Korean Circ J.
2021 Jun;51(6):477-486. 10.4070/kcj.2021.0077.
The Importance of Arrhythmia Burden for Outcomes and Management Related to Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Southlake Regional Health Centre, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- KMID: 2516208
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2021.0077
Abstract
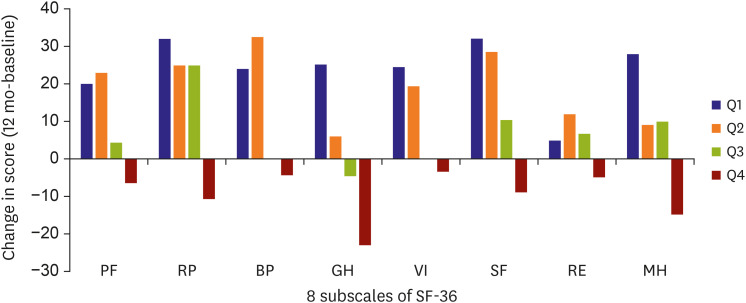
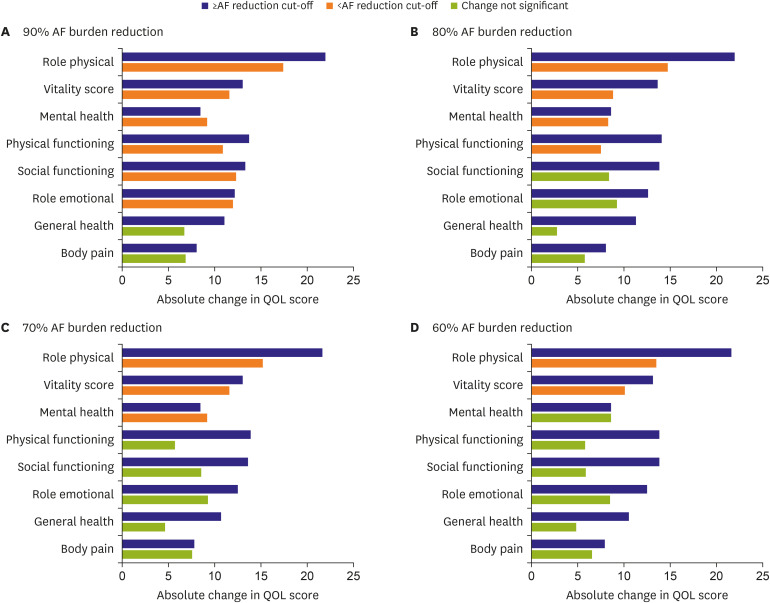
- Atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation has been shown to be an effective treatment for AF, although our understanding of AF ablation outcomes until now, has been based on AF recurrence as a dichotomous variable. Reduction in AF burden, defined as the proportion of time that an individual is in AF during a monitoring period, has been already correlated to an improvement in quality of life and is likely a better assessment of success. Clinically, many patients may still have a few short recurrences of AF but feel much better. In addition, several studies have related higher AF burden with poorer health outcomes and a higher risk of stroke. Despite the growing understanding of AF burden, it is not clear yet which threshold of AF burden would be considered an appropriate outcome measure for AF ablation. Further investigations are needed to address that question. However, the reduction of AF burden seems to be a more accurate reflection of procedural success and a better predictor of prognosis and stroke risk than a single measure of AF.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
What Is Better Predictor of Late Recurrence after Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation?
Sung Il Im, Kyoung-Min Park
Korean Circ J. 2022;52(5):379-381. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2022.0008.Rare and Elusive Arrhythmia: Atrial Tachycardia From Noncoronary Aortic Cusp During Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
Jae-Sun Uhm
Korean Circ J. 2022;52(7):527-528. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2022.0137.Machine Learning for Predicting Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Cardioversion: A Modest Leap Forward
Junbeom Park
Korean Circ J. 2023;53(10):690-692. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2023.0196.
