Ann Surg Treat Res.
2021 Jun;100(6):356-363. 10.4174/astr.2021.100.6.356.
Combined hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine therapy for septic shock with complicated intraabdominal infection: before and after cohort study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Dankook University Hospital, Dankook University School of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pharmaceutical Services, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516229
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2021.100.6.356
Abstract
- Purpose
The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of intravenous hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine (HAT) combination therapy in complicated intraabdominal infection (cIAI) patients with septic shock.
Methods
This was a single-center, retrospective before-after clinical study comparing clinical outcomes of cIAI patients with septic shock treated with HAT in a surgical intensive care unit (ICU). Delta modified sequential organ failure assessment (mSOFA) scores were evaluated to assess recovery of organ dysfunction. Additional outcomes included procalcitonin level change, daily vasopressor dosage, mean number of days free of mechanical ventilation in 28 days, and renal replacement therapy days.
Results
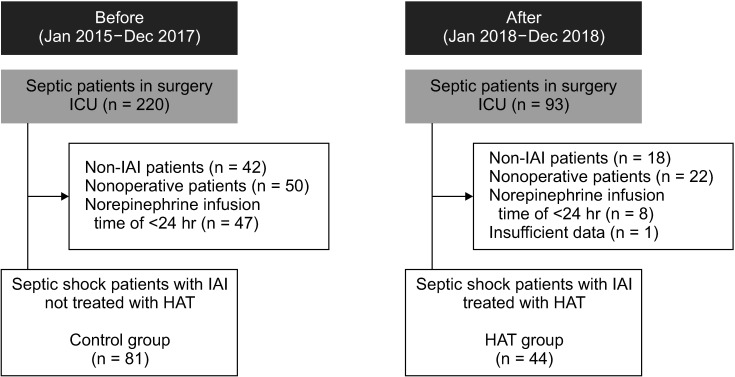
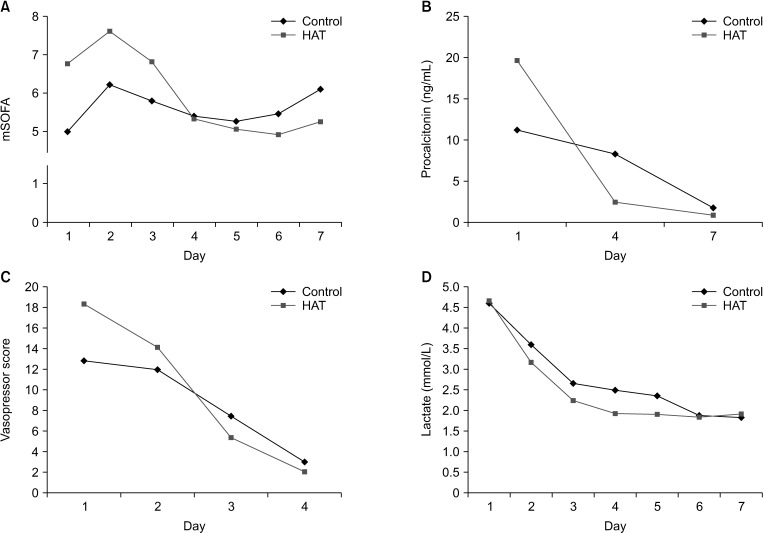
The delta mSOFA score (ICU admission mSOFA score minus 7th-day mSOFA score) was significantly higher in the HAT group than in the control group on the 7th day (2.30 vs. –0.90, P = 0.003). The median 7-day change in procalcitonin score was higher in the control group than in the HAT group (5.94 vs. 10.72, P = 0.041). The difference in vasopressor score between the 1st day and the 4th day was significantly higher in the HAT group (17.63 vs. 9.91, P = 0.005).
Conclusion
In our study of cIAI in patients with septic shock, administration of HAT therapy may improve the recovery from organ dysfunction.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Walkey AJ, Lagu T, Lindenauer PK. Trends in sepsis and infection sources in the United States. a population-based study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015; 12:216–220. PMID: 25569845.
Article2. Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NK, Machado FR, Angus DC, Calandra T, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:581–614. PMID: 25932591.
Article3. Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, Dellamonica P, Gouin F, Lepoutre A, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults. A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. French ICU Group for Severe Sepsis. JAMA. 1995; 274:968–974. PMID: 7674528.
