Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 May;25(2):171-178. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.171.
Role of liver support systems in the management of post hepatectomy liver failure: A systematic review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of HPB and Liver Transplantation, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, UK
- 2University of Birmingham, Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
- 3Institute of Translational Medicine, Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
- 4Department of Anaesthesia and Critical Care, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, UK
- 5Centre for Liver & Gastrointestinal Research, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy, College of Medical and Dental Sciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
- 6Department of Surgery, University Medical Centres (Location Amsterdam Medical Centre), University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
- KMID: 2516237
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.171
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
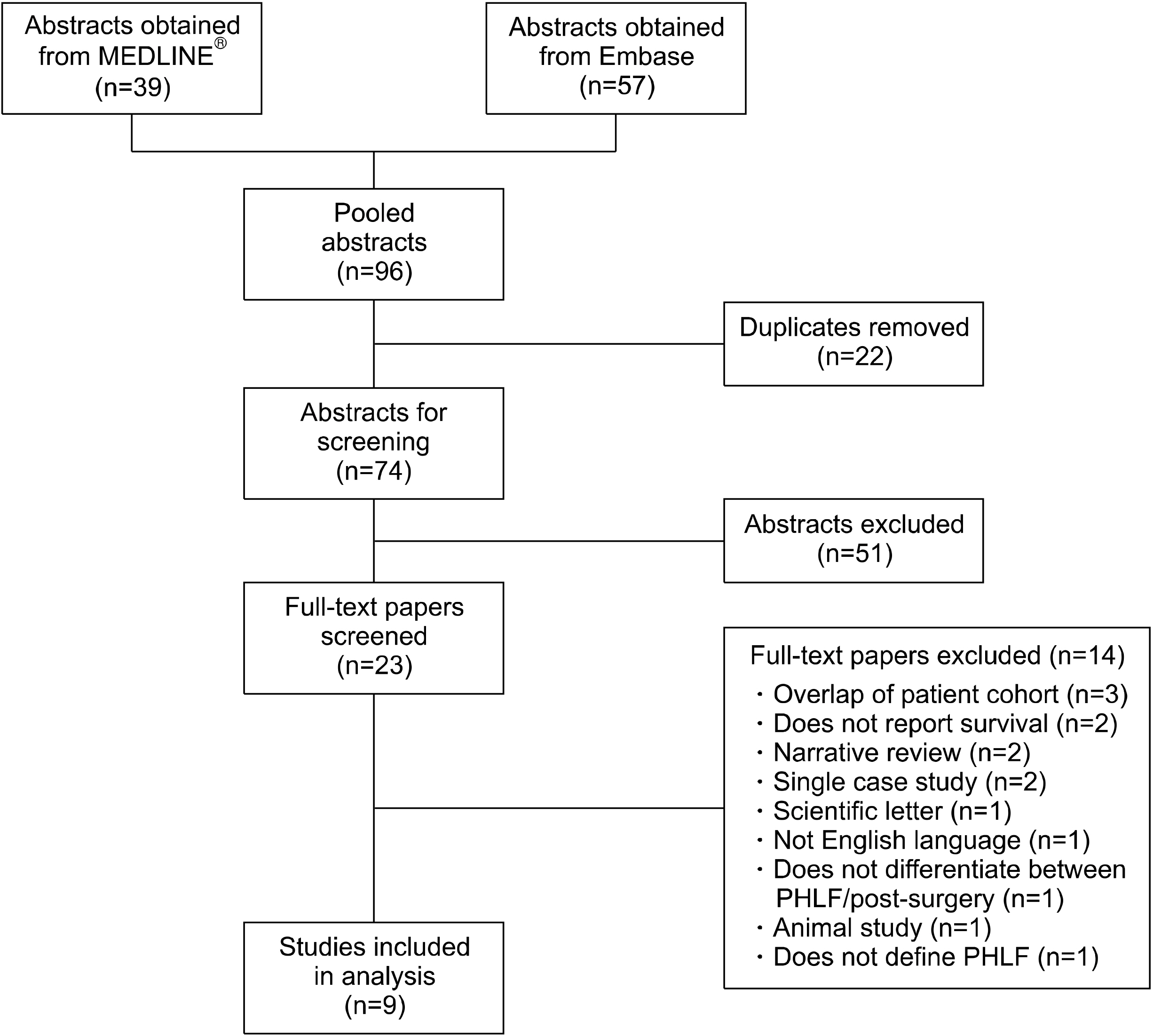
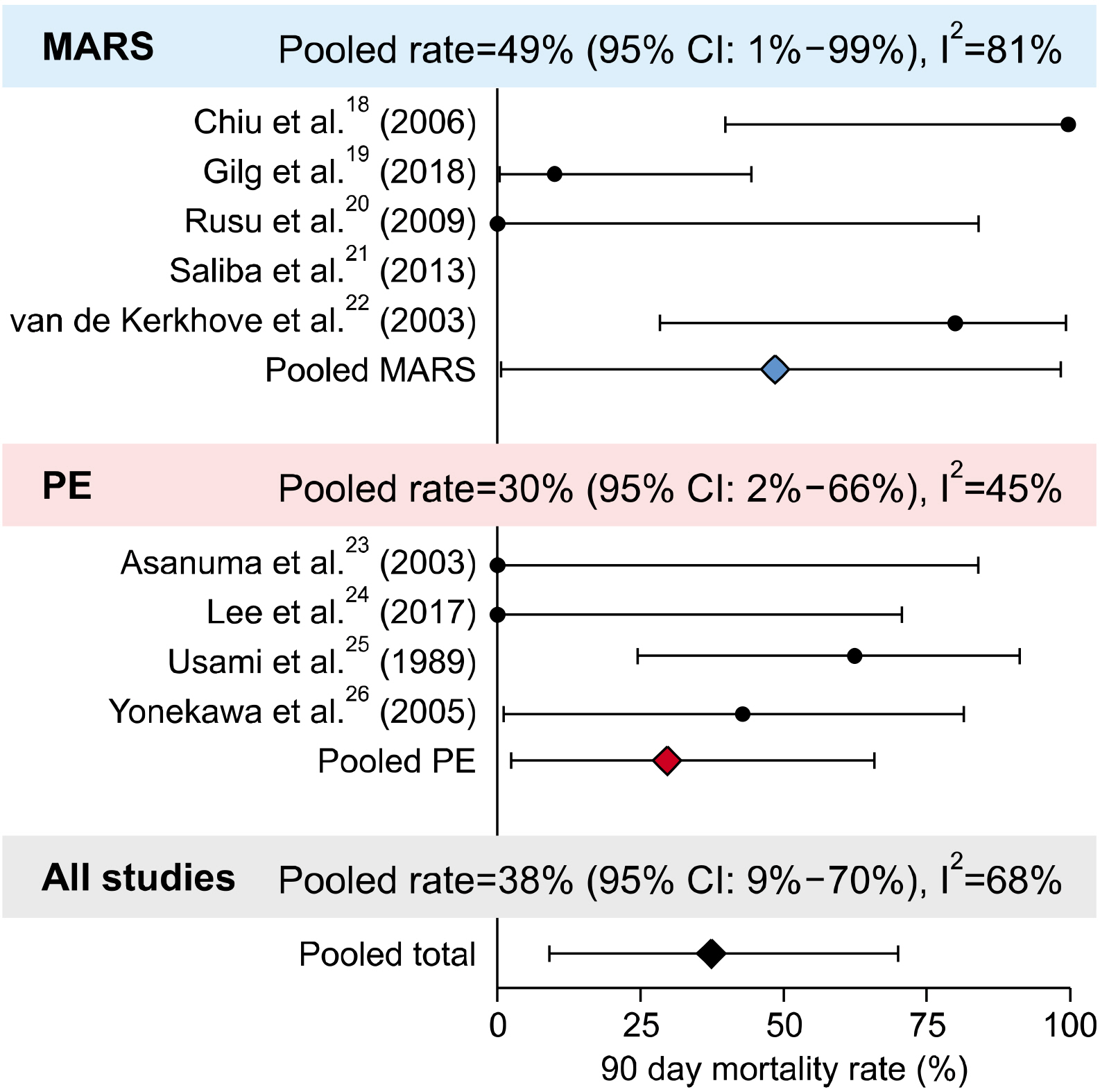
Post-hepatectomy liver failure (PHLF) is a serious complication following liver resection, with limited treatment options, and is associated with high mortality. There is a need to evaluate the role of systems that support the function of the liver after PHLF. Aims: The aim of this study was to review the literature and summarize the role of liver support systems (LSS) in the management of PHLF. Publications of interest were identified using systematically designed searches. Following screening, data from the relevant publications was extracted, and pooled where possible. Findings: Systematic review identified nine studies, which used either Plasma Exchange (PE) or Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) as