Neonatal Med.
2021 May;28(2):72-76. 10.5385/nm.2021.28.2.72.
Intussusception and Jejunal Atresia Caused by an Ectopic Pancreas in a Newborn
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatric Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2516488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2021.28.2.72
Abstract
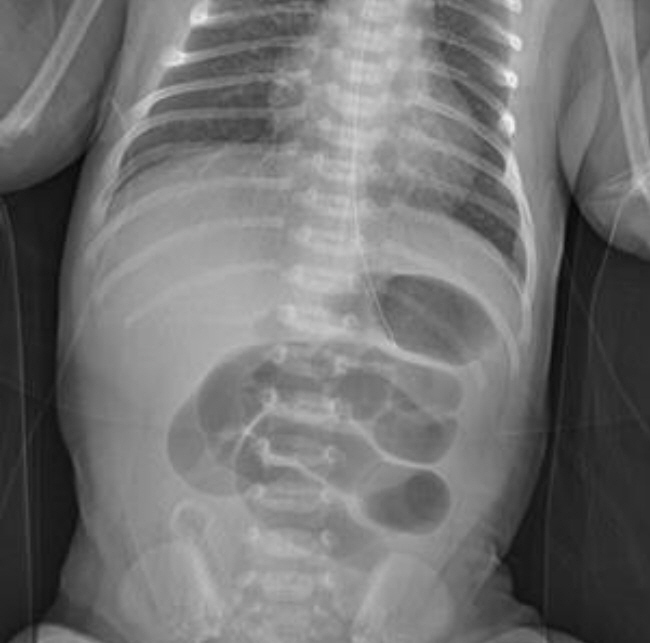
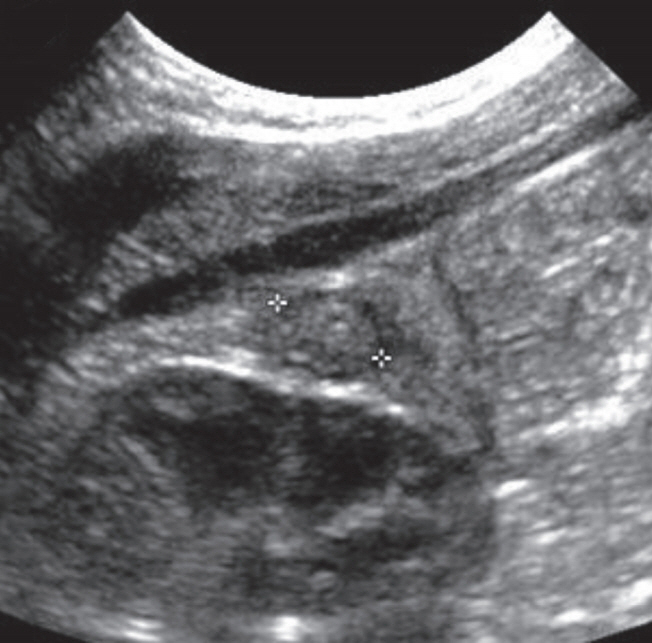
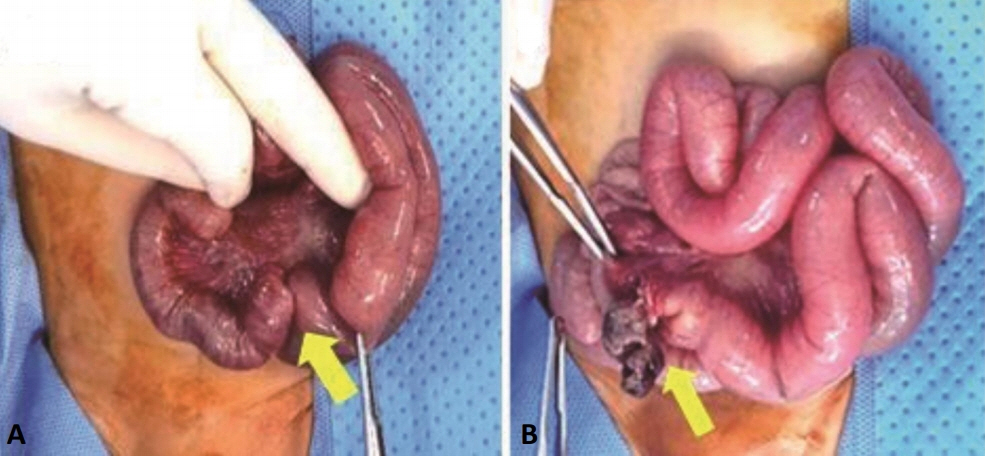
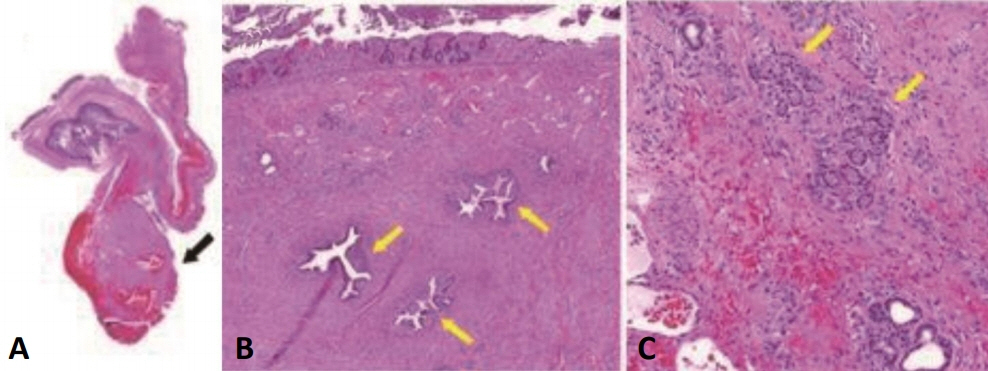
- Ectopic pancreas is defined as an abnormally located pancreatic tissue not sufficiently connected with the normal pancreas, which rarely occurs in neonates. To our knowledge, only a few cases of ectopic pancreas have been reported in newborns in South Korea. We report a case of ectopic pancreas as the cause of intussusception and jejunal atresia in a newborn. This clinical association is extremely rare, and this is the first report in South Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hirasaki S, Kubo M, Inoue A, Miyake Y, Oshiro H. Jejunal small ectopic pancreas developing into jejunojejunal intussusception: a rare cause of ileus. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:3954–6.2. Rezvani M, Menias C, Sandrasegaran K, Olpin JD, Elsayes KM, Shaaban AM. Heterotopic pancreas: histopathologic features, imaging findings, and complications. Radiographics. 2017; 37:484–99.3. Ormarsson OT, Gudmundsdottir I, Marvik R. Diagnosis and treatment of gastric heterotopic pancreas. World J Surg. 2006; 30:1682–9.4. Yoon HS, Hyun MS, Hahn JH, Ahn SW, Yang JW. One case of ectopic pancreatic tissue with gastroschisis. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1983; 26:1009–12.5. Choi JS, Park BW, Min JS. Heterotopic pancreas. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1992; 24:1403–10.6. Han HS, Han SJ, Lee HJ, Park WI, Lee KJ, Ryu BY. A case of duodenal obstruction in the newborn due to ectopic pancreas. Inkan Kwahak. 1996; 20:53–6.7. Kilius A, Samalavicius NE, Danys D, Zaldokas G, Seinin D. Asymptomatic heterotopic pancreas in Meckel's diverticulum: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2015; 9:108.8. Gokhale UA, Nanda A, Pillai R, Al-Layla D. Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach: a case report and a brief review of the literature. JOP. 2010; 11:255–7.9. Sohn KH, Kim YB, Chi JG. Heterotopic pancreas: a case report. J Korean Surg Soc. 1967; 9:793–801.10. Min BJ, Chung CK, Hwang EH. Intussusception due to heterotopic pancreas. J Korean Surg Soc. 1971; 13:49–53.11. Ueno S, Ishida H, Hayashi A, Kamagata S, Morikawa M. Heterotopic pancreas as a rare cause of gastrointestinal hemorrhage in the newborn: report of a case. Surg Today. 