J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2021 Apr;47(2):82-90. 10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.2.82.
Effectiveness of the novel impression tray “cleftray” for infants with cleft lip and palate: a randomized controlled clinical trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry, Nagpur, India.
- 2Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Government Dental College & Hospital, Nagpur, India.
- KMID: 2515306
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.2.82
Abstract
Objectives
Cleft lip and palate (CLP) is one of the most common congenital deformities with worldwide prevalence. It causes a range of issues for infants that mainly involve difficulty in feeding due to abnormal oronasal communication. For this purpose, feeding plates are provided to infants to act as an artificial palate to aid in feeding. The most crucial procedure in fabrication of a feeding plate is creation of the impression using the traditional finger technique or impression trays. This preliminary research aims to compare the effectiveness of novel impression trays with that of the traditional finger technique for recording impressions of infants with CLP.
Materials and Methods
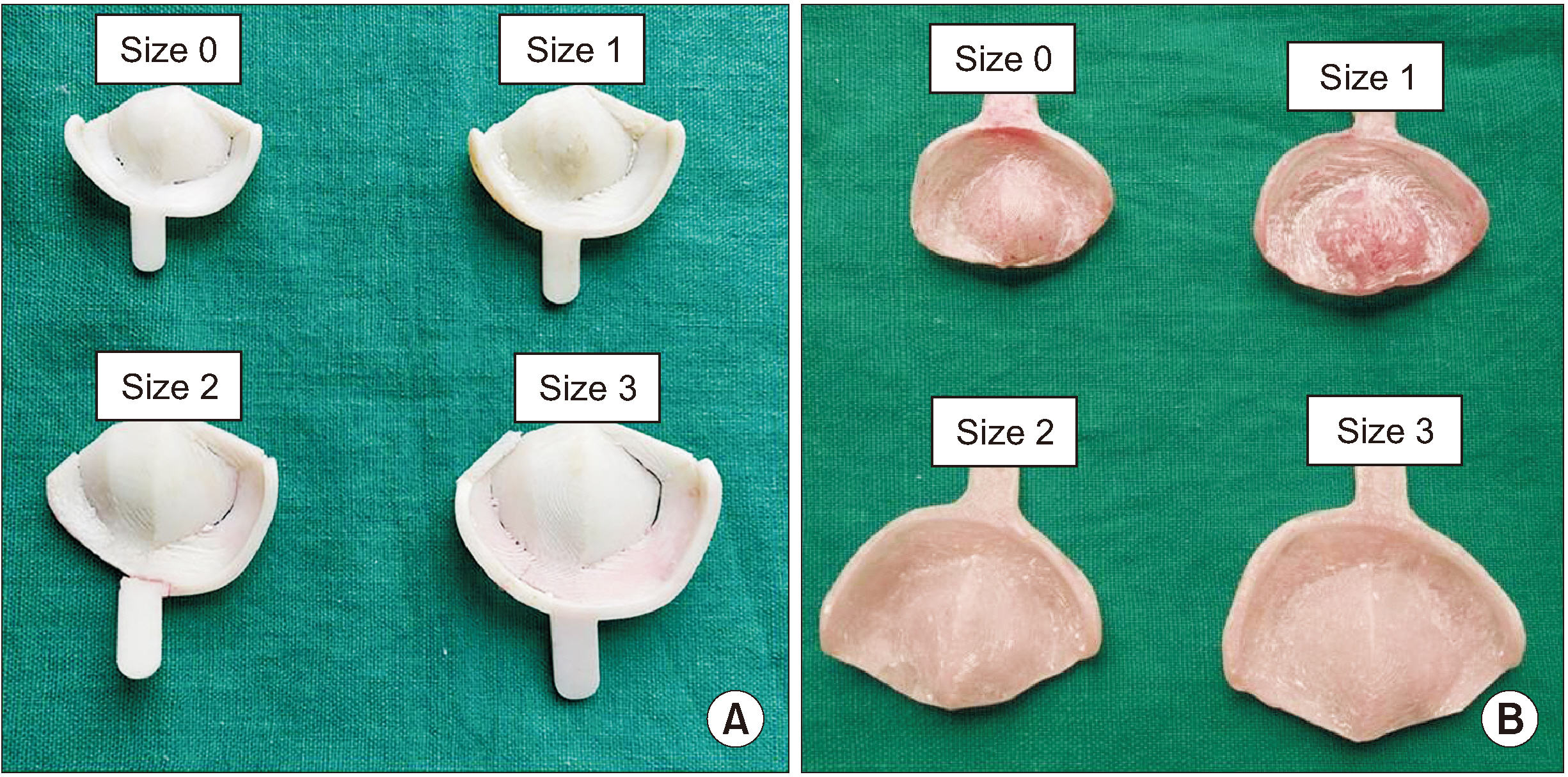
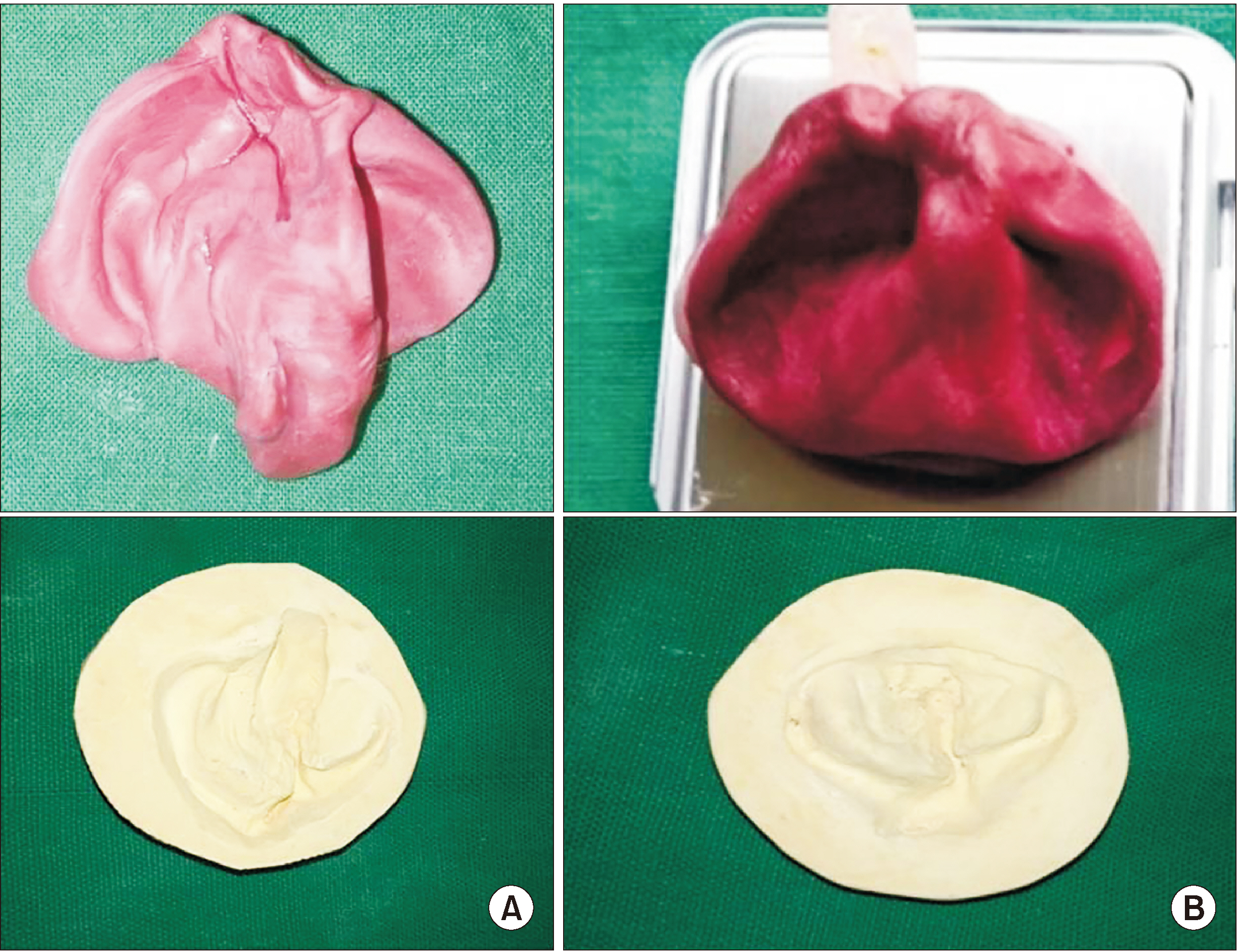
This randomized controlled trial was conducted among 30 infants who were divided into two groups based on the method of obtaining impressions: Group I, finger technique; Group II, specialized acrylic tray (cleftray).