LSS after PHLF. Across all studies, the pooled 90-day mortality rate was 38% (95% CI: 9-70%). However, there was substantial heterogeneity, likely since studies used a variety of definitions for PHLF, and had different selection criteria for patient eligibility for LSS treatment. Conclusions: The current evidence is insufficient to recommend LSS for the routine management of severe PHLF, with the current literature consisting of only a limited number of studies. There is a definite need for larger, multicenter, prospective studies, evaluating the conventional and newer modalities of support systems, with a view to improve the outcomes in this group of patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Lam CM, Yuen WK, et al. 2004; Improving perioperative outcome expands the role of hepatectomy in management of benign and malignant hepatobiliary diseases: analysis of 1222 consecutive patients from a prospective database. Ann Surg. 240:698–708. discussion 708–710. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000141195.66155.0c. PMID: 15383797. PMCID: PMC1356471.2. Zheng Y, Yang H, He L, Mao Y, Zhang H, Zhao H, et al. 2017; Reassessment of different criteria for diagnosing post-hepatectomy liver failure: a single-center study of 1683 hepatectomy. Oncotarget. 8:89269–89277. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19360. PMID: 29179518. PMCID: PMC5687688.
Article3. Andreatos N, Amini N, Gani F, Margonis GA, Sasaki K, Thompson VM, et al. 2017; Albumin-bilirubin score: predicting short- term outcomes including bile leak and post-hepatectomy liver failure following hepatic resection. J Gastrointest Surg. 21:238–248. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-016-3246-4. PMID: 27619809.4. Schreckenbach T, Liese J, Bechstein WO, Moench C. 2012; Posthepatectomy liver failure. Dig Surg. 29:79–85. DOI: 10.1159/000335741. PMID: 22441624.
