Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Jun;77(6):285-293. 10.4166/kjg.2021.043.
Changes in the Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Level According to the HBeAg Status and Drug Used in Long-term Nucleos(t)ide Analog-treated Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.043
Abstract
- Background/Aims
The HBsAg levels have been used to monitor the chronic hepatitis B (CHB) treatment response to antiviral therapy. On the other hand, it is unclear if the HBsAg quantification levels at each treatment point differ according to the HBeAg status and drug in CHB patients. This study compared the changes in HBsAg in CHB patients according to the HBeAg status and treatment drugs.
Methods
CHB patients with at least 1 year of follow-up treatment with one drug, either entecavir (ETV) or tenofovir (TDF), were enrolled in this study. The mean HBsAg levels were measured annually for up to 6 years. A linear mixed model was used to compare the HBsAg quantification levels during the follow-up period. An independent samples t-test was used to analyze the differences in the HBsAg quantification levels at each treatment time point.
Results
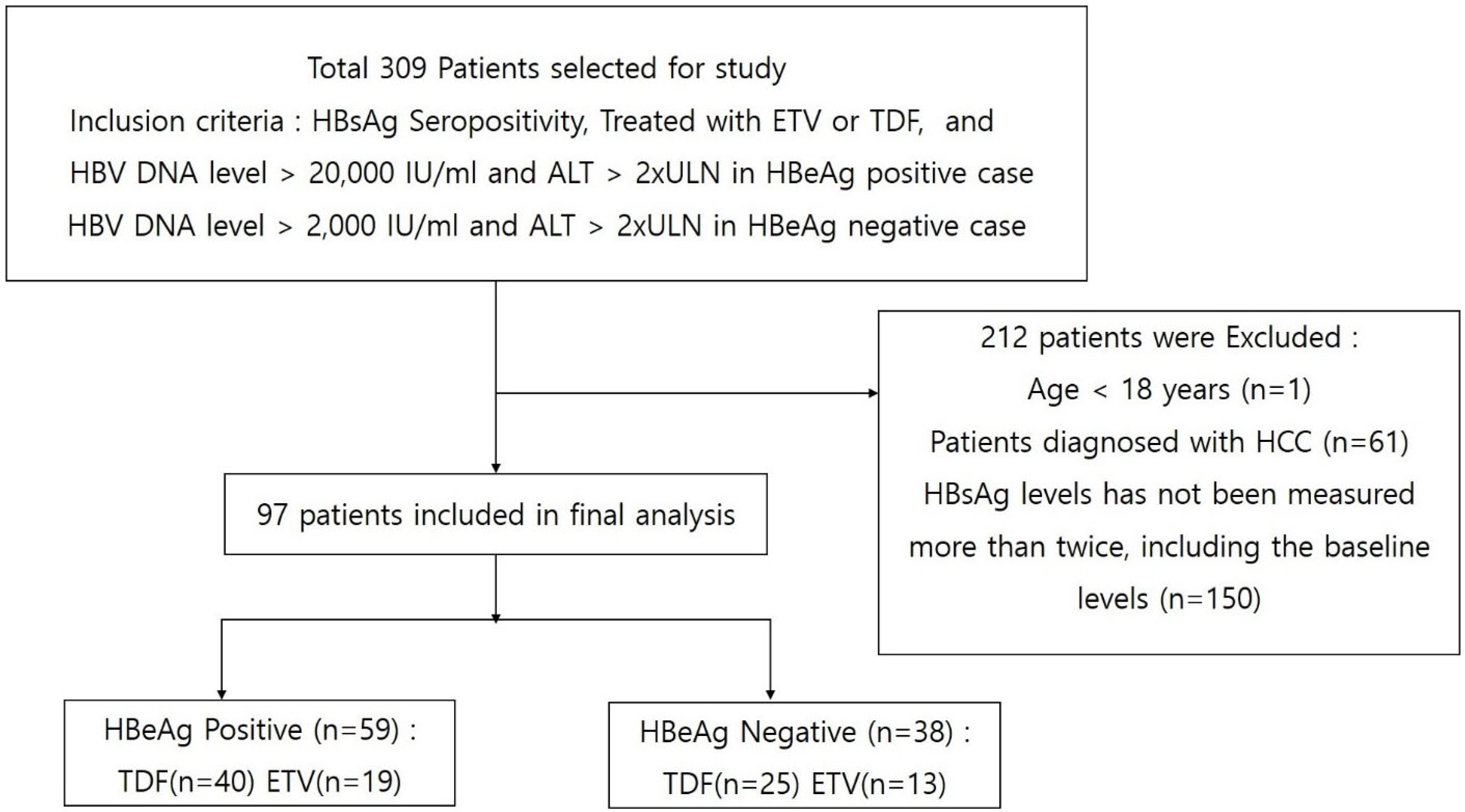
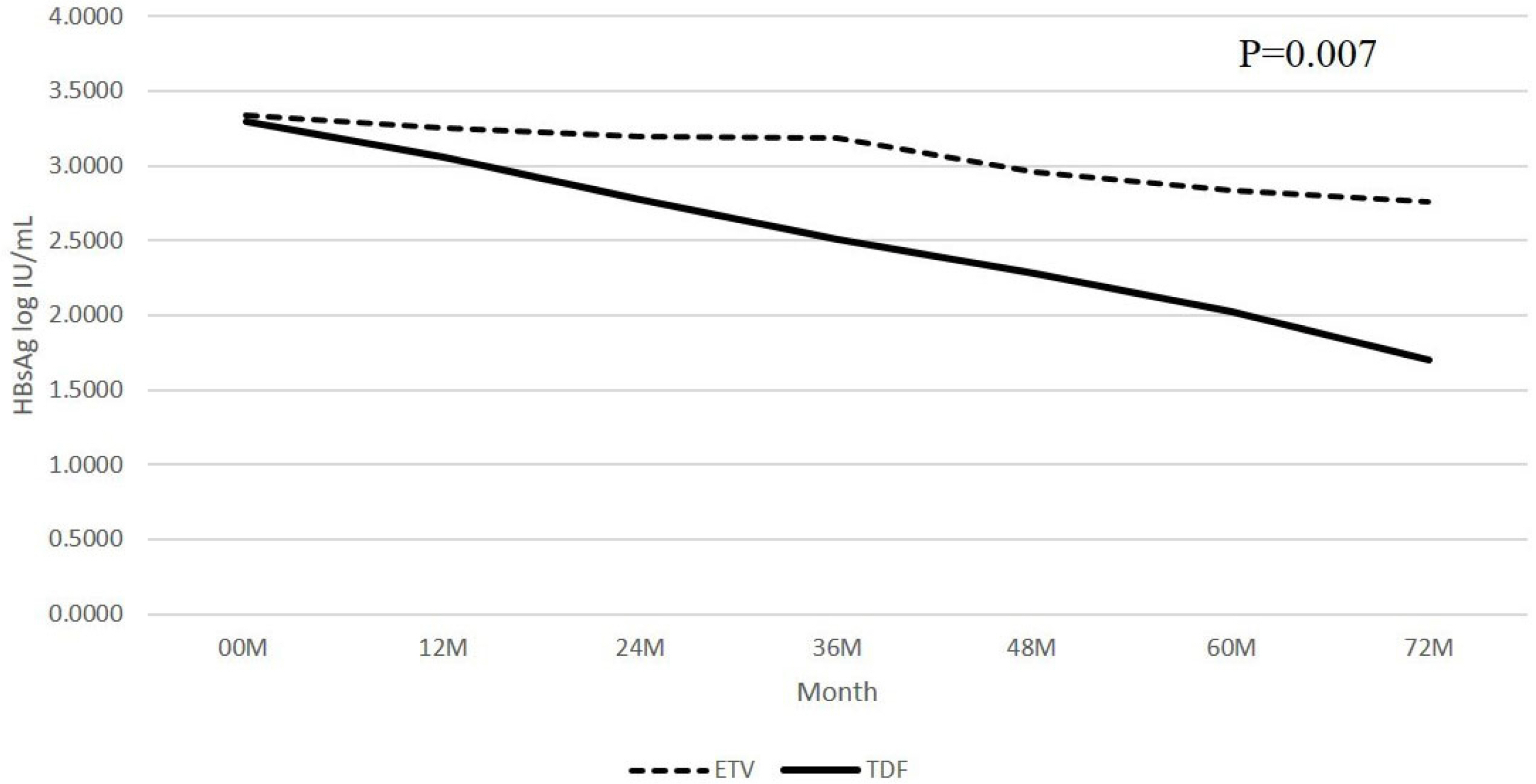
Ninety-seven patients were enrolled in this study; 59 among them were HBeAg-positive. Two patients in the TDF group achieved HBsAg seroconversion. The HBsAg level decreased during the follow-up in the ETV and TDF groups. The HBsAg level was lower in the TDF group than the ETV group during the follow-up. On the other hand, subgroup analysis showed that this trend was the same only in the HBeAg-negative patients, not in the HBeAg-positive patients. In the HBeAg-negative patients, HBsAg level in the TDF group was significantly lower than that in the ETV group at 36, 48, and 72 months. The change in HBsAg level from the baseline increased at a decreasing rate during the follow-up in both groups. Furthermore, the change in the HBsAg level in the TDF group was significantly larger than that of the ETV group at 36 months in the HBeAg-negative patients.
Conclusions
Although TDF might be more efficient than ETV in reducing the HBsAg level in HBeAg-negative patients in a few years, HBsAg seroconversion occurred very rarely. A further large-scale, long-term study will be needed to confirm the antiviral effects on the HBsAg level.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, et al. 2016; AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 63:261–283. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28156. PMID: 26566064. PMCID: PMC5987259.
Article2. Fattovich G, Bortolotti F, Donato F. 2008; Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 48:335–352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.11.011. PMID: 18096267.
