Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 May;25(2):198-205. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.198.
Is percutaneous destruction of a solitary liver colorectal metastasis as effective as a resection?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, Inserm, CRCM, Marseille, France
- 2Department of Radiology, Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, Inserm, CRCM, Marseille, France
- 3Department of Surgery, Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, Inserm, CRCM, Marseille, France
- KMID: 2516240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.198
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
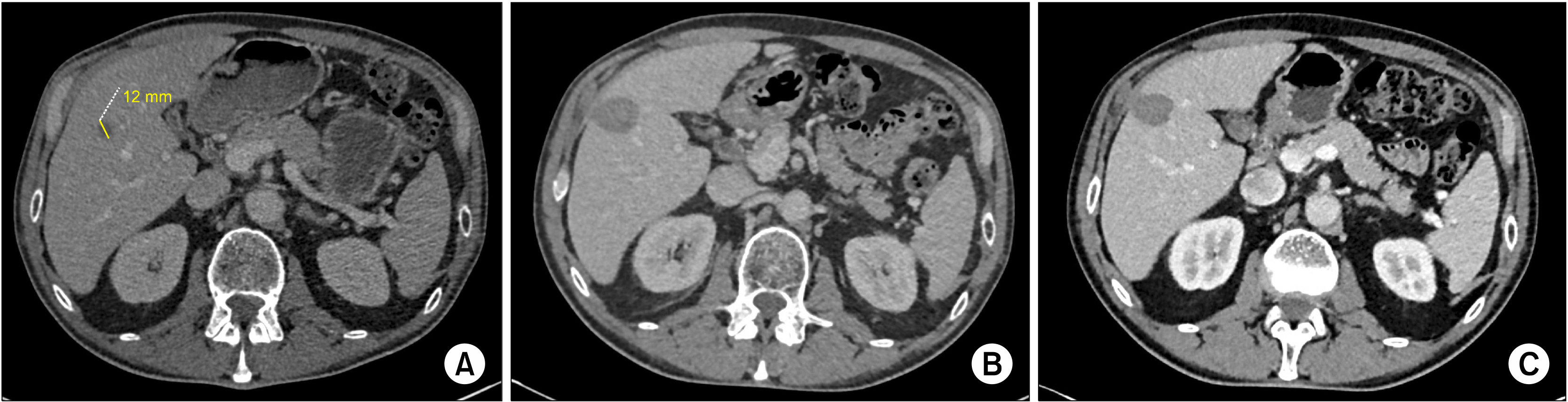
Surgical resection remains the gold standard in the treatment of colorectal liver metastasis. However, when a patient presents with a deep solitary colorectal liver metastasis (S-CLM), the balance between the hepatic volume sacrificed and the S-CLM volume is sometimes clearly unappropriated. Thus, alternatives to surgery, such as operative and percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA), have been developed. This study aimed to identify the prognostic factors affecting survival of patients with S-CLM who undergo curative-intent liver resection or local destruction (RFA or MWA).
Methods
We retrospectively identified 211 patients with synchronous or metachronous S-CLM who underwent either surgical resection (n=182) or local destruction (RFA or MWA; n=29) according to the S-CLM size, location, and surrounding Glissonian structures.