Article5. Rahbari NN, Garden OJ, Padbury R, Brooke-Smith M, Crawford M, Adam R, et al. 2011; Posthepatectomy liver failure: a definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery (ISGLS). Surgery. 149:713–724. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.10.001. PMID: 21236455.
Article6. Gilg S, Sparrelid E, Isaksson B, Lundell L, Nowak G, Strömberg C. 2017; Mortality-related risk factors and long-term survival after 4460 liver resections in Sweden-a population-based study. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 402:105–113. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-016-1512-2. PMID: 27695941. PMCID: PMC5309267.
Article7. Farges O, Goutte N, Bendersky N, Falissard B. ACHBT-French Hepatectomy Study Group. 2012; Incidence and risks of liver resection: an all-inclusive French nationwide study. Ann Surg. 256:697–704. discussion 704–705. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31827241d5. PMID: 23095612.8. Mullen JT, Ribero D, Reddy SK, Donadon M, Zorzi D, Gautam S, et al. 2007; Hepatic insufficiency and mortality in 1,059 noncirrhotic patients undergoing major hepatectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 204:854–862. discussion 862–864. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2006.12.032. PMID: 17481498.
Article9. Kantola T, Ilmakunnas M, Koivusalo AM, Isoniemi H. 2011; Bridging therapies and liver transplantation in acute liver failure, 10 years of MARS experience from Finland. Scand J Surg. 100:8–13. DOI: 10.1177/145749691110000103. PMID: 21482500.
Article10. Vaid A, Chweich H, Balk EM, Jaber BL. 2012; Molecular adsorbent recirculating system as artificial support therapy for liver failure: a meta-analysis. ASAIO J. 58:51–59. DOI: 10.1097/MAT.0b013e31823fd077. PMID: 22210651.11. van de Kerkhove MP, de Jong KP, Rijken AM, de Pont AC, van Gulik TM. 2003; MARS treatment in posthepatectomy liver failure. Liver Int. 23 Suppl 3:44–51. DOI: 10.1034/j.1478-3231.23.s.3.2.x. PMID: 12950961.