Article3. European Association for the Study of the Liver. 2017; EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 67:370–398. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.021. PMID: 28427875.4. Idilman R, Gunsar F, Koruk M, et al. 2015; Long-term entecavir or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients in the real-world setting. J Viral Hepat. 22:504–510. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12358. PMID: 25431108.
Article5. Pol S, Lampertico P. 2012; First-line treatment of chronic hepatitis B with entecavir or tenofovir in 'real-lifé settings: from clinical trials to clinical practice. J Viral Hepat. 19:377–386. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01602.x. PMID: 22571899. PMCID: PMC3489060.6. Kim SS, Lee D, Lee MH, Cheong JY, Cho SW. 2013; Association of on-treatment serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with sustained virological response to nucleos(t)ide analog in patients with hepatitis B e-antigen positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Res. 43:219–227. DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01065.x. PMID: 22835015.
Article7. Liaw YF. 2011; Clinical utility of hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a review. Hepatology. 53:2121–2129. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24364. PMID: 21503943.
Article8. Lee JM, Ahn SH, Kim HS, et al. 2011; Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers in prediction of treatment response to entecavir. Hepatology. 53:1486–1493. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24221. PMID: 21520167.
Article9. Lee MH, Lee DM, Kim SS, Cheong JY, Cho SW. 2011; Correlation of serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with response to entecavir in naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol. 83:1178–1186. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.22089. PMID: 21567421.
Article10. Shin JW, Jung SW, Park BR, et al. 2012; Prediction of response to entecavir therapy in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B based on on-treatment HBsAg, HBeAg and HBV DNA levels. J Viral Hepat. 19:724–731. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01599.x. PMID: 22967104.
Article11. Marcellin P, Heathcote EJ, Buti M, et al. 2008; Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 359:2442–2455. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0802878. PMID: 19052126.12. Heathcote EJ, Marcellin P, Buti M, et al. 2011; Three-year efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment for chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 140:132–143. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.10.011. PMID: 20955704.
Article13. Lee HW, Lee HJ, Hwang JS, et al. 2010; Lamivudine maintenance beyond one year after HBeAg seroconversion is a major factor for sustained virologic response in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 51:415–421. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23323. PMID: 19902424.
Article14. Chu CM, Liaw YF. 2010; Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance during chronic HBV infection. Antivir Ther. 15:133–143. DOI: 10.3851/IMP1497. PMID: 20386068.
Article15. Fung J, Lai CL, Yuen MF. 2010; Hepatitis B virus DNA and hepatitis B surface antigen levels in chronic hepatitis B. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 8:717–726. DOI: 10.1586/eri.10.45. PMID: 20521898.
Article16. Chen YC. 2013; Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) levels in the prediction of spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance. Hepatology. 57:1675. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25999. PMID: 22886600.
Article17. Peng CY, Lai HC, Su WP, et al. 2017; Early hepatitis B surface antigen decline predicts treatment response to entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Sci Rep. 7:42879. DOI: 10.1038/srep42879. PMID: 28220833. PMCID: PMC5318891.
Article18. Berg T, Simon KG, Mauss S, et al. 2017; Long-term response after stopping tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in non-cirrhotic HBeAg-negative patients - FINITE study. J Hepatol. 67:918–924. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.012. PMID: 28736139.
Article19. Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, et al. 2010; Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 139:474–482. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.048. PMID: 20434450.
Article20. Chu CM, Liaw YF. 2009; HBsAg seroclearance in Asian patients: too high and too bad in Hong Kong. Gastroenterology. 136:1459–1461. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.11.065. PMID: 19236966.
Article21. Yeo YH, Ho HJ, Yang HI, et al. 2019; Factors associated with rates of HBsAg seroclearance in adults with chronic HBV infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 156:635–646.e9. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.027. PMID: 30342034.
Article22. Zhu L, Zhai X, Wang Q, et al. 2018; Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance and seroconversion in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic infection patients: a population-based prospective cohort. J Viral Hepat. 25:1588–1598. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12978. PMID: 30112835.
Article23. Yuen MF, Wong DK, Fung J, et al. 2008; HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in Asian patients: replicative level and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 135:1192–1199. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.008. PMID: 18722377.
Article24. Zoutendijk R, Hansen BE, van Vuuren AJ, Boucher CA, Janssen HL. 2011; Serum HBsAg decline during long-term potent nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B and prediction of HBsAg loss. J Infect Dis. 204:415–418. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir282. PMID: 21742840.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B
- Clinical Significance of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantification in Chronic Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B virus pre-genomic RNA and hepatitis B core-related antigen reductions at week 4 predict favourable hepatitis B surface antigen response upon long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue in chronic hepatitis B
- Prophylactic Antiviral Treatment in Immunosuppressed Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- Seroreversion and Acute Decompensation in Chronic Hepatitis B after Discontinuation of Oral Nucleotide Analog in the Patients Achieving HBsAg Loss