Reference
-
1. Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998; 98:946–952. PMID: 9737513.2. Verma A, Marrouche NF, Natale A. Pulmonary vein antrum isolation: intracardiac echocardiography-guided technique. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2004; 15:1335–1340. PMID: 15574190.3. Charitos EI, Stierle U, Ziegler PD, et al. A comprehensive evaluation of rhythm monitoring strategies for the detection of atrial fibrillation recurrence: insights from 647 continuously monitored patients and implications for monitoring after therapeutic interventions. Circulation. 2012; 126:806–814. PMID: 22824434.4. Martinek M, Aichinger J, Nesser HJ, Ziegler PD, Purerfellner H. New insights into long-term follow-up of atrial fibrillation ablation: full disclosure by an implantable pacemaker device. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007; 18:818–823. PMID: 17573835.
Article5. Ziegler PD, Koehler JL, Mehra R. Comparison of continuous versus intermittent monitoring of atrial arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm. 2006; 3:1445–1452. PMID: 17161787.
Article6. Hindricks G, Pokushalov E, Urban L, et al. Performance of a new leadless implantable cardiac monitor in detecting and quantifying atrial fibrillation: results of the XPECT trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010; 3:141–147. PMID: 20160169.
Article7. Passman RS, Weinberg KM, Freher M, Schaechter A, Goldberger JJ, Kadish AH. Accuracy of mode switch algorithms for detection of atrial tachyarrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2004; 15:773–777. PMID: 15250860.
Article8. Charitos EI, Stierle U, Ziegler PD, et al. A comprehensive evaluation of rhythm monitoring strategies for the detection of atrial fibrillation recurrence: insights from 647 continuously monitored patients and implications for monitoring after therapeutic interventions. Circulation. 2012; 126:806–814. PMID: 22824434.9. Kottkamp H, Tanner H, Kobza R, et al. Time courses and quantitative analysis of atrial fibrillation episode number and duration after circular plus linear left atrial lesions: trigger elimination or substrate modification: early or delayed cure? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 44:869–877. PMID: 15312874.10. Verma A, Champagne J, Sapp J, et al. Discerning the incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic episodes of atrial fibrillation before and after catheter ablation (DISCERN AF): a prospective, multicenter study. JAMA Intern Med. 2013; 173:149–156. PMID: 23266597.11. Andrade JG, Champagne J, Dubuc M, et al. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation assessed by continuous monitoring: a randomized clinical trial. Circulation. 2019; 140:1779–1788. PMID: 31630538.12. Blomström-Lundqvist C, Gizurarson S, Schwieler J, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic medication on quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation: the CAPTAF randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019; 321:1059–1068. PMID: 30874754.13. Packer DL, Mark DB, Robb RA, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic drug therapy on mortality, stroke, bleeding, and cardiac arrest among patients with atrial fibrillation: the CABANA randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019; 321:1261–1274. PMID: 30874766.14. Mantovan R, Macle L, De Martino G, et al. Relationship of quality of life with procedural success of atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation and postablation AF burden: substudy of the STAR AF randomized trial. Can J Cardiol. 2013; 29:1211–1217. PMID: 23988341.
Article15. Verma A, Sanders P, Macle L, et al. Substrate and Trigger Ablation for Reduction of Atrial Fibrillation Trial-Part II (STAR AF II): design and rationale. Am Heart J. 2012; 164:1–6.e6. PMID: 22795275.
Article16. Terricabras M, Mantovan R, Jiang CY, et al. Association between quality of life and procedural outcome after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2020; 3:e2025473. PMID: 33275151.17. Essebag V, Azizi Z, Alipour P, et al. Relationship between quality of life and burden of recurrent atrial fibrillation following ablation: CAPCOST multicentre cohort study. Europace. 2020; 22:1017–1025. PMID: 32531030.
Article18. Piccini JP, Passman R, Turakhia M, Connolly AT, Nabutovsky Y, Varma N. Atrial fibrillation burden, progression, and the risk of death: a case-crossover analysis in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices. Europace. 2019; 21:404–413. PMID: 30462208.
