Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Mar;26(1):24-30. 10.6065/apem.2040022.011.
A cell function study on calcium regulation of a novel calcium-sensing receptor mutation (p.Tyr825Phe)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 2Laboratory Animal Center, Daegu-Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation (DGMIF), Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2514149
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2040022.011
Abstract
- Purpose
Autosomal dominant hypocalcemia with hypercalciuria is a genetic disease characterized by hypoparathyroidism with hypercalciuria. We discovered a novel variant (p.Tyr825Phe[Y825F]) of the CASR gene in a neonate with congenital hypoparathyroidism and hypercalciuria and conducted a cell function study to determine whether the CASR-Y825F variant was pathogenic.
Methods
To perform a functional study on CaSR-Y825F, we constructed expression vectors expressing wild-type (WT) CASR and CASR-Y825F. After transfection of each expression vector into HEK293 cells, we examined alterations in intracellular signaling. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling activity of HEK293 cells expressing CASR-WT or CASR-Y825F was determined. Changes in intracellular calcium ions ([Ca2+]i) by extracellular calcium ion ([Ca2+]e) stimulation were quantitatively compared and analyzed.
Results
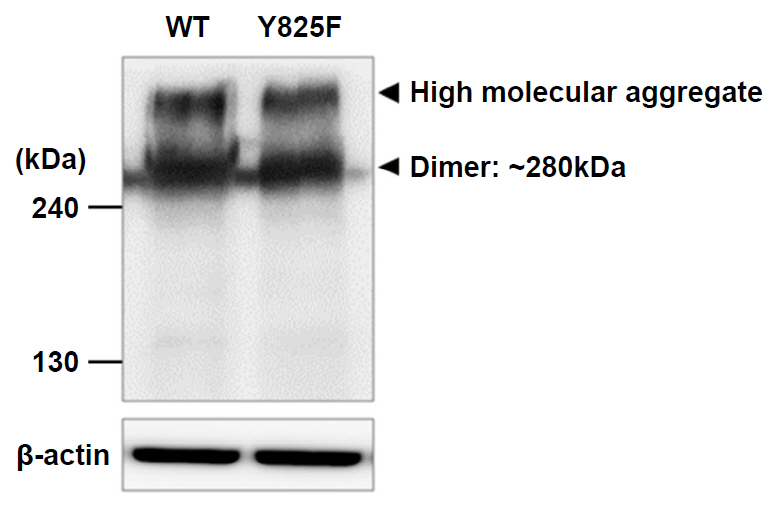
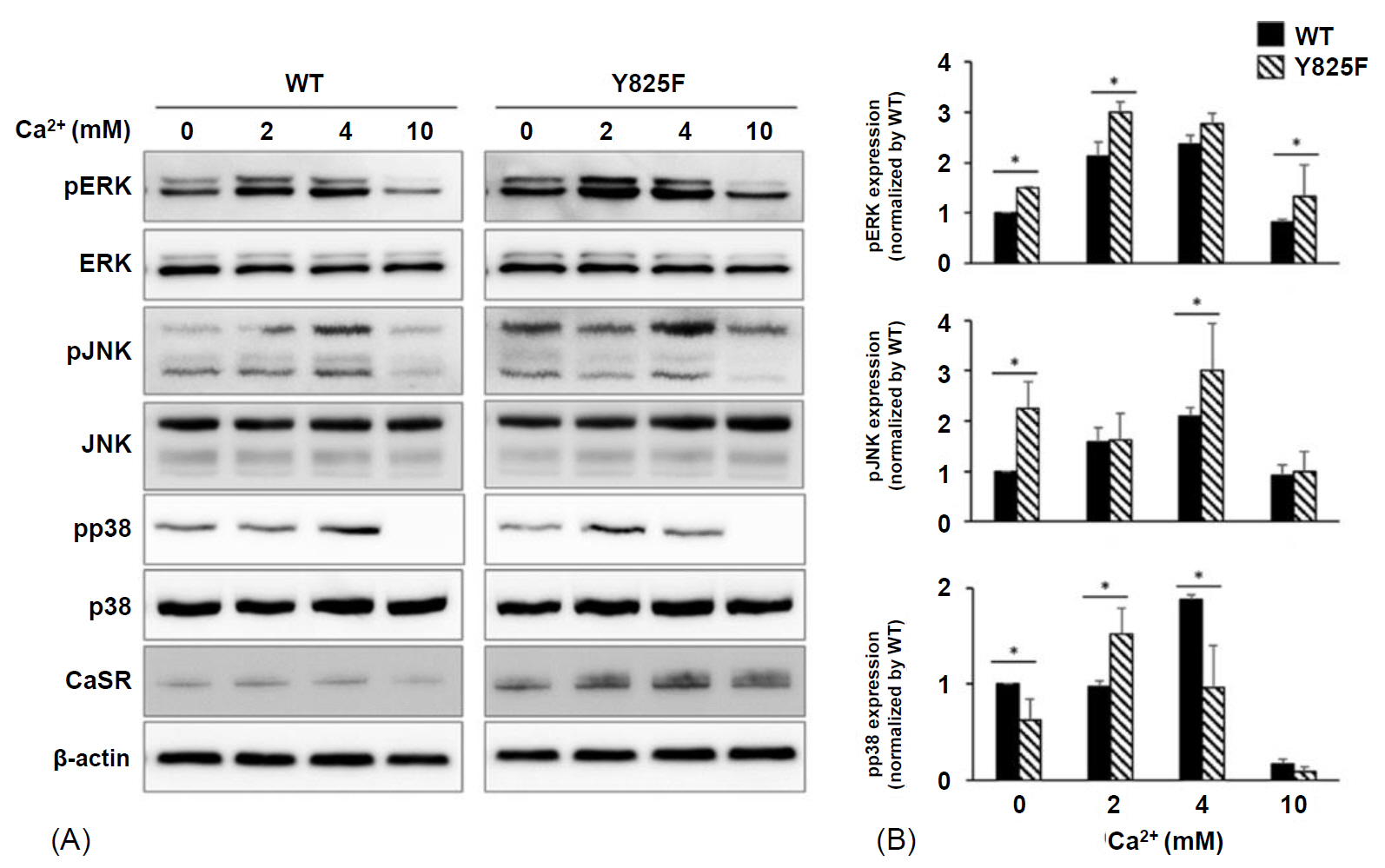
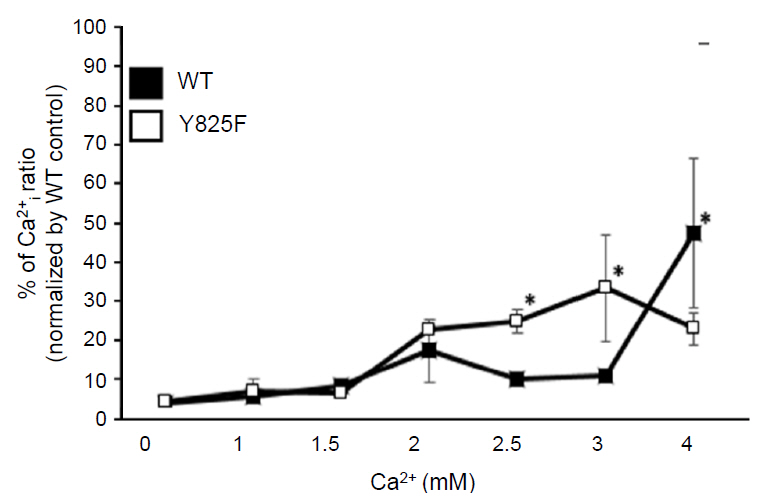
Cells expressing CASR-Y825F showed elevated of MAPK signaling (phospho-ERK [pERK], phospho-JNK [pJNK], phospho-p38 [pp38]) and increased [Ca2+]i levels at low [Ca2+]e stimulation compared with cells expressing CASR-WT. Additionally, [Ca2+]i levels in HEK293 cells expression CASR-WT and CASR-Y825F were determined at 340 nm/380 nm wavelength ratios using Fura-2 AM. At [Ca2+]e concentrations of 2.5 mM and 3 mM, the ratios of CASR-Y825F cells were higher (2.6 and 3.5, respectively) than those of CASR-WT cells (1.04 and 1.40, respectively).
