Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2021 Apr;38(2):165-168. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00493.
Delayed treatment-free response after romiplostim discontinuation in pediatric chronic immune thrombocytopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2515193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00493
Abstract
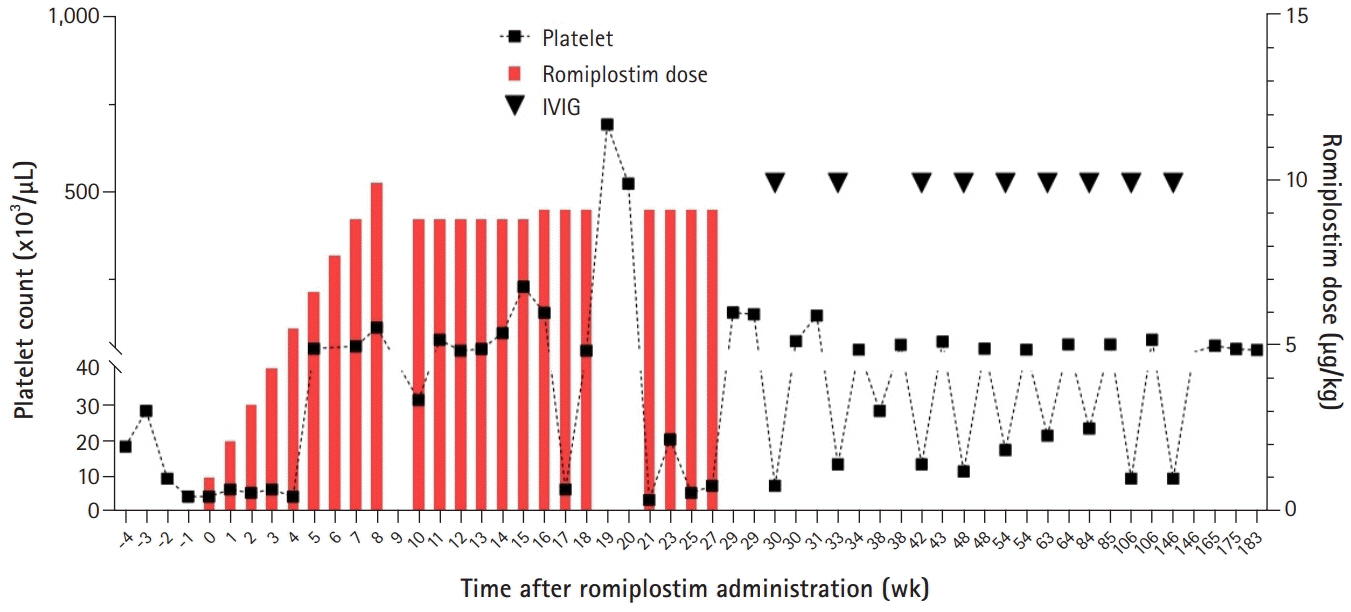
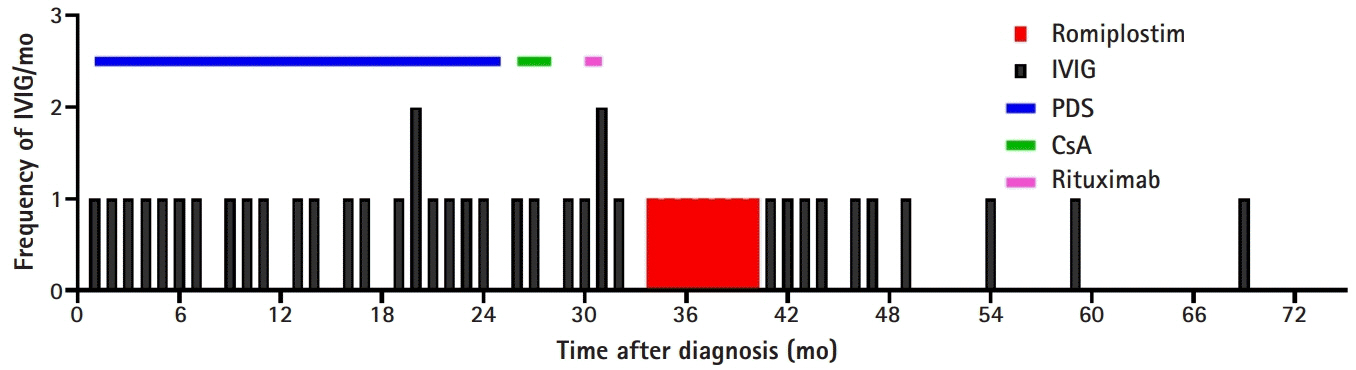
- We report the case of a 16-month-old patient with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) patient who experienced delayed treatment-free response (TFR) after romiplostim treatment. He received intravenous immunoglobulin every month to maintain a platelet count above 20,000/μL for 2 years. Thereafter, he received rituximab and cyclosporine as second-line therapy, with no response, followed by romiplostim. After 4 weeks of treatment, the platelet count was maintained above 50,000/μL. Following 7 months of treatment, he discontinued romiplostim, and the platelet count decreased. His platelet counts remained above 50,000/μL, without any bleeding symptoms, 2 years after romiplostim discontinuation. This is the first report of TFR after romiplostim treatment in pediatric chronic ITP.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim JY. Diagnostic approach of childhood immune thrombocytopenia. Clin Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018; 25:10–6.
Article2. Kim YK, Lee SS, Jeong SH, Ahn JS, Yang DH, Lee JJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of eltrombopag in adult refractory immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Res. 2015; 50:19–25.
Article3. Neunert CE, Rose MJ. Romiplostim for the management of pediatric immune thrombocytopenia: drug development and current practice. Blood Adv. 2019; 3:1907–15.
Article4. Tarantino MD, Bussel JB, Blanchette VS, Despotovic J, Bennett C, Raj A, et al. Romiplostim in children with immune thrombocytopenia: a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet. 2016; 388:45–54.