Results
Use of cleftray required less impression time, a reduced amount of material, no incidence of cyanosis/choking in infants, and lower anxiety among doctors compared to the traditional method. Additionally, there was no distortion of cleft impressions, recorded maxillary tuberosity, or other fine details. Therefore, the novel impression tray (cleftray) exhibited superior outcomes in all the parameters compared to the finger technique.
Conclusion
Within the limitations of this study, we conclude that impression trays are superior to the traditional finger, spoon, or ice cream stick methods of creating impressions of CLP. However, it is necessary to conduct more clinical trials on a larger population based on other parameters to compare the effectiveness of the two techniques to draw definitive conclusions.
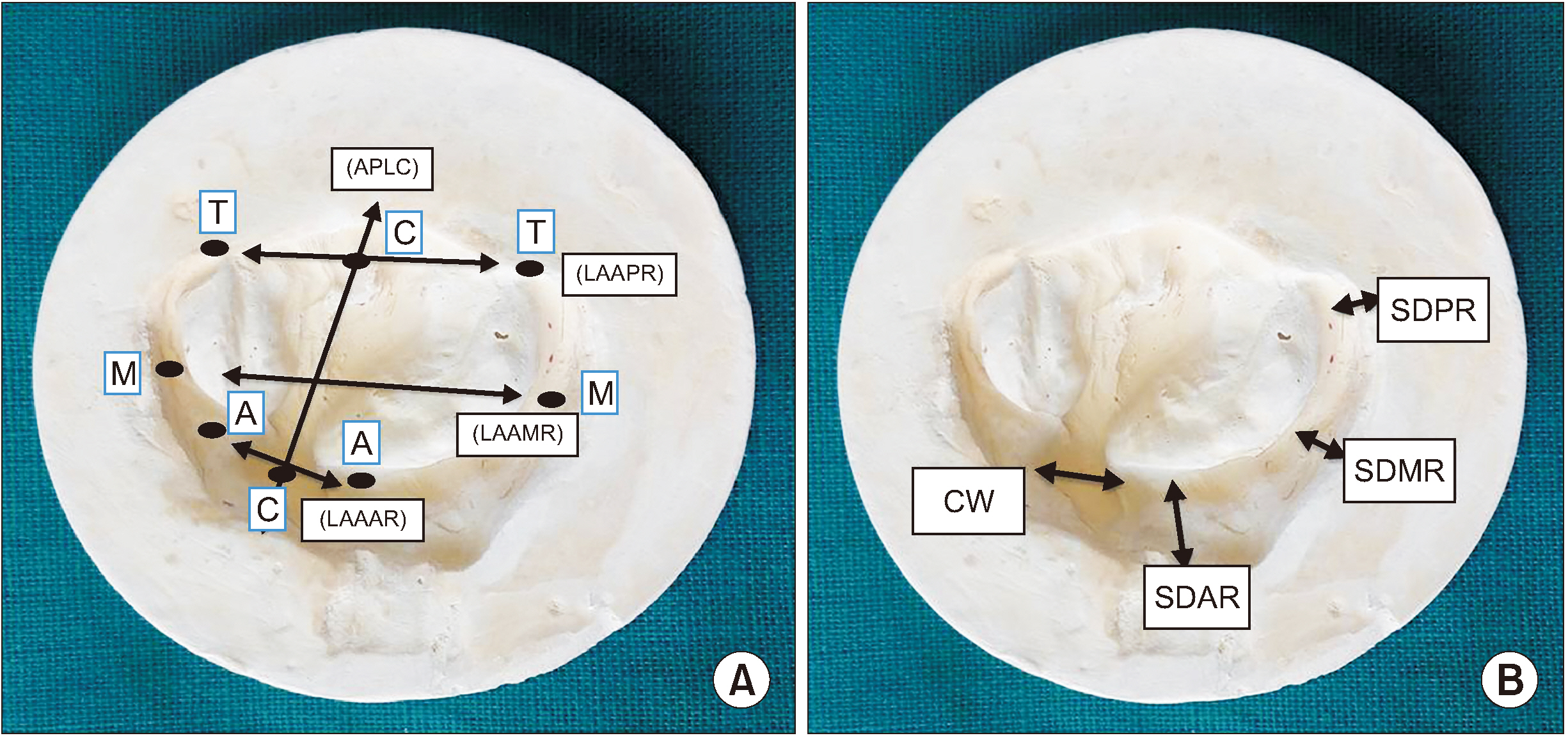
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Grayson BH, Garfinkle JS. 2014; Early cleft management: the case for nasoalveolar molding. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 145:134–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.11.011 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.11.011. PMID: 24485726.