Conclusion
This cell function study proved that the CASR-Y825F expressed in HEK293 cells elevated MAPK signaling (pERK, pJNK, pp38) and increased [Ca2+]i to induce hypocalcemia.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Pollak MR, Brown EM, Estep HL, McLaine PN, Kifor O, Park J, et al. Autosomal dominant hypocalcaemia caused by a Ca2+-sensing receptor gene mutation. Nat Genet. 1994; 83:303–7.
Article2. D'Souza-Li L, Yang B, Canaff L, Bai M, Hanley DA, Bastepe M, et al. Identification and functional characterization of novel calcium-sensing receptor mutations in familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:1309–18.3. Janicic N, Soliman E, Pausova Z, Seldin MF, Riviere M, Szpirer J, et al. Mapping of the calcium-sensing receptor gene (CASR) to human chromosome 3q13. 3-21 by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and localization to rat chromosome 11 and mouse chromosome 16. Mamm Genome. 1995; 6:798–801.
Article4. Choi KH, Shin CH, Yang SW, Cheong HI. Autosomal dominant hypocalcemia with Bartter syndrome due to a novel activating mutation of calcium sensing receptor, Y829C. Korean J Pediatr. 2015; 58:148–53.
Article5. Jianxin Hu, Allen M. Spiegel. Structure and function of the human calcium-sensing receptor: insights from natural and engineered mutations and allosteric modulators. J Cell Mol Med. 2007; 11:908–22.6. Hendy GN, D'Souza-Li L, Yang B, Canaff L, Cole DE. Mutations of the calcium-sensing receptor (CASR) in familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism, and autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. Hum Mutat. 2000; 16:281–96.
