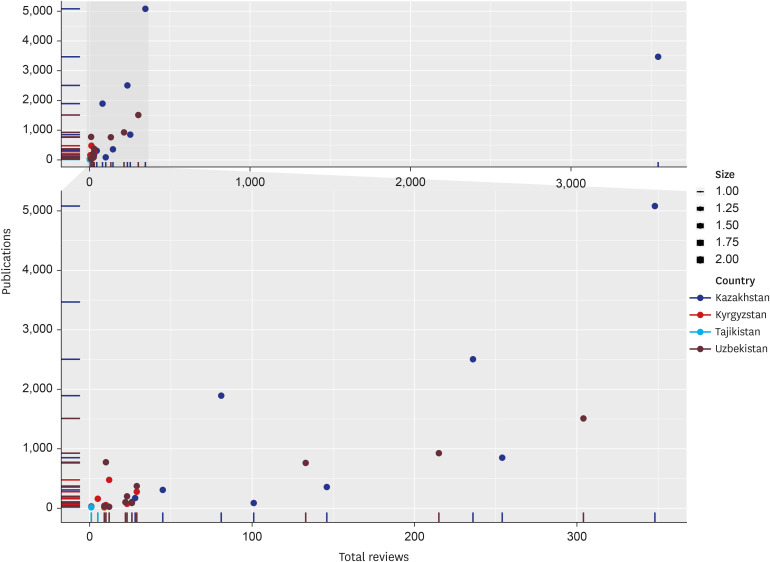
Of 15,764 researchers registered on Publons, only 370 (11.7%) have verified records of peer-reviewing. There are 8 Publons award winners. There is great heterogeneity in the number of active reviewers across the five countries. Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan account for more than 90% of verified reviewers. Only Kazakhstan has more than 100 active reviewers and 6 Publons award recipients. Amongst the top 20 reviewers from Central Asia, half of them are from the Nazarbayev University, Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan. Three countries have less than 10 universities registered on Publons.
Conclusion
Central Asia has a good number of peer reviewers on Publons though only a minority of researchers are involved in peer reviewing. However, the heterogeneity between the nations can be best dealt with by promoting awareness and international networking including e-learning and mentoring programs.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparative Analysis of Central Asian Publication Activity Using SCImago Journal & Country Rank Data in 1996–2021
Burhan Fatih Kocyigit, Ahmet Akyol, Makhmadshokh K. Gulov, Marlen Yessirkepov
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(14):e104. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e104.
Reference
-
1. Yamshchikov GV, Schmid GP. Publication practices and attitudes towards evidence-based medicine in central Asia. Lancet Glob Health. 2013; 1(2):e73–4. PMID: 25104158.
Article2. Adambekov S, Askarova S, Welburn SC, Goughnour SL, Konishi A, LaPorte R, et al. Publication productivity in Central Asia and countries of the Former Soviet Union. Cent Asian J Glob Health. 2016; 5(1):261. PMID: 29138734.
Article3. Begum M, Lewison G, Jassem J, Mixich V, Cufer T, Nurgozhin T, et al. Mapping cancer research across Central and Eastern Europe, the Russian Federation and Central Asia: Implications for future national cancer control planning. Eur J Cancer. 2018; 104:127–136. PMID: 30347288.
Article4. Ahmed S, Anirvan P. Top Central Asian educational institutions on Publons: analysis of researchers and reviewers. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(21):e144. PMID: 34060259.
Article5. Smith R. Peer review: a flawed process at the heart of science and journals. J R Soc Med. 2006; 99(4):178–182. PMID: 16574968.
Article6. Gasparyan AY, Gerasimov AN, Voronov AA, Kitas GD. Rewarding peer reviewers: maintaining the integrity of science communication. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30(4):360–364. PMID: 25829801.7. Zimba O, Gasparyan AY. Peer review guidance: a primer for researchers. Reumatologia. 2021; 59(1):3–8. PMID: 33707789.8. The Lancet. COVID-19: a stress test for trust in science. Lancet. 2020; 396(10254):799. PMID: 32950076.9. Ahmed S, Mohini . Building trust in journals and in peer review: need of the hour during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rheumatol Int. 2021; 41(2):501–502. PMID: 33161448.
Article10. Ahmed S, Pinto B. The peer review process in Asia. Cent Asian J Med Hypotheses Ethics. 2020; 1(2):136–141.
Article11. Yessirkepov M, Nurmashev B, Anartayeva M. A Scopus-based analysis of publication activity in Kazakhstan from 2010 to 2015: positive trends, concerns, and possible solutions. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30(12):1915–1919. PMID: 26713071.
Article12. Teixeira da Silva JA, Al-Khatib A. How do Clarivate Analytics and Publons propose to fortify peer review in the COVID-19 era? J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021; 16(2):139–143. PMID: 33897318.
Article13. Gasparyan AY, Nurmashev B, Yessirkepov M, Endovitskiy DA, Voronov AA, Kitas GD. Researcher and author profiles: opportunities, advantages, and limitations. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32(11):1749–1756. PMID: 28960025.
ArticleAstana YZ. Kazakhstan comes on strong. Updated September 27, 2006. Accessed May 26, 2021. http://content.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1539999,00.html.15. Ahmed S, Anirvan P. The true meaning of plagiarism. Indian J Rheumatol. 2020; 15(3):155–158.16. Misra DP, Agarwal V. Integrity of clinical research conduct, reporting, publishing, and post-publication promotion in rheumatology. Clin Rheumatol. 2020; 39(4):1049–1060. PMID: 32026178.
Article17. Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Akazhanov NA, Kitas GD. Conflicts of interest in biomedical publications: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Croat Med J. 2013; 54(6):600–608. PMID: 24382859.
Article18. Ahmed S, Zimba O, Gasparyan AY. Moving towards online rheumatology education in the era of COVID-19. Clin Rheumatol. 2020; 39(11):3215–3222. PMID: 32939569.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Top Central Asian Educational Institutions on Publons: Analysis of Researchers and Reviewers
- Practical Tips of English Expressions for Non-Native English-Speaking Peer Reviewers
- Safeguarding the Integrity of Science Communication by Restraining 'Rational Cheating' in Peer Review
- Innovative Strategies for Peer Review
- Acknowledgement to Reviewers – 2018