1993; 23:269–72.12. Fam S, O'Briain DS, Borger JA. Ectopic pancreas with acute inflammation. J Pediatr Surg. 1982; 17:86–7.13. Jo S, Lim IS, Chae SA, Yun SW, Lee NM, Kim SY, et al. Characteristics of intussusception among children in Korea: a nationwide epidemiological study. BMC Pediatr. 2019; 19:211.14. Lin XK, Xia QZ, Huang XZ, Han YJ, He GR, Zheng N. Clinical characteristics of intussusception secondary to pathologic lead points in children: a single-center experience with 65 cases. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017; 33:793–7.15. Kao KJ, Fleischer R, Bradford WD, Woodard BH. Multiple congenital septal atresias of the intestine: histomorphologic and pathogenetic implications. Pediatr Pathol. 1983; 1:443–8.16. Grosfeld JL, Ballantine TV, Shoemaker R. Operative mangement of intestinal atresia and stenosis based on pathologic findings. J Pediatr Surg. 1979; 14:368–75.17. Skandalakis LJ, Rowe JS Jr, Gray SW, Skandalakis JE. Surgical embryology and anatomy of the pancreas. Surg Clin North Am. 1993; 73:661–97.18. Armstrong CP, King PM, Dixon JM, Macleod IB. The clinical significance of heterotopic pancreas in the gastrointestinal tract. Br J Surg. 1981; 68:384–7.19. Abel R, Keen CE, Bingham JB, Maynard J, Agrawal MR, Ramachandra S. Heterotopic pancreas as lead point in intussusception: new variant of vitellointestinal tract malformation. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 1999; 2:367–70.20. Trandafir LM, Aprodu SG, Mihaila D, Anton Paduraru DT, Butnariu L, Straticiuc Ciongradi IC. Ectopic jejunal pancreas and congenital duodenal stenosis in a newborn patient: an unusual association. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014; 55(2 Suppl):707–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Retraction Notice: Intussusception and Jejunal Atresia Caused by an Ectopic Pancreas in a Newborn
- Intussusception due to Inverted Meckel Diverticulum with Ectopic Pancreas: A Case Report
- A Case of a Jejunal Ectopic Pancreas Presenting as Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- A Case of Ring Chromosome 13 Syndrome with Jejunal Atresia and Hearing Loss
- 2 Cases of Congenital Jejunal Atresia Diagnosed by Prenatal Ultrasonography