Trends in Cardiovascular Complications and Mortality among Patients with Diabetes in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 3Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2514081
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0175
Abstract
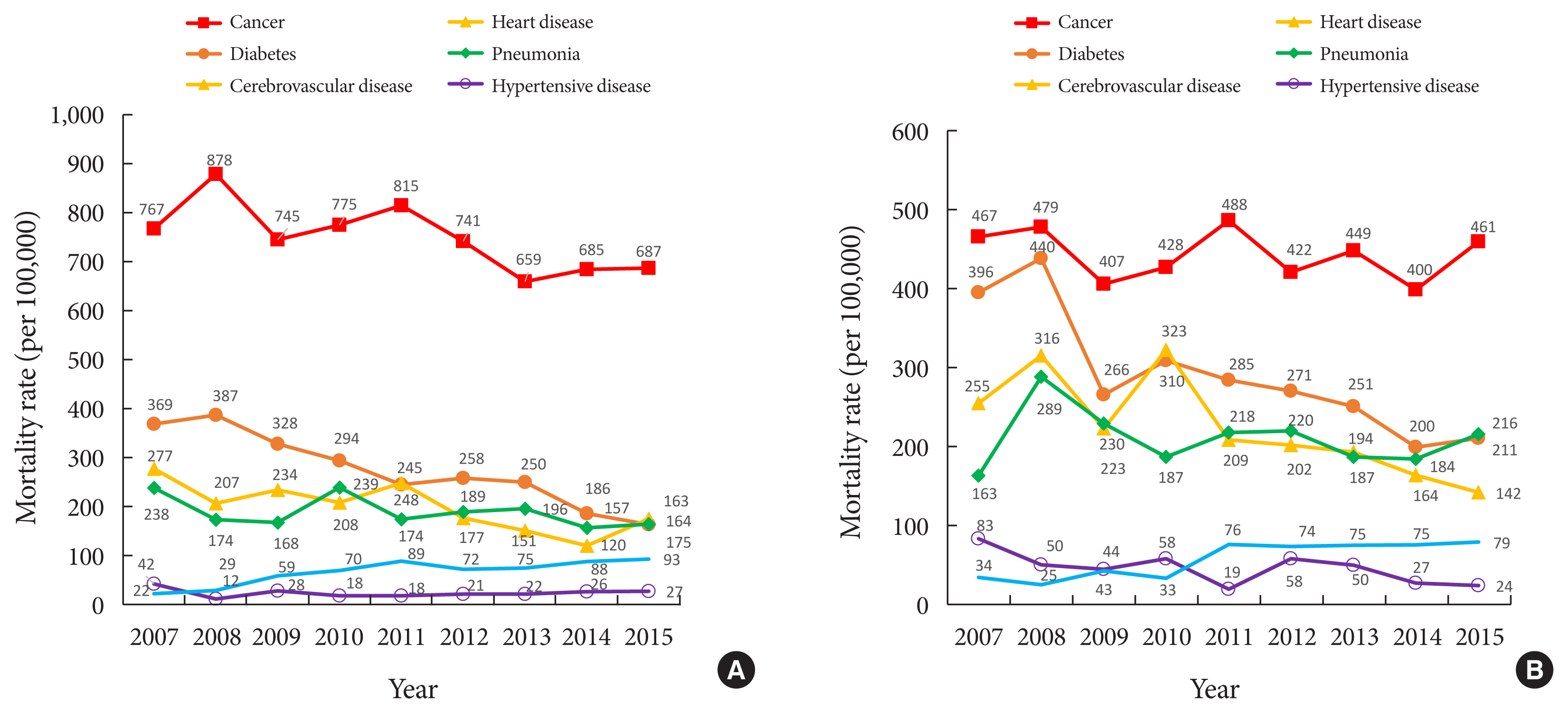
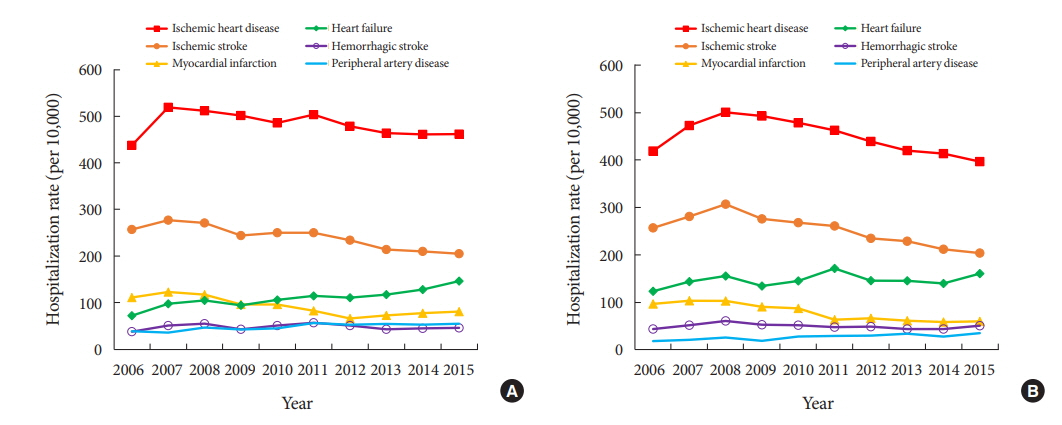
- We investigated the cardiovascular complications and mortality rates of patients with diabetes in South Korea. The rates of hospitalization due to cardiovascular complications and mortality were analyzed using the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort. From 2006 to 2015, the rates of hospitalization due to major cardiovascular complications decreased, while those due to heart failure (from 72 to 146 and 124 to 161 per 10,000 men and women, respectively) and peripheral artery disease (from 39 to 55 and 19 to 35 per 10,000 men and women, respectively) increased. In the period 2007 to 2015, the mortality rates for cancer, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, heart disease, and hypertensive disease all decreased. However, the mortality rate for pneumonia increased. We observed a continuous reduction in cardiovascular complications and mortality in adults with diabetes. However, with the increase in some diabetes complications, more efforts are needed to prevent diabetes complications.
