Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Apr;77(4):179-189. 10.4166/kjg.2020.158.
Efficacy and Safety of Biphenyl Dimethyl Dicarboxylate and Ursodeoxycholic Acid Combination in Chronic Hepatitis Related to Metabolic Syndrome Components
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2515139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.158
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Steatohepatitis related to metabolic syndrome is a chronic liver disease prevalent in patients not only with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis but also with alcoholic liver disease and chronic viral hepatitis. On the other hand, there is limited data on the effects of hepatotonic agents in these patients. Therefore, this study evaluated the efficacy of a combined hepatotonic agent in this population.
Methods
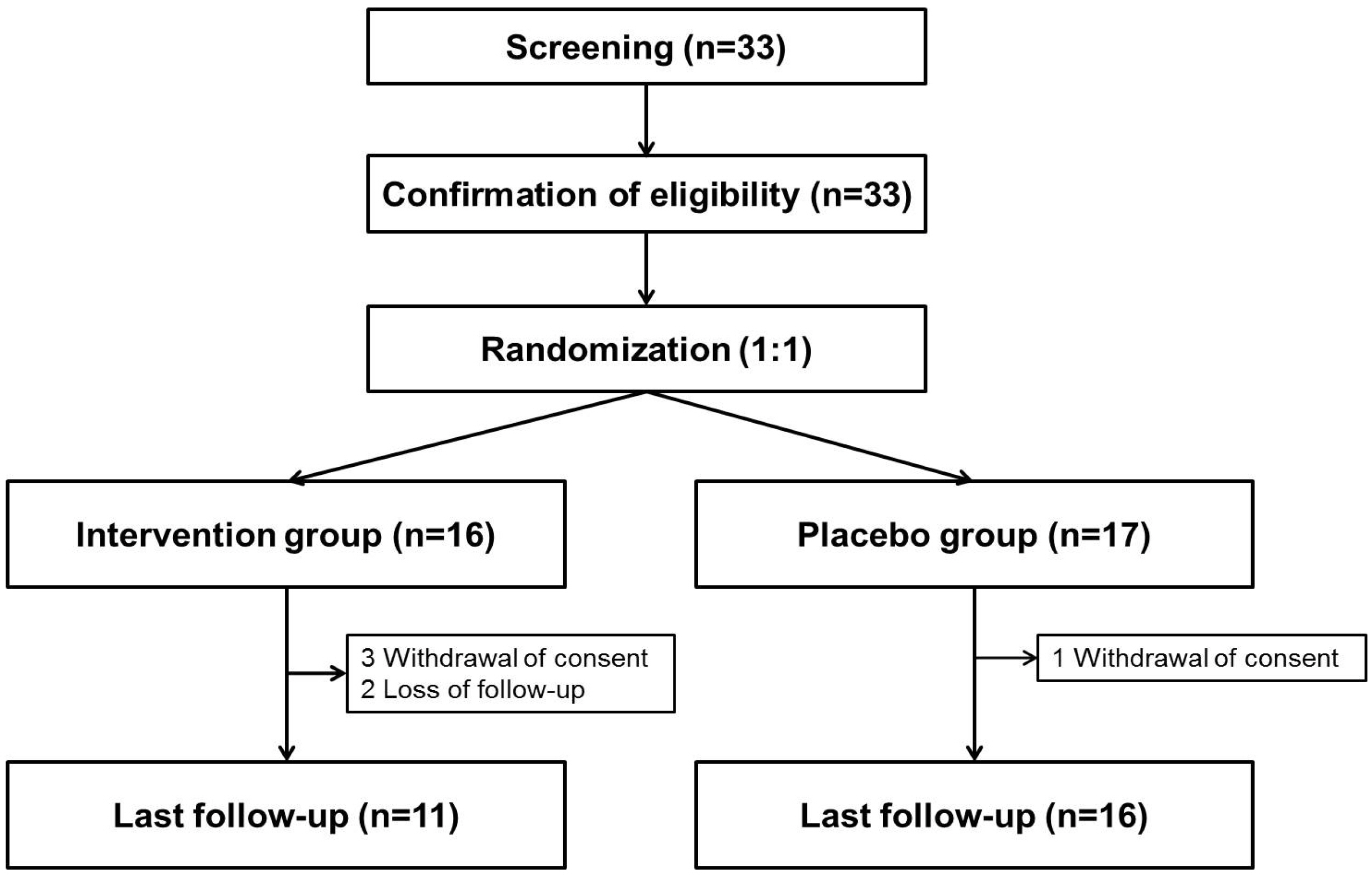
Thirty-three adults with chronic hepatitis and one or more components of metabolic syndrome were assigned randomly to receive biphenyl dimethyl dicarboxylate/ursodeoxycholic acid or a placebo for 24 weeks. The primary outcome was the normalization of ALT (≤40 U/L). The secondary outcomes were the change in controlled attenuation parameter, transient elastography, and Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire score.