Article19. Wong JA, Conen D, Van Gelder IC, et al. Progression of device-detected subclinical atrial fibrillation and the risk of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018; 71:2603–2611. PMID: 29880119.20. Hohnloser SH, Capucci A, Fain E, et al. ASymptomatic atrial fibrillation and Stroke Evaluation in pacemaker patients and the atrial fibrillation Reduction atrial pacing Trial (ASSERT). Am Heart J. 2006; 152:442–447. PMID: 16923410.21. Gonzalez M, Keating RJ, Markowitz SM, et al. Newly detected atrial high rate episodes predict long-term mortality outcomes in patients with permanent pacemakers. Heart Rhythm. 2014; 11:2214–2221. PMID: 25131667.
Article22. Ganesan AN, Chew DP, Hartshorne T, et al. The impact of atrial fibrillation type on the risk of thromboembolism, mortality, and bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:1591–1602. PMID: 26888184.
Article23. Ali AN, Abdelhafiz A. Clinical and economic implications of AF related stroke. J Atr Fibrillation. 2016; 8:1279. PMID: 27909470.24. Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2018; 20:e1–160.25. Hindricks G, Piorkowski C, Tanner H, et al. Perception of atrial fibrillation before and after radiofrequency catheter ablation: relevance of asymptomatic arrhythmia recurrence. Circulation. 2005; 112:307–313. PMID: 16009793.
Article26. Benezet-Mazuecos J, Rubio JM, Cortés M, et al. Silent ischaemic brain lesions related to atrial high rate episodes in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices. Europace. 2015; 17:364–369. PMID: 25336664.
Article27. Glotzer TV, Hellkamp AS, Zimmerman J, et al. Atrial high rate episodes detected by pacemaker diagnostics predict death and stroke: report of the Atrial Diagnostics Ancillary Study of the MOde Selection Trial (MOST). Circulation. 2003; 107:1614–1619. PMID: 12668495.28. Glotzer TV, Daoud EG, Wyse DG, et al. The relationship between daily atrial tachyarrhythmia burden from implantable device diagnostics and stroke risk: the TRENDS study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009; 2:474–480. PMID: 19843914.29. Van Gelder IC, Healey JS, Crijns HJ, et al. Duration of device-detected subclinical atrial fibrillation and occurrence of stroke in ASSERT. Eur Heart J. 2017; 38:1339–1344. PMID: 28329139.
Article30. Gage BF, van Walraven C, Pearce L, et al. Selecting patients with atrial fibrillation for anticoagulation: stroke risk stratification in patients taking aspirin. Circulation. 2004; 110:2287–2292. PMID: 15477396.31. Stroke Risk in Atrial Fibrillation Working Group. Comparison of 12 risk stratification schemes to predict stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 2008; 39:1901–1910. PMID: 18420954.32. Boriani G, Glotzer TV, Santini M, et al. Device-detected atrial fibrillation and risk for stroke: an analysis of >10,000 patients from the SOS AF project (Stroke preventiOn Strategies based on Atrial Fibrillation information from implanted devices). Eur Heart J. 2014; 35:508–516. PMID: 24334432.33. Turakhia MP, Ziegler PD, Schmitt SK, et al. Atrial fibrillation burden and short-term risk of stroke: case-crossover analysis of continuously recorded heart rhythm from cardiac electronic implanted devices. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2015; 8:1040–1047. PMID: 26175528.34. Kaplan RM, Koehler J, Ziegler PD, Sarkar S, Zweibel S, Passman RS. Stroke risk as a function of atrial fibrillation duration and CHA2DS2-VASc score. Circulation. 2019; 140:1639–1646. PMID: 31564126.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Catheter ablation for treatment of tachyarrhythmia
- Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation with Myotonic Dystrophy and Achalasia-like Esophageal Dilatation
- A Case of Successful Ablation of Right-Sided Accessory Pathway during Atrial Fibrillation
- Non-medication Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
- Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Case Management of Atrial Fibrillation with Catheter Ablation