Article4. Choi WH, Hwang SY, Jun SY, Choi YC, Lee EH, Yu WS. Usefulness of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score in patients with sepsis due to intra-abdominal infection. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009; 76:273–278.
Article5. Mulier S, Penninckx F, Verwaest C, Filez L, Aerts R, Fieuws S, et al. Factors affecting mortality in generalized postoperative peritonitis: multivariate analysis in 96 patients. World J Surg. 2003; 27:379–384. PMID: 12658477.
Article6. Lee SH, Kim HW, Lee JG. Infection control strategy for severe sepsis and septic shock in critically ill surgical patients. J Acute Care Surg. 2014; 4:1–6.
Article7. Mazuski JE, Tessier JM, May AK, Sawyer RG, Nadler EP, Rosengart MR, et al. The Surgical Infection Society revised guidelines on the management of intra-abdominal infection. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2017; 18:1–76. PMID: 28085573.
Article8. Morr M, Lukasz A, Rübig E, Pavenstädt H, Kümpers P. Sepsis recognition in the emergency department: impact on quality of care and outcome? BMC Emerg Med. 2017; 17:11. PMID: 28330460.
Article9. Sartelli M, Viale P, Catena F, Ansaloni L, Moore E, Malangoni M, et al. 2013 WSES guidelines for management of intra-abdominal infections. World J Emerg Surg. 2013; 8:3. PMID: 23294512.10. Marik PE, Khangoora V, Rivera R, Hooper MH, Catravas J. Hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock: a retrospective before-after study. Chest. 2017; 151:1229–1238. PMID: 27940189.11. Kim WY, Jo EJ, Eom JS, Mok J, Kim MH, Kim KU, et al. Combined vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine therapy for patients with severe pneumonia who were admitted to the intensive care unit: propensity score-based analysis of a before-after cohort study. J Crit Care. 2018; 47:211–218. PMID: 30029205.
Article12. Balakrishnan M, Gandhi H, Shah K, Pandya H, Patel R, Keshwani S, et al. Hydrocortisone, vitamin C and thiamine for the treatment of sepsis and septic shock following cardiac surgery. Indian J Anaesth. 2018; 62:934–939. PMID: 30636793.13. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315:801–810. PMID: 26903338.
Article14. Zabet MH, Mohammadi M, Ramezani M, Khalili H. Effect of high-dose ascorbic acid on vasopressor's requirement in septic shock. J Res Pharm Pract. 2016; 5:94–100. PMID: 27162802.
Article15. Lambden S, Laterre PF, Levy MM, Francois B. The SOFA score-development, utility and challenges of accurate assessment in clinical trials. Crit Care. 2019; 23:374. PMID: 31775846.
Article16. Schroeder S, Hochreiter M, Koehler T, Schweiger AM, Bein B, Keck FS, et al. Procalcitonin (PCT)-guided algorithm reduces length of antibiotic treatment in surgical intensive care patients with severe sepsis: results of a prospective randomized study. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009; 394:221–226. PMID: 19034493.
Article17. Russell JA, Walley KR, Singer J, Gordon AC, Hébert PC, Cooper DJ, et al. Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:877–887. PMID: 18305265.
Article18. Ensor CR, Sabo RT, Voils SA. Impact of early postoperative hydrocortisone administration in cardiac surgical patients after cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Pharmacother. 2011; 45:189–194. PMID: 21304031.
Article19. Shin TG, Kim YJ, Ryoo SM, Hwang SY, Jo IJ, Chung SP, et al. Early vitamin C and thiamine administration to patients with septic shock in emergency departments: propensity score-based analysis of a before-and-after cohort study. J Clin Med. 2019; 8:102.
Article20. Fowler AA 3rd, Truwit JD, Hite RD, Morris PE, DeWilde C, Priday A, et al. Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019; 322:1261–1270. PMID: 31573637.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Refractory gram-negative septic shock complicated by extended purpura fulminans and multiple organ failure in a 23-year-old puerpera -a case report-
- Combined treatment with vitamin C, hydrocortisone and thiamine does not attenuate morbidity and mortality of septic sheep
- Patterns of inflammatory immune responses in patients with septic shock receiving vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine: clustering analysis in Korea
- Polymyxin B Immobilized Fiber Hemoperfusion in Refractory Intra-abdominal Septic Shock
- The Effect of the Vitamin Protocol for Treating Sepsis or Septic Shock in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit