Ann Surg Treat Res.
2021 Apr;100(4):235-245. 10.4174/astr.2021.100.4.235.
Postoperative outcomes of purely laparoscopic donor hepatectomy compared to open living donor hepatectomy: a preliminary observational study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2514721
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2021.100.4.235
Abstract
- Purpose
To lessen the physical, cosmetic, and psychological burden of donors, purely laparoscopic donor hepatectomy (PLDH) has been proposed as an ideal method for living donors. Our study aimed to prospectively compare the effect of PLDH and 2 other types of open living donor hepatectomy (OLDH) on postoperative pain and recovery.
Methods
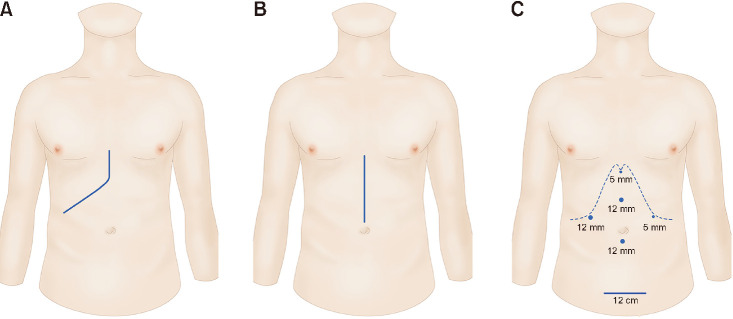
Sixty donors scheduled to undergo donor hepatectomy between March 2015 and November 2017 were included. Donors were divided into 3 groups by surgical technique: OLDH with a subcostal incision (n = 20), group S; OLDH with an upper midline incision (n = 20), group M; and PLDH (n = 20), group L. The primary outcomes were postoperative pain and analgesic requirement during postoperative day (POD) 3. Other variables regarding postoperative recovery were also analyzed.
Results
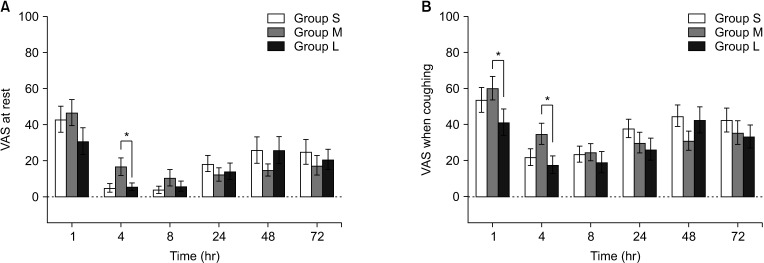
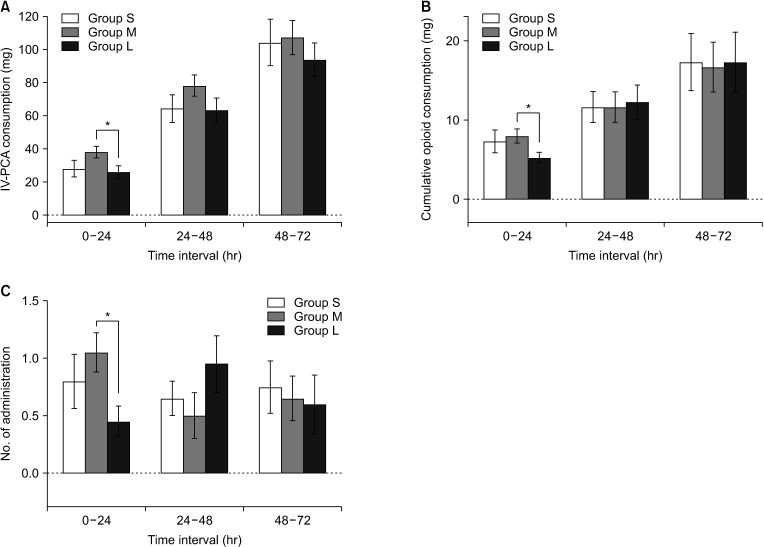
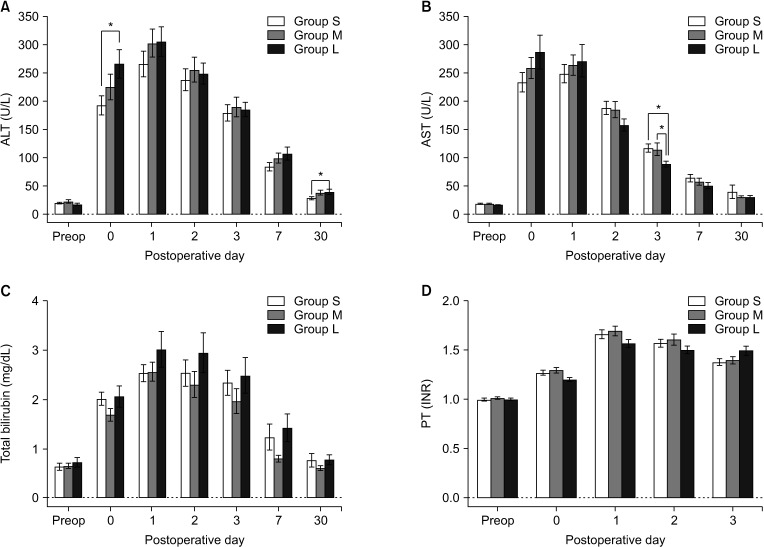
Although pain relief during POD 3, assessed by visual analog scale (VAS) score and analgesic requirement, was similar among the 3 groups, group L showed lower VAS scores and opioid requirements than group M. Moreover, group L was associated with a rapid postoperative recovery evidenced by the shorter hospital length of stay and more frequent return to normal activity on POD 30.
Conclusion
This pilot study failed to verify the hypothesis that PLDH reduces postoperative pain. PLDH did not reduce postoperative pain but showed faster recovery than OLDH.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Broelsch CE, Burdelski M, Rogiers X, Gundlach M, Knoefel WT, Langwieler T, et al. Living donor for liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1994; 20(1 Pt 2):49S–55S. PMID: 8005580.
Article2. Jurim O, Shackleton CR, McDiarmid SV, Martin P, Shaked A, Millis JM, et al. Living-donor liver transplantation at UCLA. Am J Surg. 1995; 169:529–532. PMID: 7538267.
Article3. Ishizaki M, Kaibori M, Matsui K, Kwon AH. Change in donor quality of life after living donor liver transplantation surgery: a single-institution experience. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44:344–346. PMID: 22410012.
Article4. Rhu J, Kim JM, Choi GS, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Soubrane O. Laparoscopy of hepatocellular carcinoma is helpful in minimizing intra-abdominal adhesion during salvage transplantation. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2018; 95:258–266. PMID: 30402444.
Article5. Carroll IR, Angst MS, Clark JD. Management of perioperative pain in patients chronically consuming opioids. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2004; 29:576–591. PMID: 15635517.
Article6. Ko JS, Choi SJ, Gwak MS, Kim GS, Ahn HJ, Kim JA, et al. Intrathecal morphine combined with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia is an effective and safe method for immediate postoperative pain control in live liver donors. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:381–389. PMID: 19326422.
Article7. Gordon DB, Stevenson KK, Griffie J, Muchka S, Rapp C, Ford-Roberts K. Opioid equianalgesic calculations. J Palliat Med. 1999; 2:209–218. PMID: 15859817.
Article8. Stark PA, Myles PS, Burke JA. Development and psychometric evaluation of a postoperative quality of recovery score: the QoR-15. Anesthesiology. 2013; 118:1332–1340. PMID: 23411725.9. Kleif J, Waage J, Christensen KB, Gögenur I. Systematic review of the QoR-15 score, a patient-reported outcome measure measuring quality of recovery after surgery and anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2018; 120:28–36. PMID: 29397134.10. Bang SR, Ahn HJ, Kim GS, Yang M, Gwak MS, Ko JS, et al. Predictors of high intraoperative blood loss derived by simple and objective method in adult living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:4148–4150. PMID: 21168648.
Article11. Takeishi K, Shirabe K, Yoshida Y, Tsutsui Y, Kurihara T, Kimura K, et al. Correlation between portal vein anatomy and bile duct variation in 407 living liver donors. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15:155–160. PMID: 25521764.
Article12. Rhu J, Choi GS, Kwon CH, Kim JM, Joh JW. Learning curve of laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy. Br J Surg. 2020; 107:278–288. PMID: 31652003.
Article13. Rhu J, Choi GS, Kim JM, Joh JW, Kwon CH. Feasibility of total laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy compared with open surgery: comprehensive review of 100 cases of the initial stage. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2020; 27:16–25. PMID: 31271522.
Article14. Kwon CH, Choi GS, Kim JM, Cho CW, Rhu J, Soo Kim G, et al. Laparoscopic donor hepatectomy for adult living donor liver transplantation recipients. Liver Transpl. 2018; 24:1545–1553. PMID: 30021060.
Article15. Kwon CH, Choi GS, Joh JW. Laparoscopic right hepatectomy for living donor. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2019; 24:167–174. PMID: 30676401.
Article16. Jeong JS, Wi W, Chung YJ, Kim JM, Choi GS, Kwon CH, et al. Comparison of perioperative outcomes between pure laparoscopic surgery and open right hepatectomy in living donor hepatectomy: propensity score matching analysis. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:5314. PMID: 32210359.
Article17. Park J, Kwon DC, Choi GS, Kim SJ, Lee SK, Kim JM, et al. Safety and risk factors of pure laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy: comparison to open technique in propensity score-matched analysis. Transplantation. 2019; 103:e308–e316. PMID: 31283680.
Article18. Park J, Kwon CH, Choi GS, Lee SK, Kim JM, Oh J, et al. One-year recipient morbidity of liver transplantation using pure laparoscopic versus open living donor right hepatectomy: propensity score analysis. Liver Transpl. 2019; 25:1642–1650. PMID: 31271699.
Article19. Wu CL, Rowlingson AJ, Partin AW, Kalish MA, Courpas GE, Walsh PC, et al. Correlation of postoperative pain to quality of recovery in the immediate postoperative period. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2005; 30:516–522. PMID: 16326335.
Article20. Nagai S, Brown L, Yoshida A, Kim D, Kazimi M, Abouljoud MS. Mini-incision right hepatic lobectomy with or without laparoscopic assistance for living donor hepatectomy. Liver Transpl. 2012; 18:1188–1197. PMID: 22685084.
Article21. Demirbas T, Bulutcu F, Dayangac M, Yaprak O, Guler N, Oklu L, et al. Which incision is better for living-donor right hepatectomy? Midline, J-shaped, or Mercedes. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45:218–221. PMID: 23375303.
Article22. Liu Q, Liu F, Ding J, Wei Y, Li B. Surgical outcomes and quality of life between laparoscopic and open approach for hepatic hemangioma: a propensity score matching analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98:e14485. PMID: 30732219.23. Buell JF, Thomas MT, Rudich S, Marvin M, Nagubandi R, Ravindra KV, et al. Experience with more than 500 minimally invasive hepatic procedures. Ann Surg. 2008; 248:475–486. PMID: 18791368.
Article24. Kim WJ, Kim KH, Kim SH, Kang WH, Lee SG. Laparoscopic versus open liver resection for centrally located hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a propensity score-matching analysis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2018; 28:394–400. PMID: 30180138.
Article25. Nguyen KT, Gamblin TC, Geller DA. World review of laparoscopic liver resection: 2,804 patients. Ann Surg. 2009; 250:831–841. PMID: 19801936.26. Topal B, Fieuws S, Aerts R, Vandeweyer H, Penninckx F. Laparoscopic versus open liver resection of hepatic neoplasms: comparative analysis of short-term results. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:2208–2213. PMID: 18622562.
Article27. Yoon YI, Kim KH, Kang SH, Kim WJ, Shin MH, Lee SK, et al. Pure laparoscopic versus open right hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a propensity score matched analysis. Ann Surg. 2017; 265:856–863. PMID: 27849661.28. Artinyan A, Nunoo-Mensah JW, Balasubramaniam S, Gauderman J, Essani R, Gonzalez-Ruiz C, et al. Prolonged postoperative ileus: definition, risk factors, and predictors after surgery. World J Surg. 2008; 32:1495–1500. PMID: 18305994.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Single Center Experience for a Feasibility of Totally Laparoscopic Living Donor Right Hepatectomy
- Laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy
- Pure laparoscopic donor right hepatectomy for adult living donor liver transplantation: initial report from Southeast Asia liver transplant center
- Complete transition from open to laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy: 8-year experience with more than 500 laparoscopy cases
- Successful implementation of pure laparoscopic right donor hepatectomy in a small center with limited experience: the role of proctorship program