Article12. Stange J, Ramlow W, Mitzner S, Schmidt R, Klinkmann H. 1993; Dialysis against a recycled albumin solution enables the removal of albumin-bound toxins. Artif Organs. 17:809–813. DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.1993.tb00635.x. PMID: 8240075.
Article13. Stange J, Mitzner SR, Risler T, Erley CM, Lauchart W, Goehl H, et al. 1999; Molecular adsorbent recycling system (MARS): clinical results of a new membrane-based blood purification system for bioartificial liver support. Artif Organs. 23:319–330. DOI: 10.1046/j.1525-1594.1999.06122.x. PMID: 10226696.
Article14. Larsen FS, Schmidt LE, Bernsmeier C, Rasmussen A, Isoniemi H, Patel VC, et al. 2016; High-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure: an open randomised controlled trial. J Hepatol. 64:69–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.018. PMID: 26325537.
Article15. European Association for the Study of the Liver. 2017; EASL clinical practical guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J Hepatol. 66:1047–1081. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.12.003. PMID: 28417882.16. Richardson WS, Wilson MC, Nishikawa J, Hayward RS. 1995; The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP J Club. 123:A12–A13.17. Miller JJ. 1978; The inverse of the Freeman - Tukey double arcsine transformation. Am Stat. 32:138. DOI: 10.2307/2682942.
Article18. Chiu A, Chan LM, Fan ST. 2006; Molecular adsorbent recirculating system treatment for patients with liver failure: the Hong Kong experience. Liver Int. 26:695–702. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01293.x. PMID: 16842326.
Article19. Gilg S, Sparrelid E, Saraste L, Nowak G, Wahlin S, Strömberg C, et al. 2018; The molecular adsorbent recirculating system in posthepatectomy liver failure: results from a prospective phase I study. Hepatol Commun. 2:445–454. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1167. PMID: 29619422. PMCID: PMC5880195.
Article20. Rusu EE, Voiculescu M, Zilisteanu DS, Ismail G. 2009; Molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with severe liver failure. Experience of a single Romanian centre. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 18:311–316.21. Saliba F, Camus C, Durand F, Mathurin P, Letierce A, Delafosse B, et al. 2013; Albumin dialysis with a noncell artificial liver support device in patients with acute liver failure: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 159:522–531. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-8-201310150-00005. PMID: 24126646.22. van de Kerkhove MP, de Jong KP, Rijken AM, de Pont AC, van Gulik TM. 2003; MARS treatment in posthepatectomy liver failure. Liver Int. 23 Suppl 3:44–51. DOI: 10.1034/j.1478-3231.23.s.3.2.x. PMID: 12950961.
Article23. Asanuma Y, Sato T, Yasui O, Kurokawa T, Koyama K. 2003; Treatment for postoperative liver failure after major hepatectomy under hepatic total vascular exclusion. J Artif Organs. 6:152–156. DOI: 10.1007/s10047-003-0213-0. PMID: 14621697.
Article24. Lee HJ, Shin KH, Song D, Lee SM, Chang CL, Chu CW, et al. 2017; Increasing use of therapeutic apheresis as a liver-saving modality. Transfus Apher Sci. 56:385–388. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2017.03.001. PMID: 28366590.
Article25. Usami M, Ohyanagi H, Nishimatsu S, Kasahara H, Shiroiwa H, Ishimoto S, et al. 1989; Therapeutic plasmapheresis for liver failure after hepatectomy. ASAIO Trans. 35:564–567. DOI: 10.1097/00002216-198907000-00127. PMID: 2597535.
Article26. Yonekawa C, Nakae H, Tajimi K, Asanuma Y. 2005; Effectiveness of combining plasma exchange and continuous hemodiafiltration in patients with postoperative liver failure. Artif Organs. 29:324–328. DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2005.29054.x. PMID: 15787627.