Figure
Cited by 12 articles
-
Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0088.Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):417-426. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0106.Effects of physical activity on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in Korean patients with diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovasc Prev Pharmacother. 2022;4(1):42-55. doi: 10.36011/cpp.2022.4.e3.Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):759-769. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1515.Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):667-674. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0215.Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):543-551. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0209.Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0448.Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):10-26. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0420.The Role of Echocardiography in Evaluating Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Sun Hwa Lee, Jae-Hyeong Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):470-483. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0036.Cardiovascular Disease & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2010 to 2019
Jin Hwa Kim, Junyeop Lee, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Taek Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(6):1084-1092. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0275.Different Associations between Lipid Levels and Risk for Heart Failure according to Diabetes Progression
Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyu Na Lee, Jong-Chan Youn, Hun Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):105-116. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0066.The connection between diabetes mellitus and stroke: a brief review
Junghyun Noh
Cardiovasc Prev Pharmacother. 2025;7(2):55-60. doi: 10.36011/cpp.2025.7.e7.
Reference
-
1. Matheus AS, Tannus LR, Cobas RA, Palma CC, Negrato CA, Gomes MB. Impact of diabetes on cardiovascular disease: an update. Int J Hypertens. 2013; 2013:653789.
Article2. Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzen S, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Miftaraj M, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:1407–18.
Article3. Lee J, Lee JS, Park SH, Shin SA, Kim K. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:e15.
Article4. Jung CH, Chung JO, Han K, Ko SH, Ko KS, Park JY, et al. Improved trends in cardiovascular complications among subjects with type 2 diabetes in Korea: a nationwide study (2006–2013). Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017; 16:1.
Article5. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31:845–50.
Article6. OECD. Cardiovascular disease and diabetes: policies for better health and quality of care. Available from: https://www.oecd.org/publications/cardiovascular-disease-and-diabetes-policies-for-better-health-and-quality-of-care-9789264233010-en.htm(cited 2020 Oct 26).7. Chang Y, Kang HY, Lim D, Cho HJ, Khang YH. Long-term trends in smoking prevalence and its socioeconomic inequalities in Korea, 1992–2016. Int J Equity Health. 2019; 18:148.
Article8. Kang SH, Kim SH, Cho JH, Yoon CH, Hwang SS, Lee HY, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in Korea. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:10970.
Article9. Son M, Yun JW. Cancer mortality projections in Korea up to 2032. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:892–901.
Article10. Canto JG, Kiefe CI, Rogers WJ, Peterson ED, Frederick PD, French WJ, et al. Number of coronary heart disease risk factors and mortality in patients with first myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2011; 306:2120–7.
Article11. Chen J, Normand SL, Wang Y, Krumholz HM. National and regional trends in heart failure hospitalization and mortality rates for Medicare beneficiaries, 1998–2008. JAMA. 2011; 306:1669–78.
Article12. Kim RB, Kim HS, Kang DR, Choi JY, Choi NC, Hwang S, et al. The trend in incidence and case-fatality of hospitalized acute myocardial infarction patients in Korea, 2007 to 2016. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34:e322.
Article13. Youn JC, Han S, Ryu KH. Temporal trends of hospitalized patients with heart failure in Korea. Korean Circ J. 2017; 47:16–24.
Article14. Lee JH, Lim NK, Cho MC, Park HY. Epidemiology of heart failure in Korea: present and future. Korean Circ J. 2016; 46:658–64.
Article15. Song P, Rudan D, Zhu Y, Fowkes FJI, Rahimi K, Fowkes FGR, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2015: an updated systematic review and analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019; 7:e1020–30.
Article16. Kim J, Chun DI, Kim S, Yang HJ, Kim JH, Cho JH, et al. Trends in lower limb amputation in patients with diabetic foot based on vascular intervention of peripheral arterial disease in Korea: a population-based nationwide study. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34:e178.
Article17. Park YY, Joh JH, Han SA, Kim SH, Cho S, Park HC, et al. National trends for the treatment of peripheral arterial disease in Korea between 2004 and 2013. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 89:319–24.
Article18. Kim EJ, Ha KH, Kim DJ, Choi YH. Diabetes and the risk of infection: a national cohort study. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:804–14.
Article19. Koh GC, Peacock SJ, van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ. The impact of diabetes on the pathogenesis of sepsis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:379–88.
Article20. van Vught LA, Wiewel MA, Klein Klouwenberg PM, Hoogendijk AJ, Scicluna BP, Ong DS, et al. Admission hyperglycemia in critically ill sepsis patients: association with outcome and host response. Crit Care Med. 2016; 44:1338–46.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ten-Year Mortality Trends for Adults with and without Diabetes Mellitus in South Korea, 2003 to 2013
- Trends in Cardiovascular Complications and Mortality among Patients with Diabetes in South Korea
- Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of End-Stage Kidney Disease in South Korea
- Treatment Strategy for Diabetes with Cardiovascular Disease
- Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Safety