Article2. Mossey PA, Shaw WC, Munger RG, Murray JC, Murthy J, Little J. 2011; Global oral health inequalities: challenges in the prevention and management of orofacial clefts and potential solutions. Adv Dent Res. 23:247–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034511402083 . DOI: 10.1177/0022034511402083. PMID: 21490237. PMCID: PMC6699117.
Article3. Kalaskar R, Kalaskar A, Naqvi FS, Tawani GS, Walke DR. 2013; Prevalence and evaluation of environmental risk factors associated with cleft lip and palate in a central Indian population. Pediatr Dent. 35:279–83. PMID: 23756316.4. Rangeeth BN, Ahmed S, Cholan R, Russia M, Mohammed Raffi AJ. 2013; Role of the pediatric dentist and prosthodontist in early cleft management: presentation of two case reports. SRM J Res Dent Sci. 4:173–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-433X.125600 . DOI: 10.4103/0976-433X.125600.
Article5. Lodaya R, Dave A, Kunte S, Shah R. 2017; A feeding appliance for a 2 day old neonate with cleft lip and palate: a case report. Int J Oral Health Med Res. 3:86–9.6. Ravichandra KS, Vijayaprasad KE, Vasa AA, Suzan S. 2010; A new technique of impression making for an obturator in cleft lip and palate patient. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 28:311–4. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-4388.76165 . DOI: 10.4103/0970-4388.76165. PMID: 21273723.
Article7. Emeka CI, Adeyemo WL, Ladeinde AL, Butali A. 2017; A comparative study of quality of life of families with children born with cleft lip and/or palate before and after surgical treatment. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 43:247–55. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.4.247 . DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.4.247. PMID: 28875139. PMCID: PMC5583199.
Article8. Agarwal A, Rana V, Shafi S. 2010; A feeding appliance for a newborn baby with cleft lip and palate. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 1:91–3. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-5950.69149 . DOI: 10.4103/0975-5950.69149. PMID: 22442561. PMCID: PMC3304172.
Article9. Rizwaan AS, Sujoy B, Rajlakshmi B, Atif K. 2010; Prosthetic rehabilitation of cleft compromised newborns: a review. J Clin Diagn Res. 4:3632–8.10. Lipp MJ, Lubit EC. 1988; An impression procedure for the neonatal patient with a cleft palate. Spec Care Dentist. 8:224–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1754-4505.1988.tb00741.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1754-4505.1988.tb00741.x. PMID: 3078386.
Article11. Xepapadeas AB, Weise C, Frank K, Spintzyk S, Poets CF, Wiechers C, et al. 2020; Technical note on introducing a digital workflow for newborns with craniofacial anomalies based on intraoral scans - part I: 3D printed and milled palatal stimulation plate for trisomy 21. BMC Oral Health. 20:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-020-1001-4 . DOI: 10.1186/s12903-020-1001-4. PMID: 31973720. PMCID: PMC6979345.
Article12. Taib BG, Taib AG, Swift AC, van Eeden S. 2015; Cleft lip and palate: diagnosis and management. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 76:584–5. 588–91. https://doi.org/10.12968/hmed.2015.76.10.584 . DOI: 10.12968/hmed.2015.76.10.584. PMID: 26457939.
Article13. Proffit WR, Fields HW. 2000. Contemporary orthodontics. Mosby;St.Louis: p. 287–8.14. Jones JE, Henderson L, Avery DR. 1982; Use of a feeding obturator for infants with severe cleft lip and palate. Spec Care Dentist. 2:116–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1754-4505.1982.tb01297.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1754-4505.1982.tb01297.x. PMID: 6955979.
Article15. Brine EA, Rickard KA, Brady MS, Liechty EA, Manatunga A, Sadove M, et al. 1994; Effectiveness of two feeding methods in improving energy intake and growth of infants with cleft palate: a randomized study. J Am Diet Assoc. 94:732–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-8223(94)91938-0 . DOI: 10.1016/0002-8223(94)91938-0. PMID: 8021413.