Article5. Franchini M, Veneri D, Lippi G. Thrombocytopenia and infections. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017; 10:99–106.
Article6. Thota S, Kistangari G, Daw H, Spiro T. Immune thrombocytopenia in adults: an update. Cleve Clin J Med. 2012; 79:641–50.
Article7. Kistangari G, McCrae KR. Immune thrombocytopenia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013; 27:495–520.
Article8. Kuter DJ, Bussel JB, Lyons RM, Pullarkat V, Gernsheimer TB, Senecal FM, et al. Efficacy of romiplostim in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008; 371:395–403.
Article9. Mathias SD, Li X, Eisen M, Carpenter N, Crosby RD, Blanchette VS. A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to determine the effect of romiplostim on health-related quality of life in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia and associated burden in their parents. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016; 63:1232–7.
Article10. Tarantino MD, Bussel JB, Blanchette VS, Beam D, Roy J, Despotovic J, et al. Long-term treatment with romiplostim and treatment-free platelet responses in children with chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Haematologica. 2019; 104:2283–91.
Article11. Lozano ML, Mingot-Castellano ME, Perera MM, Jarque I, Campos-Alvarez RM, González-López TJ, et al. Deciphering predictive factors for choice of thrombopoietin receptor agonist, treatment free responses, and thrombotic events in immune thrombocytopenia. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:16680.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Advances in management of pediatric chronic immune thrombocytopenia: a narrative review
- Efficacy and safety of eltrombopag in adult refractory immune thrombocytopenia
- Diagnostic Approach of Childhood Immune Thrombocytopenia
- IVIG Treatment Response and Age are Important for the Prognosis of Pediatric Immune Thrombocytopenia
- New synergistic efficacy of combination of romiplostim and steroid in refractory immune thrombocytopenia patients