Article27. Golriz M, Majlesara A, El Sakka S, Ashrafi M, Arwin J, Fard N, et al. 2016; Small for size and flow (SFSF) syndrome: an alternative description for posthepatectomy liver failure. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 40:267–275. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.06.024. PMID: 26516057.
Article28. Eipel C, Abshagen K, Vollmar B. 2010; Regulation of hepatic blood flow: the hepatic arterial buffer response revisited. World J Gastroenterol. 16:6046–6057. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6046. PMID: 21182219. PMCID: PMC3012579.
Article29. Allard MA, Adam R, Bucur PO, Termos S, Cunha AS, Bismuth H, et al. 2013; Posthepatectomy portal vein pressure predicts liver failure and mortality after major liver resection on noncirrhotic liver. Ann Surg. 258:822–829. discussion 829–830. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a64b38. PMID: 24045452.
Article30. Fan M, Wang X, Xu G, Yan Q, Huang W. 2015; Bile acid signaling and liver regeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:196–200. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.05.021. PMID: 24878541. PMCID: PMC4246016.
Article31. Simpson KJ, Lukacs NW, Colletti L, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL. 1997; Cytokines and the liver. J Hepatol. 27:1120–1132. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(97)80160-2.
Article32. Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, DeAngelis RA, Ciliberto G, Furth EE, Poli V, et al. 1996; Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science. 274:1379–1383. DOI: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1379. PMID: 8910279.
Article33. Dello SA, Bloemen JG, van de Poll MC, van Dam RM, Stoot JH, van den Broek MA, et al. 2011; Gut and liver handling of interleukin-6 during liver resection in man. HPB (Oxford). 13:324–331. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00289.x. PMID: 21492332. PMCID: PMC3093644.
Article34. Blindenbacher A, Wang X, Langer I, Savino R, Terracciano L, Heim MH. 2003; Interleukin 6 is important for survival after partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatology. 38:674–682. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50378. PMID: 12939594.
Article35. Donati G, La Manna G, Cianciolo G, Grandinetti V, Carretta E, Cappuccilli M, et al. 2014; Extracorporeal detoxification for hepatic failure using molecular adsorbent recirculating system: depurative efficiency and clinical results in a long-term follow-up. Artif Organs. 38:125–134. DOI: 10.1111/aor.12106. PMID: 23834711.
Article36. Dominik A, Stange J, Pfensig C, Borufka L, Weiss-Reining H, Eggert M. 2014; Reduction of elevated cytokine levels in acute/acute- on-chronic liver failure using super-large pore albumin dialysis treatment: an in vitro study. Ther Apher Dial. 18:347–352. DOI: 10.1111/1744-9987.12146. PMID: 24215331.37. Roth GA, Faybik P, Hetz H, Ankersmit HJ, Hoetzenecker K, Bacher A, et al. 2009; MCP-1 and MIP3-alpha serum levels in acute liver failure and molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS) treatment: a pilot study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 44:745–751. DOI: 10.1080/00365520902770086. PMID: 19247846.
Article38. Stutchfield BM, Simpson K, Wigmore SJ. 2011; Systematic review and meta-analysis of survival following extracorporeal liver support. Br J Surg. 98:623–631. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.7418. PMID: 21462172.
Article39. Balzan S, Belghiti J, Farges O, Ogata S, Sauvanet A, Delefosse D, et al. 2005; The "50-50 criteria" on postoperative day 5: an accurate predictor of liver failure and death after hepatectomy. Ann Surg. 242:824–828. discussion 828–829. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000189131.90876.9e. PMID: 16327492. PMCID: PMC1409891.40. Sparrelid E, Gilg S, van Gulik TM. 2020; Systematic review of MARS treatment in post-hepatectomy liver failure. HPB (Oxford). 22:950–960. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.03.013. PMID: 32249030.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two-stage liver transplantation in a surgically complicated liver failure patient after hepatic tumor resection: A case report
- Portal vein embolization prior to hepatectomy: Techniques, outcomes and novel therapeutic approaches
- Current status of robotic surgery for liver transplantation
- Two-Stage Hepatectomy for Bilateral Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Tumor Thrombi
- Deceased donor liver transplantation for post-hepatectomy liver failure with fixed pupils