Results
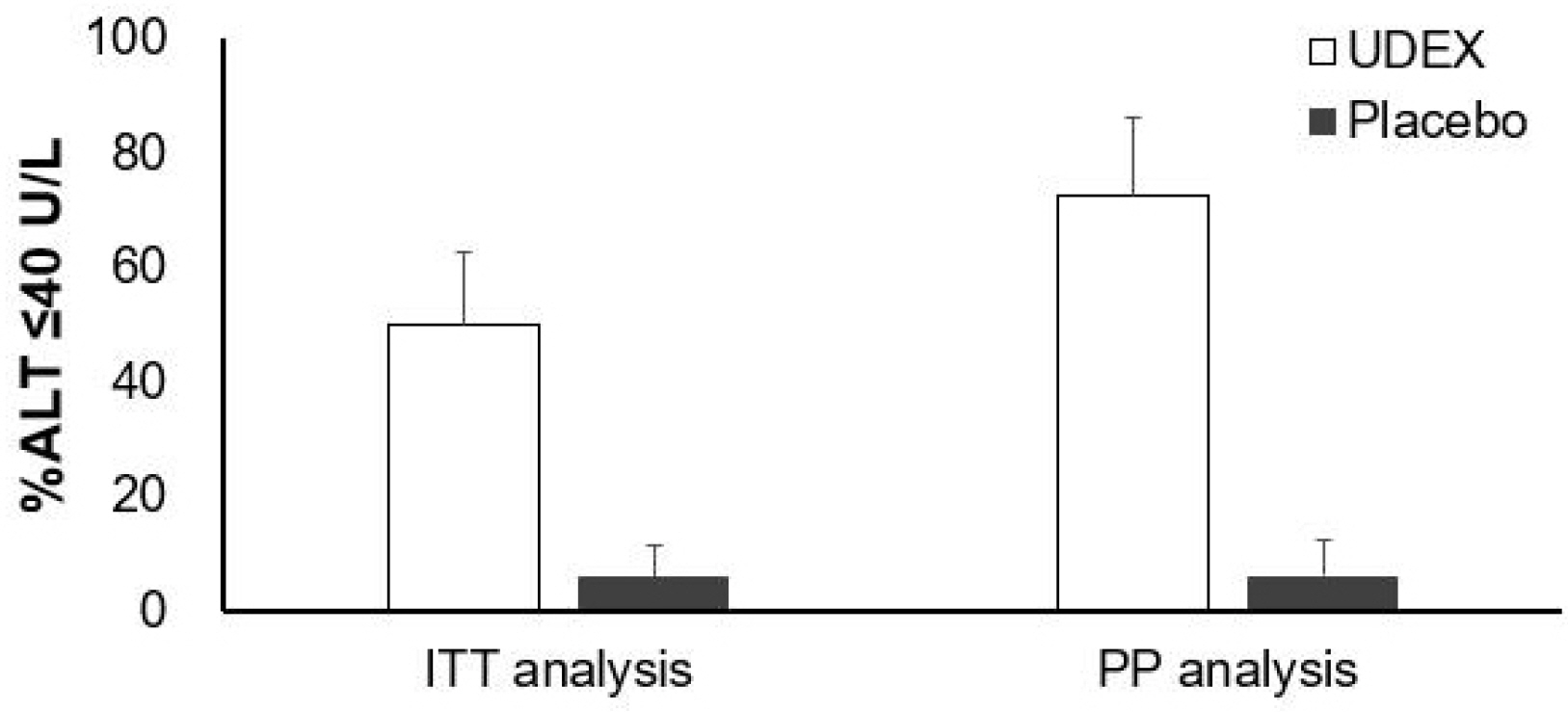
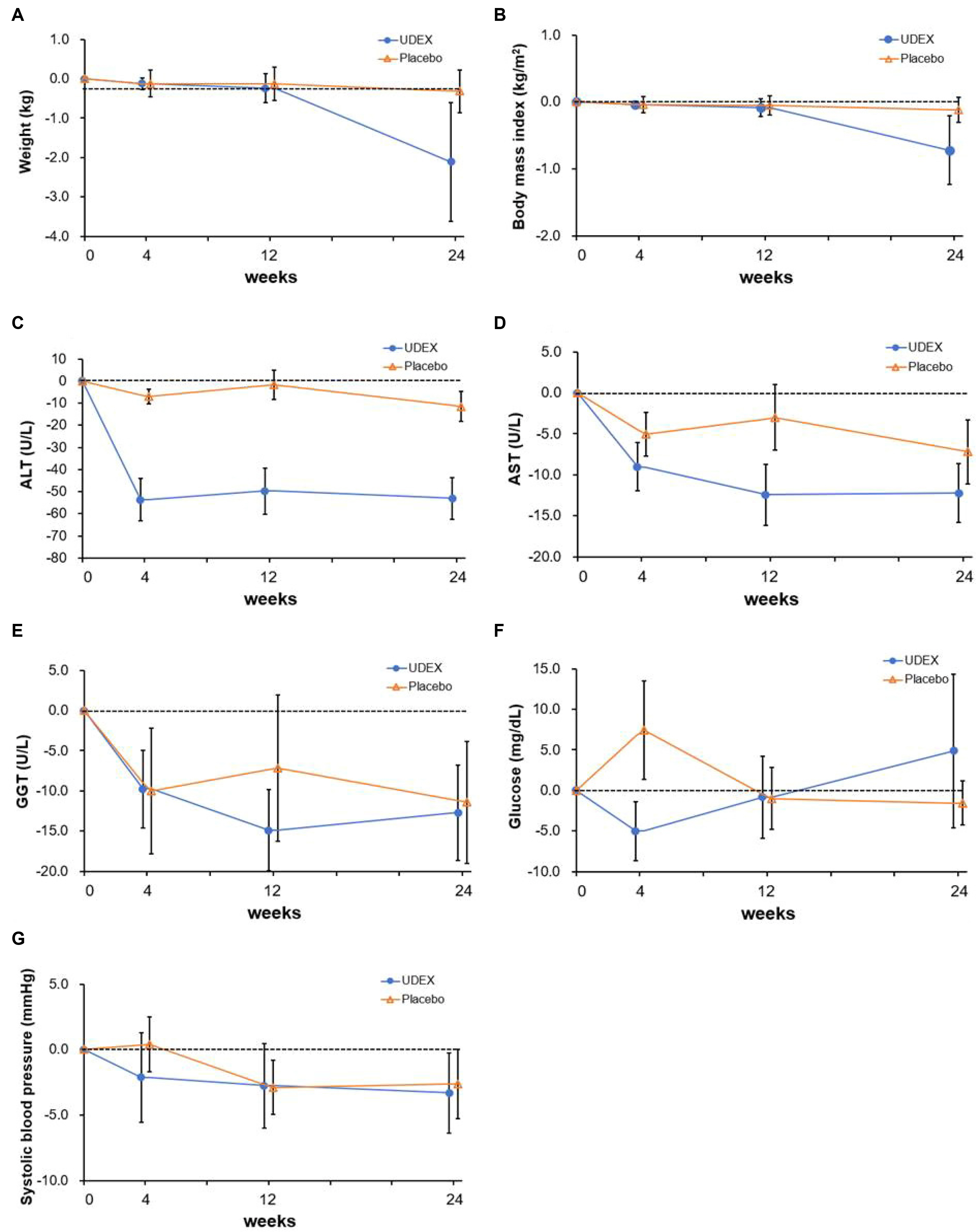
The 33 patients were assigned randomly to two groups. Eight (50%) of 16 patients who received the intervention drug showed the normalization of ALT, whereas only one (6%) of 17 patients in the placebo group did so. In contrast, the change in controlled attenuation, transient elastography, and Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire were similar in the two groups. ALT was changed significantly during the four assessment periods, and this change was affected by the group. The interaction between the group and time was also significant. AST was changed significantly during the same period. This change was not affected by the group.
Conclusions
Biphenyl dimethyl dicarboxylate/ursodeoxycholic acid combination reduced ALT in chronic liver disease related to metabolic syndrome. On the other hand, there is no evidence that this leads to improved hepatic steatosis and fibrosis within 6 months.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, et al. 2010; The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 56:1113–1132. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.034. PMID: 20863953.2. Yki-Järvinen H. 2014; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:901–910. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70032-4.