Results
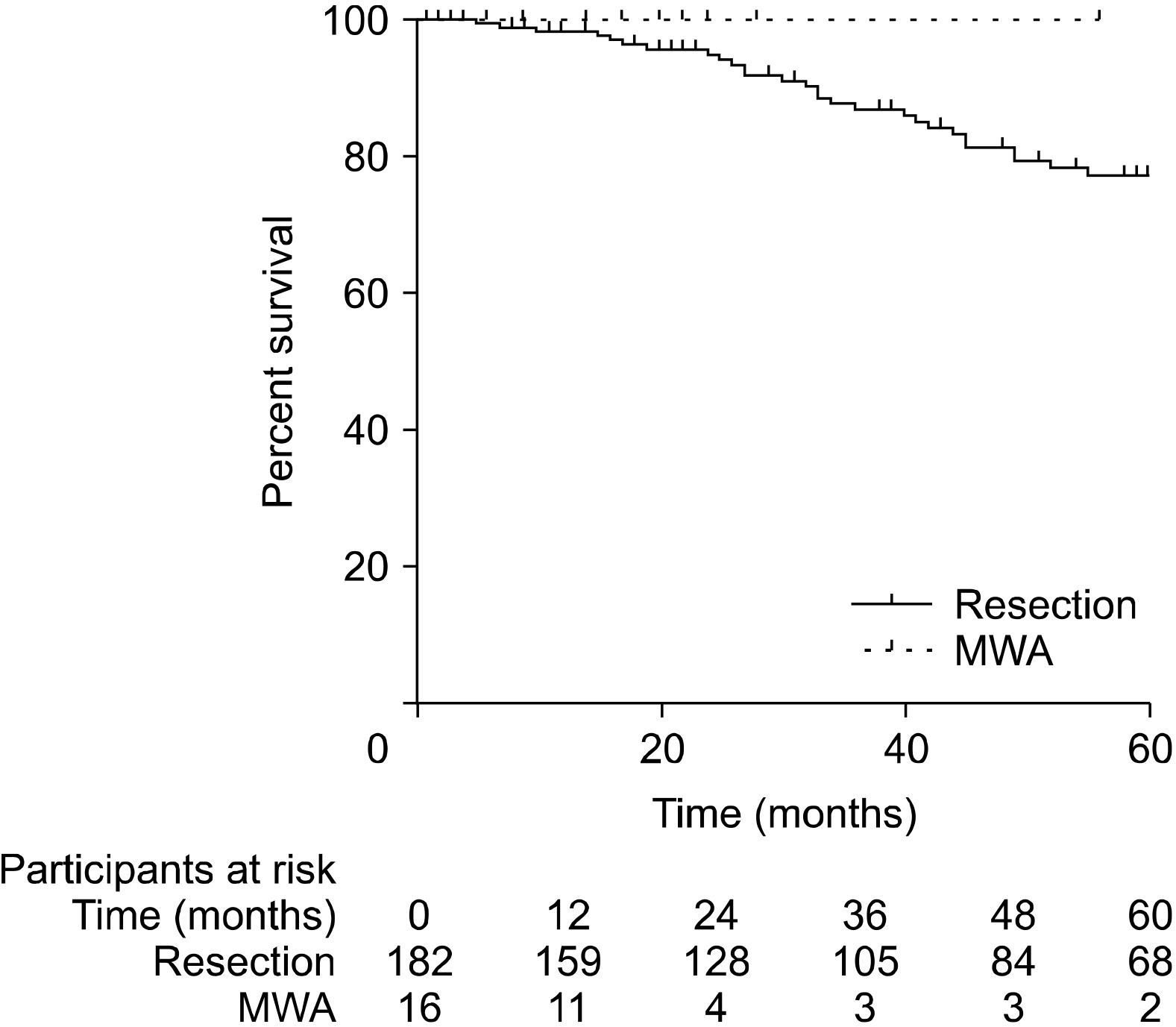
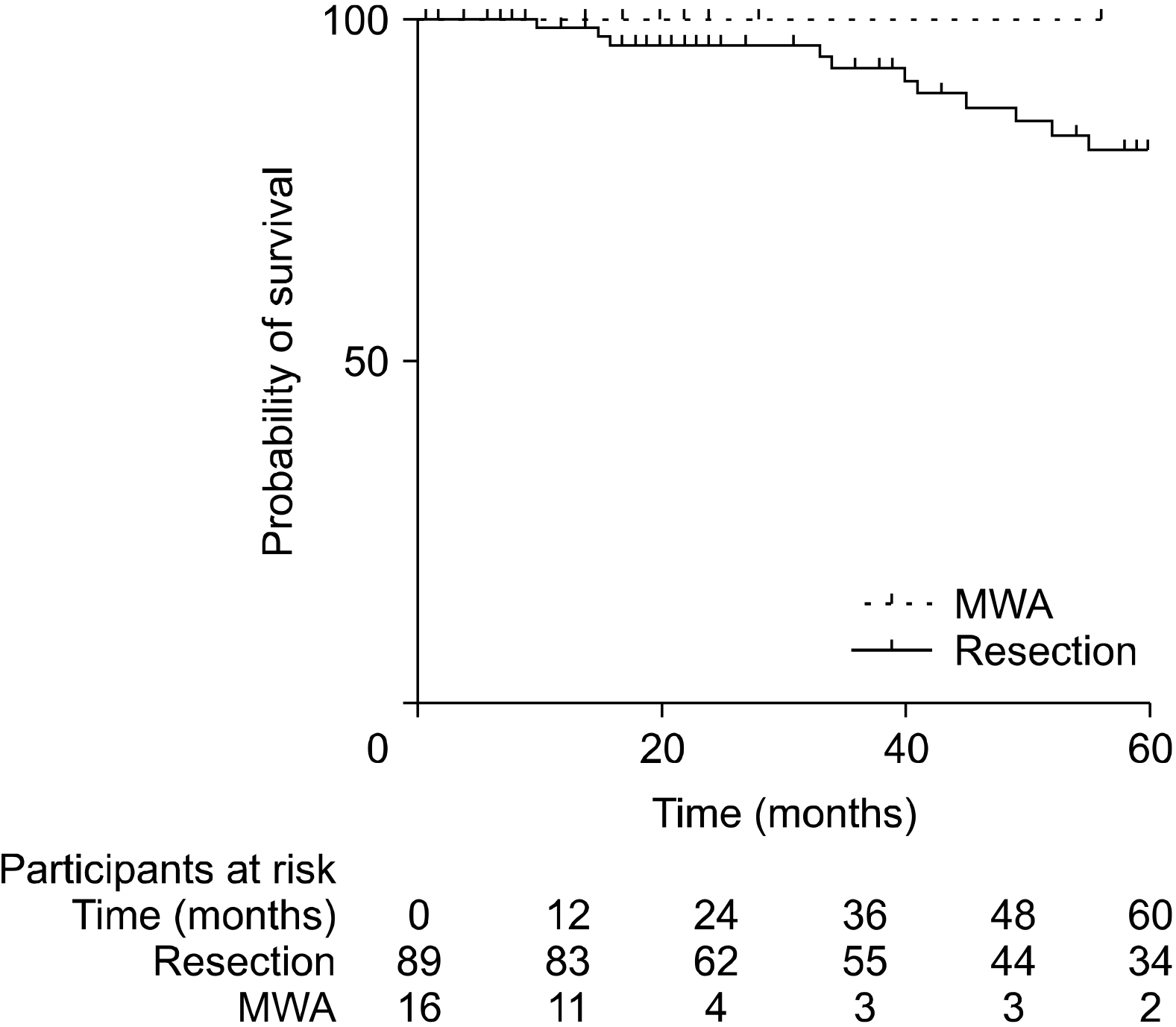
Patients who underwent RFA or MWA had S-CLM of a smaller size than those who underwent resection (mean 19.7 vs. 37.3 mm, p<.01). The 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 97.4%, 84.9%, and 74.9%, respectively. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) rates were 77.9%, 47%, and 38.9%, respectively. S-CLM located in the left liver (p=.04), S-CLM KRAS mutation (p<.01), and extra-hepatic recurrence (p<.01) were identified as independent poor risk factors for overall survival (OS); the OS and DFS were comparable in patients with surgical procedure or percutaneous MWA.
Conclusions
In eligible S-CLM cases, percutaneous MWA seems to be as oncologically efficient as surgical resection and should be include in the decision-tree for treatment strategies.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moris D, Ronnekleiv-Kelly S, Kostakis ID, Tsilimigras DI, Beal EW, Papalampros A, et al. 2018; Operative results and oncologic outcomes of associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) versus two-stage hepatectomy (TSH) in patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg. 42:806–815. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-017-4181-6. PMID: 28798996.