Article7. Hofer AM, Brown EM. Calcium: extracellular calcium sensing and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 4:530–8.8. Brown EM. Clinical lessons from the calcium-sensing receptor. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2007; 3:122.
Article9. Hannan FM, Nesbit MA, Zhang C, Cranston T, Curley AJ, Harding B, et al. Identification of 70 calcium-sensing receptor mutations in hyper-and hypo-calcaemic patients: evidence for clustering of extracellular domain mutations at calcium-binding sites. Hum Mol Genet. 2012; 21:2768–78.10. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Medical Genetics and Human Variation [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): NCBI;[cited 2018 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/variation.11. Thakker RV. Diseases associated with the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor. Cell calcium. 2004; 35:275–82.
Article12. Moon JE, Lee SJ, Park SH, Kim JS, Jin DK, Ko CW. De novo a novel variant of CASR gene in a neonate with congenital hypoparathyroidism. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 23:107–11.
Article13. Baran N, ter Braak M, Saffrich R, Woelfle J, Schmitz U. Novel activating mutation of human calcium-sensing receptor in a family with autosomal dominant hypocalcaemia. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015; 407:18–25.
Article14. Arora NK, Paul VK, Singh M. Morbidity and mortality in term infants with intrauterine growth retardation. J Trop Pediatr. 1987; 33:186–9.
Article15. Tsang RC, Chen I, Hayes W, Atkinson W, Atherton H, Edwards N. Neonatal hypocalcemia in infants with birth asphyxia. J Pediatr. 1974; 84:428–33.
Article16. Arthur JM, Lawrence MS, Payne CR, Rane MJ, McLeish KR. The calcium-sensing receptor stimulates JNK in MDCK cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 275:538–41.
Article17. Brown EM. Calcium sensing by endocrine cells. Endocr Pathol. 2004; 153:187–219.
Article18. Huang C, Miller RT. The calcium-sensing receptor and its interacting proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 2007; 11:923–34.
Article19. Chattopadhyay N, Yano S, Tfelt-Hansen J, Rooney P, Kanuparthi D, Bandyopadhyay S, et al. Mitogenic action of calcium-sensing receptor on rat calvarial osteoblasts. Endocrinology. 2004; 145:3451–62.
Article20. Pearce SH, Williamson C, Kifor O, Bai M, Coulthard MG, Davies M, et al. A familial syndrome of hypocalcemia with hypercalciuria due to mutations in the calcium-sensing receptor. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335:1115–22.
Article21. Bräuner-Osborne H, Jensen AA, Sheppard PO, O'Hara P, Krogsgaard-Larsen P. The agonist-binding domain of the calcium-sensing receptor is located at the amino-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:18382–6.
Article22. Holstein DM, B erg KA, Leeb-Lundberg LF, Olson MS, Saunders C. Calcium-sensing receptor-mediated ERK1/2 activation requires Gαi2 coupling and dynamin-independent receptor internalization. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:10060–9.
Article23. Kifor O, MacLeod RJ, Diaz R, Bai M, Yamaguchi T, Yao T, et al. Regulation of MAP kinase by calcium-sensing receptor in bovine parathyroid and CaR-transfected HEK293 cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 280:F291–302.
Article24. Handlogten ME, Shiraishi N, Awata H, Huang C, Miller RT. Extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor is a promiscuous divalent cation sensor that responds to lead. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 279:F1083–91.25. Handlogten ME, Huang C, Shiraishi N, Awata H, Miller RT. The Ca2+-sensing receptor activates cytosolic phospholipase A2 via a Gqα-dependent ERK-independent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:13941–8.
Article26. Bai M, Quinn S, Trivedi S, Kifor O, Pearce SH, Pollak MR, et al. Expression and characterization of inactivating and activating mutations in the human Ca2+(o)-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:19537–45.27. Leach K, Wen A, Davey AE, Sexton PM, Conigrave AD, Christopoulos A. Identification of molecular phenotypes and biased signaling induced by naturally occurring mutations of the human calcium-sensing receptor. Endocrinology. 2012; 159:4304–16.
Article28. Zhao XM, Hauache O, Goldsmith PK, Collins R, Spiegel AM. A missense mutation in the seventh transmembrane domain constitutively activates the human Ca2+ receptor. FEBS Lett. 1999; 448:180–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Calcium Sensing Receptor
- A Case Report of Familial Benign Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia: A Mutation in the Calcium-Sensing Receptor Gene
- De novo a novel variant of CaSR gene in a neonate with congenital hypoparathyroidism
- Autosomal Dominant Hypocalcemia Caused by an Activating Mutation of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor Gene: The First Case Report in Korea
- Functional Analysis and Immunochemical Analyses of Ca²⺠Homeostasis-Related Proteins Expression of Glaucoma-Induced Retinal Degeneration in Rats