Ewha Med J.
2021 Apr;44(2):46-49. 10.12771/emj.2021.44.2.46.
Unusual Case of Vesicoureteral Reflux and Chronic Kidney Disease in a 10-Year-old Boy with Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2515273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2021.44.2.46
Abstract
- Primary vesicoureteral reflux is a common genetically determined condition that is associated with varying degrees of renal scarring and represents one of the main causes of chronic kidney disease in children. Usually vesicoureteral reflux is common in urinary tract infection patient under 5 years of age. However, we report a rare case of high-grade vesicoureteral reflux and chronic kidney disease in a 10-year-old boy who was referred to the pediatric department for incidentally detected asymptomatic bacteriuria. Our case demonstrated that high grade vesicoureteral reflux patient with reduced renal function, bladder and bowel dysfunction at presentation is more likely to progress to chronic kidney disease.
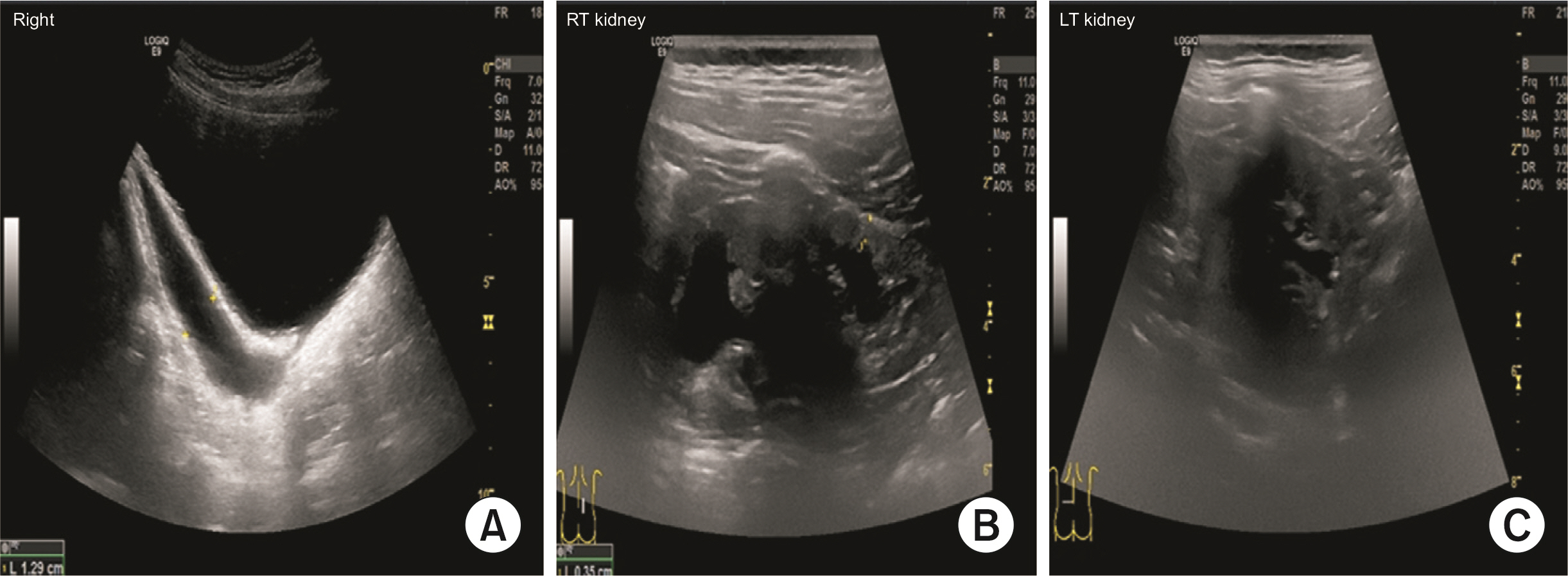
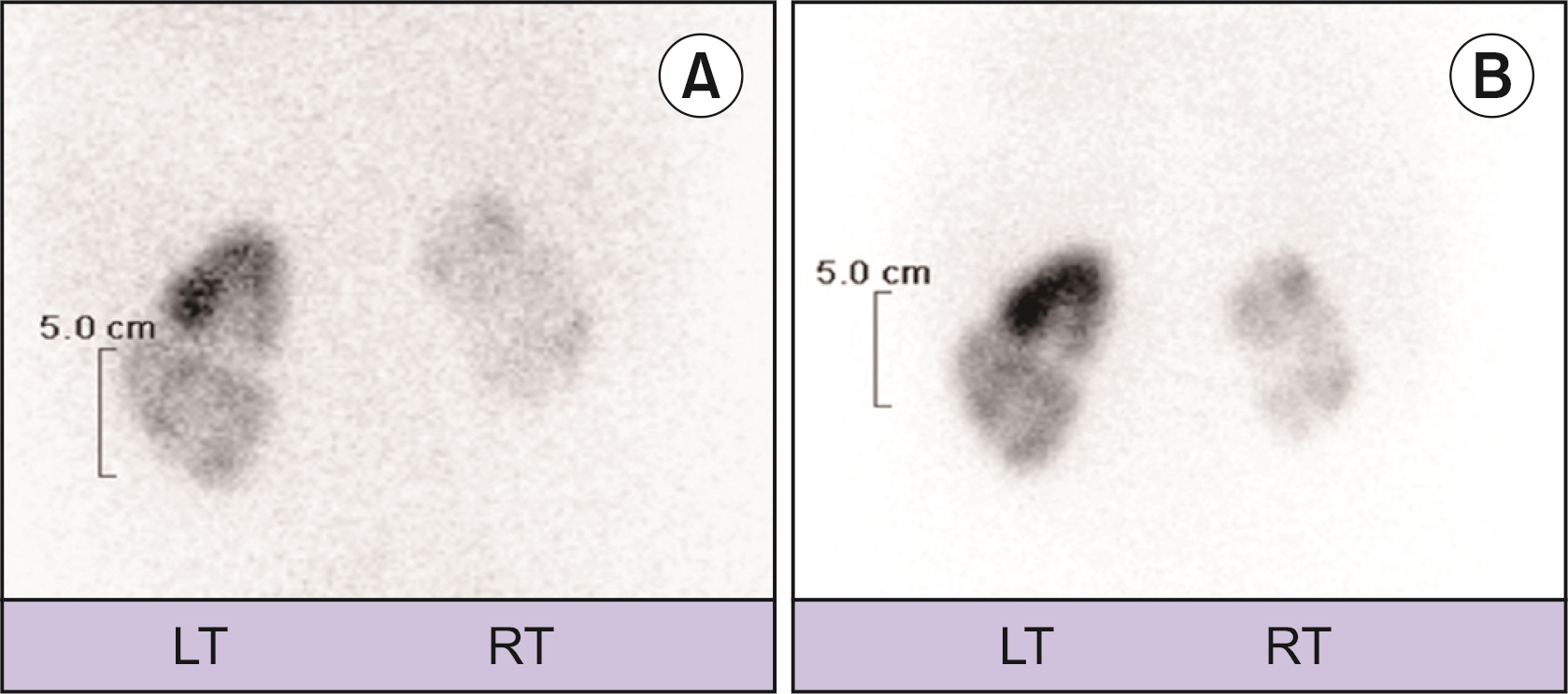
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smellie JM, Normand C. Hodson J, Kincaid-Smith P, editors. 1979. Reflux nephropathy in childhood. Reflux nephropathy. Masson Publishing;New York: p. 14–20.2. Nicolle LE, Gupta K, Bradley SF, Colgan R, DeMuri GP, Drekonja D, et al. 2019; Clinical practice guideline for the management of asymptomatic bacteriuria: 2019 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 68:1611–1615. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz021. PMID: 31506700.3. Dahiya A, Goldman RD. 2018; Management of asymptomatic bacteriuria in children. Can Fam Physician. 64:821–824.4. Sargent MA. 2000; What is the normal prevalence of vesicoureteral reflux? Pediatr Radiol. 30:587–593. DOI: 10.1007/s002470000263. PMID: 11009294.5. Chen MJ, Cheng HL, Chiou YY. 2013; Risk factors for renal scarring and deterioration of renal function in primary vesico-ureteral reflux children: a long-term follow-up retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 8:e57954. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057954. PMID: 23469116. PMCID: PMC3585242.