Article3. Jinjuvadia R, Antaki F, Lohia P, Liangpunsakul S. 2017; The association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic abnormalities in the United States population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 51:160–166. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000666. PMID: 27580477. PMCID: PMC5218881.
Article4. Sun K, Ren M, Liu D, Wang C, Yang C, Yan L. 2014; Alcohol consumption and risk of metabolic syndrome: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin Nutr. 33:596–602. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2013.10.003. PMID: 24315622.
Article5. Abdel-Salam OM, Sleem AA, Morsy FA. 2007; Effects of biphenyldimethyl-dicarboxylate administration alone or combined with silymarin in the CCL4 model of liver fibrosis in rats. ScientificWorldJournal. 7:1242–1255. DOI: 10.1100/tsw.2007.193. PMID: 17721639. PMCID: PMC5901054.6. Son DK, Kim JK, Cheung DY, et al. 2004; A 8 week, double blind, randomized comparative clinical trial comparing the efficacy and safety between UDB and DDB for chronic hepatitis: phase III study. J Korean Soc Clin Pharmacol Ther. 12:57–66. DOI: 10.12793/jkscpt.2004.12.1.57.7. Bae JC, Lee WY, Yoon KH, et al. 2015; Improvement of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with carnitine-orotate complex in type 2 diabetes (CORONA): a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 38:1245–1252. DOI: 10.2337/dc14-2852. PMID: 25877813.