Article2. Donadon M, Cescon M, Cucchetti A, Cimino M, Costa G, Pesi B, et al. 2018; Parenchymal-sparing surgery for the surgical treatment of multiple colorectal liver metastases is a safer approach than major hepatectomy not impairing patients' prognosis: a bi-institutional propensity score-matched analysis. Dig Surg. 35:342–349. DOI: 10.1159/000479336. PMID: 29032372.
Article3. McGahan JP, Browning PD, Brock JM, Tesluk H. 1990; Hepatic ablation using radiofrequency electrocautery. Invest Radiol. 25:267–270. DOI: 10.1097/00004424-199003000-00011. PMID: 2185179.
Article4. Shibata T, Niinobu T, Ogata N. 2000; Comparison of the effects of in-vivo thermal ablation of pig liver by microwave and radiofrequency coagulation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 7:592–598. DOI: 10.1007/s005340070009. PMID: 11180892.
Article5. White RR, Avital I, Sofocleous CT, Brown KT, Brody LA, Covey A, et al. 2007; Rates and patterns of recurrence for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and open wedge resection for solitary colorectal liver metastasis. J Gastrointest Surg. 11:256–263. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-007-0100-8. PMID: 17458595.
Article6. Lee WS, Yun SH, Chun HK, Lee WY, Kim SJ, Choi SH, et al. 2008; Clinical outcomes of hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation in patients with solitary colorectal liver metastasis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 42:945–949. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318064e752. PMID: 18438208.
Article7. Oshowo A, Gillams A, Harrison E, Lees WR, Taylor I. 2003; Comparison of resection and radiofrequency ablation for treatment of solitary colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg. 90:1240–1243. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.4264. PMID: 14515293.
Article8. Nordlinger B, Sorbye H, Glimelius B, Poston GJ, Schlag PM, Rougier P, et al. 2013; Perioperative FOLFOX4 chemotherapy and surgery versus surgery alone for resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer (EORTC 40983): long-term results of a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:1208–1215. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70447-9.
Article9. Belghiti J, Noun R, Zante E, Ballet T, Sauvanet A. 1996; Portal triad clamping or hepatic vascular exclusion for major liver resection. A controlled study. Ann Surg. 224:155–161. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199608000-00007. PMID: 8757378. PMCID: PMC1235336.10. Brauer DG, Nywening TM, Jaques DP, Doyle MB, Chapman WC, Fields RC, et al. 2016; Operative site drainage after hepatectomy: a propensity score matched analysis using the American College of Surgeons NSQIP targeted hepatectomy database. J Am Coll Surg. 223:774–783.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.09.004. PMID: 27793459. PMCID: PMC5125822.
Article11. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. 2004; Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 240:205–213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. PMID: 15273542. PMCID: PMC1360123.12. Rajaganeshan R, Prasad R, Guillou PJ, Chalmers CR, Scott N, Sarkar R, et al. 2007; The influence of invasive growth pattern and microvessel density on prognosis in colorectal cancer and colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 96:1112–1117. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603677. PMID: 17353920. PMCID: PMC2360131.
Article13. de Jong MC, Pulitano C, Ribero D, Strub J, Mentha G, Schulick RD, et al. 2009; Rates and patterns of recurrence following curative intent surgery for colorectal liver metastasis: an international multi-institutional analysis of 1669 patients. Ann Surg. 250:440–448. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b4539b. PMID: 19730175.14. Bai H, Huangz X, Jing L, Zeng Q, Han L. 2015; The effect of radiofrequency ablation vs. liver resection on survival outcome of colorectal liver metastases (CRLM): a meta-analysis. Hepatogastroenterology. 62:373–377.15. Ng KM, Chua TC, Saxena A, Zhao J, Chu F, Morris DL. 2012; Two decades of experience with hepatic cryotherapy for advanced colorectal metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:1276–1283. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-011-2025-4. PMID: 21913018.
