Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2021 Apr;9(1):40-43. 10.14791/btrt.2021.9.e2.
Arrested Pneumatization of the Sphenoid Sinus in the Skull Base
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2515082
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2021.9.e2
Abstract
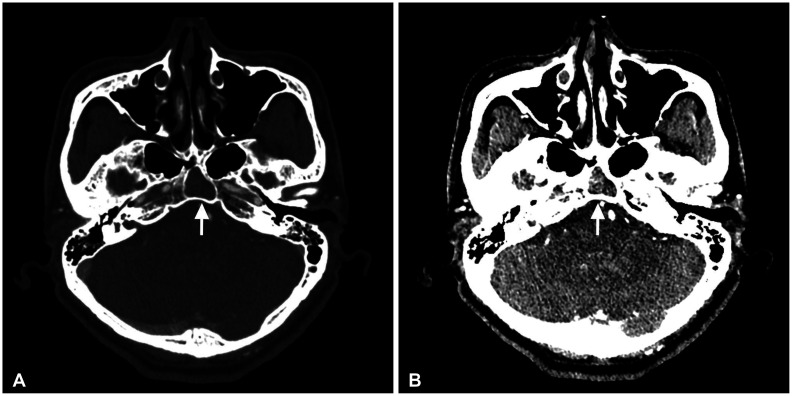
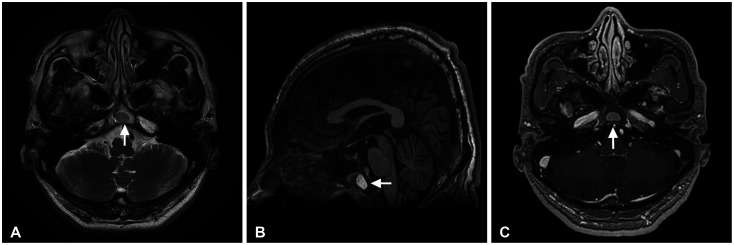
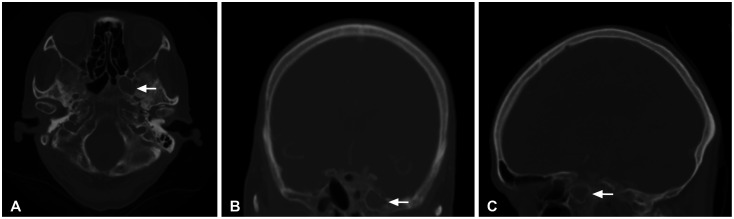
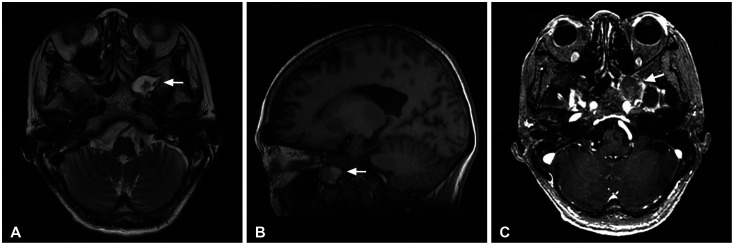
- We report 2 cases of arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus, a normal variant commonly misdiagnosed as a serious condition of the skull base. A 65-year-old man visited a local clinic for regular checkups. Brain CT showed a non-expansile lesion of the soft tissue with a well-defined sclerotic margin in the clivus but without destruction or mass effect on the surrounding bony structures. Subsequent brain MRI revealed that the lesion within the clivus was a high-signal lesion on the T2-weighted image, containing a low-signal round mass seen on a high-intensity signal on the T1-weighted image without contrast enhancement. Thus, the lesion was considered to contain internal fat. A 70-year-old woman diagnosed with a tumor in the greater sphenoid bone visited our hospital. Her brain CT revealed a non-expansile lesion of mixed density and a well-demarcated lesion and internal curvilinear calcification in the left greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The margin was osteosclerotic and the adjacent bony structure was intact. Her brain MRI showed that the lesion within the greater sphenoid bone had multiple low-signal lesions within a high-signal lesion on the T2-weighted image, suggesting internal fat contents. The lesions were diagnosed as arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus and no further examination or treatment was performed. Arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus should be considered in the presence of non-expansile lesion with an osteosclerotic boundary and internal fat component in the skull base.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah RK, Dhingra JK, Carter BL, Rebeiz EE. Paranasal sinus development: a radiographic study. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113:205–209. PMID: 12567069.2. Sirikci A, Bayazit YA, Bayram M, Mumbuç S, Güngör K, Kanlikama M. Variations of sphenoid and related structures. Eur Radiol. 2000; 10:844–848. PMID: 10823645.3. Aoki S, Dillon WP, Barkovich AJ, Norman D. Marrow conversion before pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus: assessment with MR imaging. Radiology. 1989; 172:373–375. PMID: 2748818.4. Scuderi AJ, Harnsberger HR, Boyer RS. Pneumatization of the paranasal sinuses: normal features of importance to the accurate interpretation of CT scans and MR images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993; 160:1101–1104. PMID: 8470585.5. Welker KM, DeLone DR, Lane JI, Gilbertson JR. Arrested pneumatization of the skull base: imaging characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:1691–1696. PMID: 18492926.6. Kuntzler S, Jankowski R. Arrested pneumatization: witness of paranasal sinuses development? Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2014; 131:167–170. PMID: 24709406.7. Prabhu AV, Branstetter BF 4th. The CT prevalence of arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus in patients with sickle cell disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37:1916–1919. PMID: 27151749.8. Jang YJ, Kim SC. Pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus in children evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Rhinol. 2000; 14:181–185. PMID: 10887625.9. Jalali E, Tadinada A. Arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus mimicking intraosseous lesions of the skull base. Imaging Sci Dent. 2015; 45:67–72. PMID: 25793186.10. Adin ME, Ozmen CA, Aygun N. Utility of the vidian canal in endoscopic skull base surgery: detailed anatomy and relationship to the internal carotid artery. World Neurosurg. 2019; 121:e140–e146. PMID: 30240854.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus mimicking intraosseous lesions of the skull base
- A Case of Massive Skull Base Erosion by Fungus Ball in the Sphenoid Sinus
- A Case of Endoscopic Reconstruction of Skull Base Defect Combined with Meningoencephalocele in the Sphenoid Sinus
- Chondroma of the Sphenoid Sinus: Case Report
- Normal Development of Sutures and Synchondroses in the Central Skull Base: CT Study