J Korean Med Sci.
2021 May;36(21):e153. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e153.
Adverse Reactions of the Second Dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Healthcare Workers in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Clinical Research Center, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Office for Infection Control, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516503
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e153
Abstract
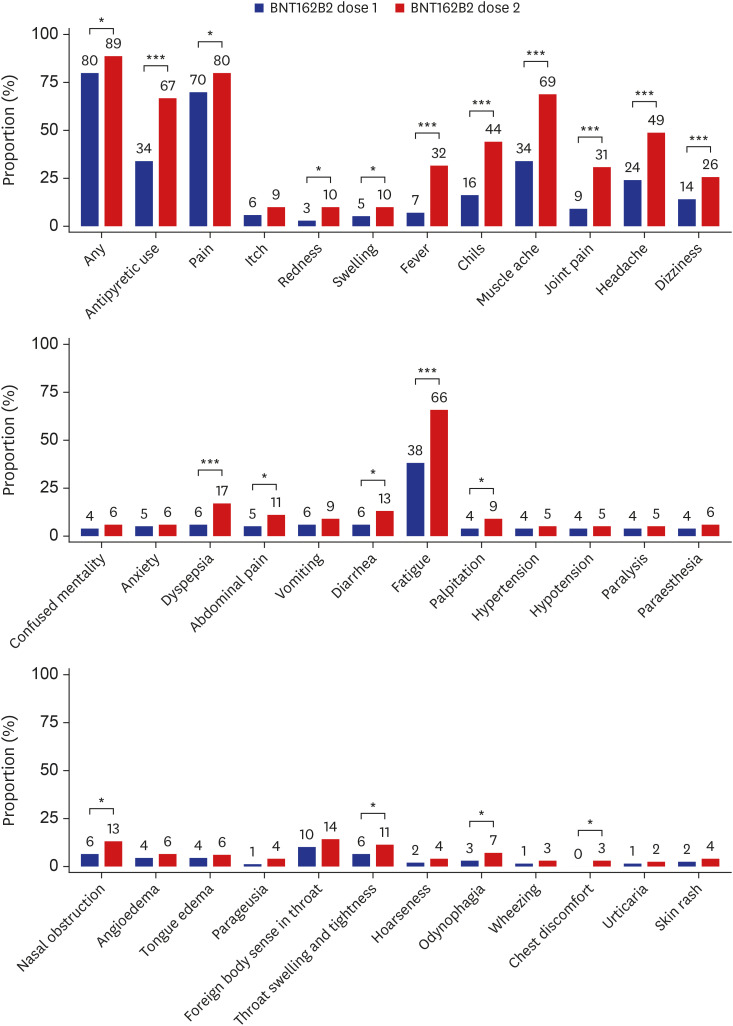
- We conducted a prospective, mobile-based survey on the self-reported adverse reactions in healthcare workers (HCWs) who received both doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Of the 342 HCWs who completed the two-dose vaccination, 265 (77.5%) responded to the survey at least once. Overall, the rates of adverse reactions were higher after the second dose compared with the first dose (89.1% vs. 80.1%, P = 0.006). The most common systemic reactions were muscle ache (69.1%), fatigue (65.7%), headache (48.7%), chills (44.2%), and fever (32.1%), and were notably more common after the second dose vaccine as well. We also noted a sex difference in which the frequency of adverse reactions after the second dose of the vaccine was significantly higher in females, which was not observed after the first dose. The rates of adverse reactions were lower in older age groups, and the rates and severities of the adverse reactions decreased during the 3-day period following vaccination.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Safety Monitoring after the BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine among Adults Aged 75 Years or Older
Youn Young Choi, Min-Kyung Kim, Hyeok Choon Kwon, Gunn Hee Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(45):e318. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e318.Clinical Features of Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Tae Hoon Oh, Seon Hee Woo, Sungyoup Hong, Carol Lee, Woon Jeong Lee, Si Kyoung Jeong
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(9):e73. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e73.
Reference
-
1. Chapin-Bardales J, Gee J, Myers T. Reactogenicity following receipt of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. JAMA. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.5374.
Article2. Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383(27):2603–2615. PMID: 33301246.
Article3. Walsh EE, Frenck RW Jr, Falsey AR, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-based Covid-19 vaccine candidates. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383(25):2439–2450. PMID: 33053279.
Article4. Bae S, Lee YW, Lim SY, Lee JH, Lim JS, Lee S, et al. Adverse reactions following the first dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine and BNT162b2 vaccine for healthcare workers in South Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(17):e115. PMID: 33942579.
Article5. Menni C, Klaser K, May A, Polidori L, Capdevila J, Louca P, et al. Vaccine side-effects and SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccination in users of the COVID Symptom Study app in the UK: a prospective observational study. Lancet Infect Dis. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00224-3.
Article6. Monin L, Laing AG, Muñoz-Ruiz M, McKenzie DR, Del Molino Del Barrio I, Alaguthurai T, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of one versus two doses of the COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 for patients with cancer: interim analysis of a prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00213-8.
Article7. Rabinowich L, Grupper A, Baruch R, Ben-Yehoyada M, Halperin T, Turner D, et al. Low immunogenicity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among liver transplant recipients. J Hepatol. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.020.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Adverse Events of the First Dose and the Second Dose after Vaccination of the COVID-19 Pfizer Vaccine
- BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine adverse reactions needing medical support: a vaccine center experience
- Adverse Reactions Following the First Dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine and BNT162b2 Vaccine for Healthcare Workers in South Korea
- mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine-Associated Subserosal Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: A Case Report
- Reactogenicity after the first and second doses of BNT162b2 mRNA coronavirus disease vaccine: a single-center study