Article8. Wang C, Xu YQ. 2008; Diphenyl dimethyl bicarboxylate in the treatment of viral hepatitis, adjuvant or curative? Gastroenterology Res. 1:2–7. DOI: 10.4021/gr2008.10.1231. PMID: 27994699. PMCID: PMC5154208.
Article9. Lee HS, Kim YT, Yoon YB, Song IS, Kim CY, Jung HC. 1999; Prospective, randomized controlled trial biphenyl dimethyl dicarboxylate in chronic active liver disease: the effect in lowering serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Korean J Med. 40:172–179.10. Liu KT, Lesca P. 1982; Pharmacological properties of Dibenzo[a,c]cyclooctene derivatives isolated from Fructus Schizandrae Chinensis III. Inhibitory effects on carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation, metabolism and covalent binding of carbon tetrachloride to lipids. Chem Biol Interact. 41:39–47. DOI: 10.1016/0009-2797(82)90015-1.
Article11. Yu HQ, Yang XY, Zhang YX, Shi JZ. 1987; Biphenyl-dimethyl dicarboxylate in treating and preventing hepatitis due to drug poisoning. Chin Med J (Engl). 100:122–123.12. Kim HJ, Lee JS, Lee HW, et al. 2014; The PERFECT Study (pennel real life efficacy clinical trial), a double-blind, randomized, multicenter trial examining the efficacy of biphenyl dimethyl dicarboxylate combined with garlic oil in patients with transaminase elevated chronic liver disease. Korean J Med. 86:179–189. DOI: 10.3904/kjm.2014.86.2.179.
Article13. Perez MJ, Briz O. 2009; Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1677–1689. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.1677. PMID: 19360911. PMCID: PMC2668773.
Article14. Poupon RE, Balkau B, Eschwège E, Poupon R. 1991; A multicenter, controlled trial of ursodiol for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. UDCA-PBC Study Group. N Engl J Med. 324:1548–1554. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199105303242204. PMID: 1674105.15. Ratziu V, de Ledinghen V, Oberti F, et al. 2011; A randomized controlled trial of high-dose ursodesoxycholic acid for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 54:1011–1019. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.08.030. PMID: 21145828.
Article16. Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV, et al. 2010; Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 362:1675–1685. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907929. PMID: 20427778. PMCID: PMC2928471.
Article17. Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Loomba R, Sanyal AJ, et al. 2015; Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 385:956–965. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61933-4.
Article18. Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, et al. 2016; Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. 387:679–690. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X.
Article19. Kim SN, Kim SY, Yim HK, et al. 1999; Effect of dimethyl-4,4'-dimethoxy-5,6,5',6'-dimethylenedioxybiphenyl-2,2'- dicarboxylate (DDB) on chemical-induced liver injury. Biol Pharm Bull. 22:93–95. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.22.93. PMID: 9989671.20. El-Bahy AA, Kassem LA, Heikal OA, Mahran LG. 2011; Antiapoptotic effect of DDB against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Toxicol Sci. 36:145–154. DOI: 10.2131/jts.36.145. PMID: 21467741.21. Buko VU, Kuzmitskaya-Nikolaeva IA, Naruta EE, Lukivskaya OY, Kirko SN, Tauschel HD. 2011; Ursodeoxycholic acid dose-dependently improves liver injury in rats fed a methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Hepatol Res. 41:647–659. DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00820.x. PMID: 21711424.
Article22. Tsuchida T, Shiraishi M, Ohta T, Sakai K, Ishii S. 2012; Ursodeoxycholic acid improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis by inducing the excretion of hepatic lipids in high-fat diet-fed KK-Ay mice. Metabolism. 61:944–953. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.10.023. PMID: 22154323.
Article23. Huber R, Hockenjos B, Blum HE. 2004; DDB treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis. Hepatology. 39:1732–1733. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20247. PMID: 15185315.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison on the Efficacy and Safety of Biphenyl Dimethyl Dicarboxylate and Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Patients with Abnormal Alanine Aminotransferase: Multicenter, Double-blinded, Randomized, Active-controlled Clinical Trial
- Ursodeoxycholic acid in hepatobiliary diseases
- Comparison on the Efficacy and Safety of Biphenyl Dimethyl Dicarboxylate and Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Patients with Abnormal Alanine Aminotransferase: Multicenter, Double-blinded, Randomized, Active-controlled Clinical Trial
- Effects of a combination of chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid for gallstone dissolution
- A Study on the Efficacy and Safety of Dipheny-dimethyl-dicarboxylate in Patients with Chronic Liver disease