Article16. Takahashi H, Kahramangil B, Kose E, Berber E. 2018; A comparison of microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency thermal ablation in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases. HPB (Oxford). 20:1157–1162. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.05.012. PMID: 29929785.
Article17. Shady W, Petre EN, Do KG, Gonen M, Yarmohammadi H, Brown KT, et al. 2018; Percutaneous microwave versus radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: ablation with clear margins (A0) provides the best local tumor control. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 29:268–275.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.08.021. PMID: 29203394. PMCID: PMC5803367.18. Puijk RS, Ruarus AH, Vroomen LGPH, van Tilborg AAJM, Scheffer HJ, Nielsen K, et al. 2018; Colorectal liver metastases: surgery versus thermal ablation (COLLISION)- a phase III single-blind prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer. 18:821. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4716-8. PMID: 30111304. PMCID: PMC6094448.
Article19. Wagner JS, Adson MA, Van Heerden JA, Adson MH, Ilstrup DM. 1984; The natural history of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. A comparison with resective treatment. Ann Surg. 199:502–508. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-198405000-00002. PMID: 6721600. PMCID: PMC1353475.20. Goffredo P, Utria AF, Beck AC, Chun YS, Howe JR, Weigel RJ, et al. 2019; The prognostic impact of KRAS mutation in patients having curative resection of synchronous colorectal liver metastases. J Gastrointest Surg. 23:1957–1963. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-018-3978-4. PMID: 30276588.
Article21. Creasy JM, Sadot E, Koerkamp BG, Chou JF, Gonen M, Kemeny NE, et al. 2018; The impact of primary tumor location on long-term survival in patients undergoing hepatic resection for metastatic colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 25:431–438. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-017-6264-x. PMID: 29181680. PMCID: PMC7480216.
Article22. Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D, et al. 2016; ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 27:1386–1422. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdw235. PMID: 27380959.
Article23. Acciuffi S, Meyer F, Bauschke A, Settmacher U, Lippert H, Croner R, et al. 2018; Analysis of prognostic factors after resection of solitary liver metastasis in colorectal cancer: a 22-year bicentre study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:593–599. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-018-2583-y. PMID: 29340767.
Article24. Hosokawa I, Allard MA, Mirza DF, Kaiser G, Barroso E, Lapointe R, et al. 2017; Outcomes of parenchyma-preserving hepatectomy and right hepatectomy for solitary small colorectal liver metastasis: a LiverMetSurvey study. Surgery. 162:223–232. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.02.012. PMID: 28434557.
Article25. Shin H, Kim CW, Lee JL, Yoon YS, Park IJ, Lim SB, et al. 2019; Solitary colorectal liver metastasis after curative intent surgery: prognostic factors affecting outcomes and survival. ANZ J Surg. 89:61–67. DOI: 10.1111/ans.14933. PMID: 30484933.
Article26. Ou S, Xu R, Li K, Chen Y, Kong Y, Liu H, et al. 2018; Radiofrequency ablation with systemic chemotherapy in the treatment of colorectal cancer liver metastasis: a 10-year single-center study. Cancer Manag Res. 10:5227–5237. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S170160. PMID: 30464620. PMCID: PMC6217171.
Article27. Pathak S, Palkhi E, Dave R, White A, Pandanaboyana S, Prasad KR, et al. 2016; Relationship between primary colorectal tumour and location of colorectal liver metastases. ANZ J Surg. 86:408–410. DOI: 10.1111/ans.12767. PMID: 25040656.
Article28. Shady W, Petre EN, Vakiani E, Ziv E, Gonen M, Brown KT, et al. 2017; Kras mutation is a marker of worse oncologic outcomes after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Oncotarget. 8:66117–66127. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19806. PMID: 29029497. PMCID: PMC5630397.
Article29. Deshwar A, Margonis GA, Andreatos N, Barbon C, Wang J, Buettner S, et al. 2018; Double KRAS and BRAF mutations in surgically treated colorectal cancer liver metastases: an international, multi-institutional case series. Anticancer Res. 38:2891–2895. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.12535.
Article