J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Apr;36(14):e89. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e89.
Entecavir versus Tenofovir for the Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Treatment-naïve Chronic Hepatitis B Patients in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea
- 2Healthcare Review and Assessment Committee, Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Wonju, Korea
- 3College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2514900
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e89
Abstract
- Background
The occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a major concern during antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B. There are conflicting opinions regarding the effects of entecavir (ETV) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) on HCC prevention. We assessed these two antiviral medications for preventing HCC in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B.
Methods
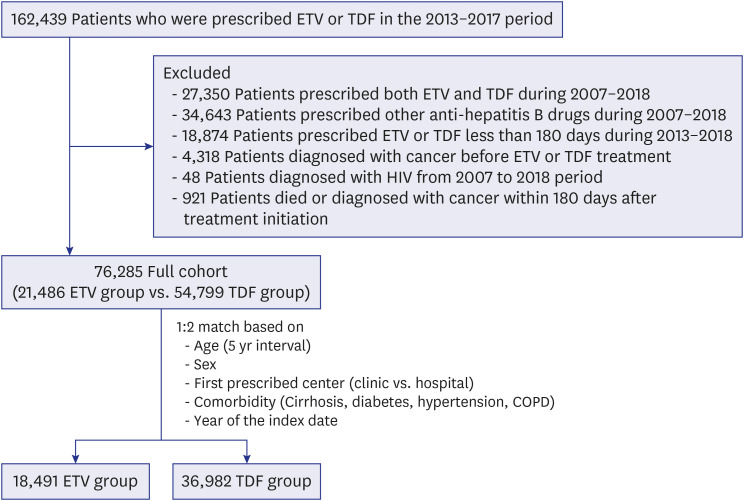
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using nationwide claims data from the Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. We included 55,473 treatmentnaïve adult cases where ETV or TDF treatment was started between 2013 and 2017 (cohort 1). The ETV and TDF groups were matched 1:2 based on age, sex, comorbidities, hospital type, and index date year. Patients were followed up until December 2018. The outcome was the development of HCC. Subgroup analyses were conducted according to sex, age, hospital type and the presence of cirrhosis. We also compared the outcomes of patients who had started antiviral therapy during the 2012–2014 period (cohort 2).
Results
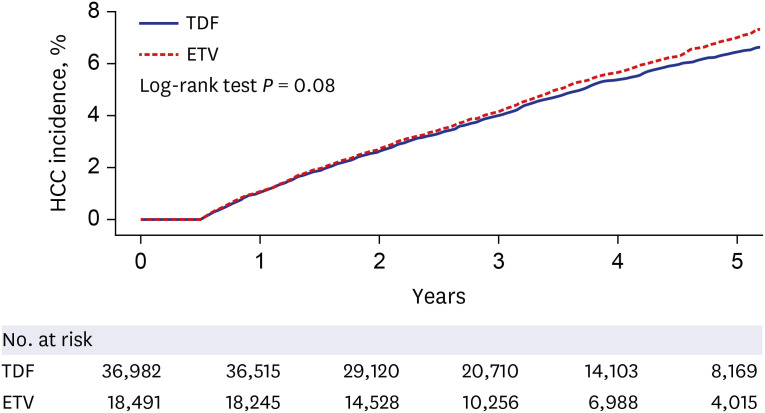
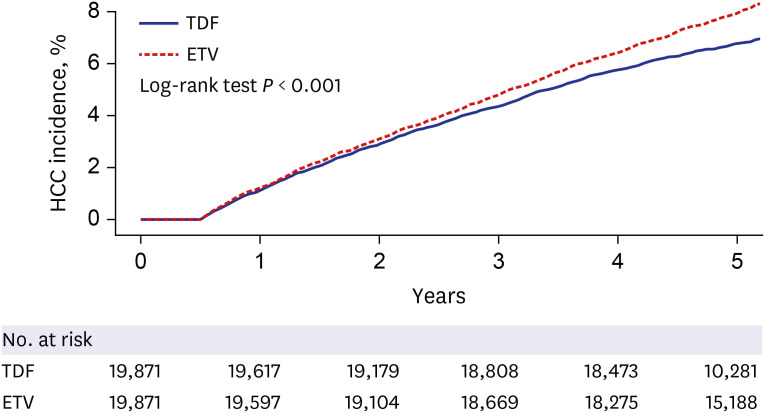
The matched participants (18,491 in the ETV and 36,982 in the TDF groups) were a part of the study for, on average, 41.2 months. The incidence of HCC did not differ significantly between the ETV (1.46 per 100 patient-years) and the TDF (1.36 per 100 patient-years) treatments (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.86–1.01; P = 0.081). By contrast, HCC incidence was significantly higher in the ETV group than tenofovir group of cohort 2.
Conclusion
In patients with chronic hepatitis B, the ETV treatment did not result in a higher rate of HCC than the TDF treatment.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):1-120. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2022.11.07.
Reference
-
1. Lampertico P, Agarwal K, Berg T, Buti M, Janssen HL, Papatheodoridis G, et al. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017; 67(2):370–398. PMID: 28427875.