Article16. Shaw WC, Bannister RP, Roberts CT. 1999; Assisted feeding is more reliable for infants with clefts--a randomized trial. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 36:262–8. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1999_036_0262_afimrf_2.3.co_2 . DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_1999_036_0262_afimrf_2.3.co_2. PMID: 10342616.
Article17. Saunders ID, Geary L, Fleming P, Gregg TA. 1989; A simplified feeding appliance for the infant with a cleft lip and palate. Quintessence Int. 20:907–10. PMID: 2639405.18. McNeil CK. 1956; Congenital oral deformities. Br Dent J. 101:191–6.19. Goldberg WB, Ferguson FS, Miles RJ. 1988; Successful use of a feeding obturator for an infant with a cleft palate. Spec Care Dentist. 8:86–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1754-4505.1988.tb00699.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1754-4505.1988.tb00699.x. PMID: 3272045.
Article20. Oliver HT. 1969; Construction of orthodontic appliances for the treatment of newborn infants with clefts of the lip and palate. Am J Orthod. 56:468–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9416(69)90208-5 . DOI: 10.1016/0002-9416(69)90208-5. PMID: 5261160.
Article21. Sabarinath VP, Hazarey PV, Ramakrishna Y, Vasanth R, Girish K. 2009; Caring for cleft lip and palate infants: impression procedures and appliances in use. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 9:76–80. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-4052.55248 . DOI: 10.4103/0972-4052.55248.
Article22. Rathee M. 2015; Single visit feeding appliance for 1-day-old neonate with cleft palate using safe dental putty-gauze hybrid impression technique for maxillary impression. J Surg Tech Case Rep. 7:7–11. https://doi.org/10.4103/2006-8808.184938 . DOI: 10.4103/2006-8808.184938. PMID: 27512543. PMCID: PMC4959410.
Article23. Chate RA. 1995; A report on the hazards encountered when taking neonatal cleft palate impressions (1983-1992). Br J Orthod. 22:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1179/bjo.22.4.299 . DOI: 10.1179/bjo.22.4.299. PMID: 8580095.
Article24. Jacobson BN, Rosenstein SW. 1984; Early maxillary orthopedics for the newborn cleft lip and palate patient. An impression and an appliance. Angle Orthod. 54:247–63. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(1984)054<0247:EMOFTN>2.0.CO;2 . DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1984)054<0247:EMOFTN>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 6385784.
Article25. Brecht LE, Grayson BH, Cutting CB. Taylor TD, editor. 2000. Nasoalveolar molding in early management of cleft lip and palate. Clinical maxillofacial prosthetics. Quintessence;Chicago: p. 63–84.26. Kamble VD, Parkhedkar RD, Sarin SP, Patil PG, Kothari B. 2013; Simplifying cleft surgery by presurgical nasoalveolar molding (PNAM) for infant born with unilateral cleft lip, alveolus, and palate: a clinical report. J Prosthodont Res. 57:224–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpor.2013.03.002 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jpor.2013.03.002. PMID: 23773376.
Article27. Yılmaz RBN, Çakan DG, Noyan A. 2017; Comparison of oxygen saturation during impression taking before and after presurgical orthopedic therapy in babies with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 54:582–7. https://doi.org/10.1597/15-132 . DOI: 10.1597/15-132. PMID: 27427934.
Article28. Dalessandri D, Tonni I, Laffranchi L, Migliorati M, Isola G, Bonetti S, et al. 2019; Evaluation of a digital protocol for pre-surgical orthopedic treatment of cleft lip and palate in newborn patients: a pilot study. Dent J (Basel). 7:111. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7040111 . DOI: 10.3390/dj7040111. PMID: 31835442. PMCID: PMC6960660.
Article29. Strobel-Schwarthoff K, Hirschfelder U, Hofmann E. 2012; Individualized erlanger KS-impression trays for infants with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 49:237–9. https://doi.org/10.1597/10-103 . DOI: 10.1597/10-103. PMID: 21269046.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Orthodontic consideration of cleft lip and palate (Report 1)
- The use of classification in primary and secondary cleft lip and nose deformities in medical records
- A cephalometric study on the position of the hyoid bone in cleft lip and palate individuals
- Cleft lip and Palate Incidence Among the Live Births in the Republic of Korea
- A study on the craniofacial morphology of operated congenital cleft lip & palate