Article6. Swerkersson S, Jodal U, Sixt R, Stokland E, Hansson S. 2007; Relationship among vesicoureteral reflux, urinary tract infection and renal damage in children. J Urol. 178:647–651. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.04.004. PMID: 17574623.
Article7. Novak TE, Mathews R, Martz K, Neu A. 2009; Progression of chronic kidney disease in children with vesicoureteral reflux: the North American Pediatric Renal Trials Collaborative Studies Database. J Urol. 182(4 Suppl):1678–1681. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.085. PMID: 19692051.
Article8. Coulthard MG. 2009; Vesicoureteric reflux is not a benign condition. Pediatr Nephrol. 24:227–232. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-008-0911-1. PMID: 18584210.
Article9. Venhola M, Uhari M. 2009; Vesicoureteral reflux, a benign condition. Pediatr Nephrol. 24:223–226. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-008-0912-0. PMID: 18604562.
Article10. Silva JM, Diniz JS, Silva AC, Azevedo MV, Pimenta MR, Oliveira EA. 2006; Predictive factors of chronic kidney disease in severe vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Nephrol. 21:1285–1292. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-006-0166-7. PMID: 16791605.
Article11. Sjostrom S, Jodal U, Sixt R, Bachelard M, Sillen U. 2009; Longitudinal development of renal damage and renal function in infants with high grade vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 181:2277–2283. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.01.051. PMID: 19303099.12. Ishikura K, Uemura O, Hamasaki Y, Nakai H, Ito S, Harada R, et al. 2016; Insignificant impact of VUR on the progression of CKD in children with CAKUT. Pediatr Nephrol. 31:105–112. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-015-3196-1. PMID: 26404649.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of High Grade Vesicoureteral Reflux in Infancy Detected Early through the Sibling Screening Test
- Asymptomatic Urinary Abnormalities
- Vesicoureteral Reflux Secondary to a Simple Diverticulectomy: A Case Report
- Reflux Nephropathy in Children
- Antirefluxing Augmentation Cystoplasty with Ileocolic Pouch in Single Kidney with Refluxing Contracted Bladder