Article2. Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan HL, Chen CJ, et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: a 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 2016; 10(1):1–98.
Article3. Terrault NA, Lok AS, McMahon BJ, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology. 2018; 67(4):1560–1599. PMID: 29405329.
Article4. Choi J, Kim HJ, Lee J, Cho S, Ko MJ, Lim YS. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with entecavir vs tenofovir for chronic hepatitis B: a Korean nationwide cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2019; 5(1):30–36. PMID: 30267080.5. Kim SU, Seo YS, Lee HA, Kim MN, Lee YR, Lee HW, et al. A multicenter study of entecavir vs. tenofovir on prognosis of treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B in South Korea. J Hepatol. 2019; 71(3):456–464. PMID: 30959156.
Article6. Köklü S, Tuna Y, Gülşen MT, Demir M, Köksal AŞ, Koçkar MC, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of lamivudine, entecavir, and tenofovir for treatment of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11(1):88–94. PMID: 23063679.
Article7. Papatheodoridis GV, Idilman R, Dalekos GN, Buti M, Chi H, van Boemmel F, et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma decreases after the first 5 years of entecavir or tenofovir in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2017; 66(5):1444–1453. PMID: 28622419.
Article8. Kim BG, Park NH, Lee SB, Lee H, Lee BU, Park JH, et al. Mortality, liver transplantation and hepatic complications in patients with treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir vs tenofovir. J Viral Hepat. 2018; 25(12):1565–1575. PMID: 29998592.
Article9. Yu JH, Jin YJ, Lee JW, Lee DH. Remaining hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving entecavir/tenofovir in South Korea. Hepatol Res. 2018; 48(11):862–871. PMID: 29761604.
Article10. Wu IT, Hu TH, Hung CH, Lu SN, Wang JH, Lee CM, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of entecavir and tenofovir in nucleos(t)ide analogue-naive chronic hepatitis B patients with high viraemia: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017; 23(7):464–469. PMID: 28189857.
Article11. Chen J, Zhao SS, Liu XX, Huang ZB, Huang Y. Comparison of the efficacy of tenofovir versus tenofovir plus entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in patients with poor efficacy of entecavir: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2017; 39(9):1870–1880. PMID: 28797777.
Article12. Yip TC, Wong VW, Chan HL, Tse YK, Lui GC, Wong GL. Tenofovir is associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma than entecavir in patients with chronic HBV infection in China. Gastroenterology. 2020; 158(1):215–225.e6. PMID: 31574268.
Article13. Lee SW, Kwon JH, Lee HL, Yoo SH, Nam HC, Sung PS, et al. Comparison of tenofovir and entecavir on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and mortality in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B in Korea: a large-scale, propensity score analysis. Gut. 2019; 69(7):1301–1308. PMID: 31672838.14. Hsu YC, Wong GL, Chen CH, Peng CY, Yeh ML, Cheung KS, et al. Tenofovir versus entecavir for hepatocellular carcinoma prevention in an international consortium of chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020; 115(2):271–280. PMID: 31634265.15. Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Yang J, Hu K, Huang Y. The effectiveness of TDF versus ETV on incidence of HCC in CHB patients: a meta analysis. BMC Cancer. 2019; 19(1):511. PMID: 31142283.
Article16. Li M, Lv T, Wu S, Wei W, Wu X, Ou X, et al. Tenofovir versus entecavir in lowering the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a critical systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 2020; 14(1):105–114. PMID: 31898210.
Article17. Wang X, Liu X, Dang Z, Yu L, Jiang Y, Wang X, et al. Nucleos (t) ide analogues for reducing hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Liver. 2020; 14(2):232–247. PMID: 31158948.18. Cheol Seong S, Kim YY, Khang YH, Heon Park J, Kang HJ, Lee H, et al. Data resource profile: the National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46(3):799–800. PMID: 27794523.
Article19. Kim JA, Yoon S, Kim LY, Kim DS. Towards actualizing the value potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) data as a resource for health research: strengths, limitations, applications, and strategies for optimal use of HIRA data. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32(5):718–728. PMID: 28378543.
Article20. Ayoub WS, Cohen E, Hepatitis B. Hepatitis B management in the pregnant patient: an update. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016; 4(3):241–247. PMID: 27777892.
Article21. Zimmermann AE, Pizzoferrato T, Bedford J, Morris A, Hoffman R, Braden G. Tenofovir-associated acute and chronic kidney disease: a case of multiple drug interactions. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42(2):283–290. PMID: 16355343.
Article22. World Health Organization. Guidelines for the prevention, care and treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis B infection. Updated 2015. Accessed November 14, 2019. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/hepatitis-b-guidelines/en/.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Entecavir versus tenofovir in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Enemies or partners in the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Is tenofovir and entecavir combination therapy still the optimal treatment for chronic hepatitis B patients with prior suboptimal response?
- Long Term Efficacy of Antiviral Therapy: Mortality and Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Lamivudine: fading into the mists of time
- Is tenofovir monotherapy a sufficient defense line against multi-drug resistant hepatitis B virus?