Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Feb;77(2):84-87. 10.4166/kjg.2020.154.
Cap-assisted Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Rectal Perineurioma Mimicking a Neuroendocrine Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Departments of Pathology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2513418
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.154
Abstract
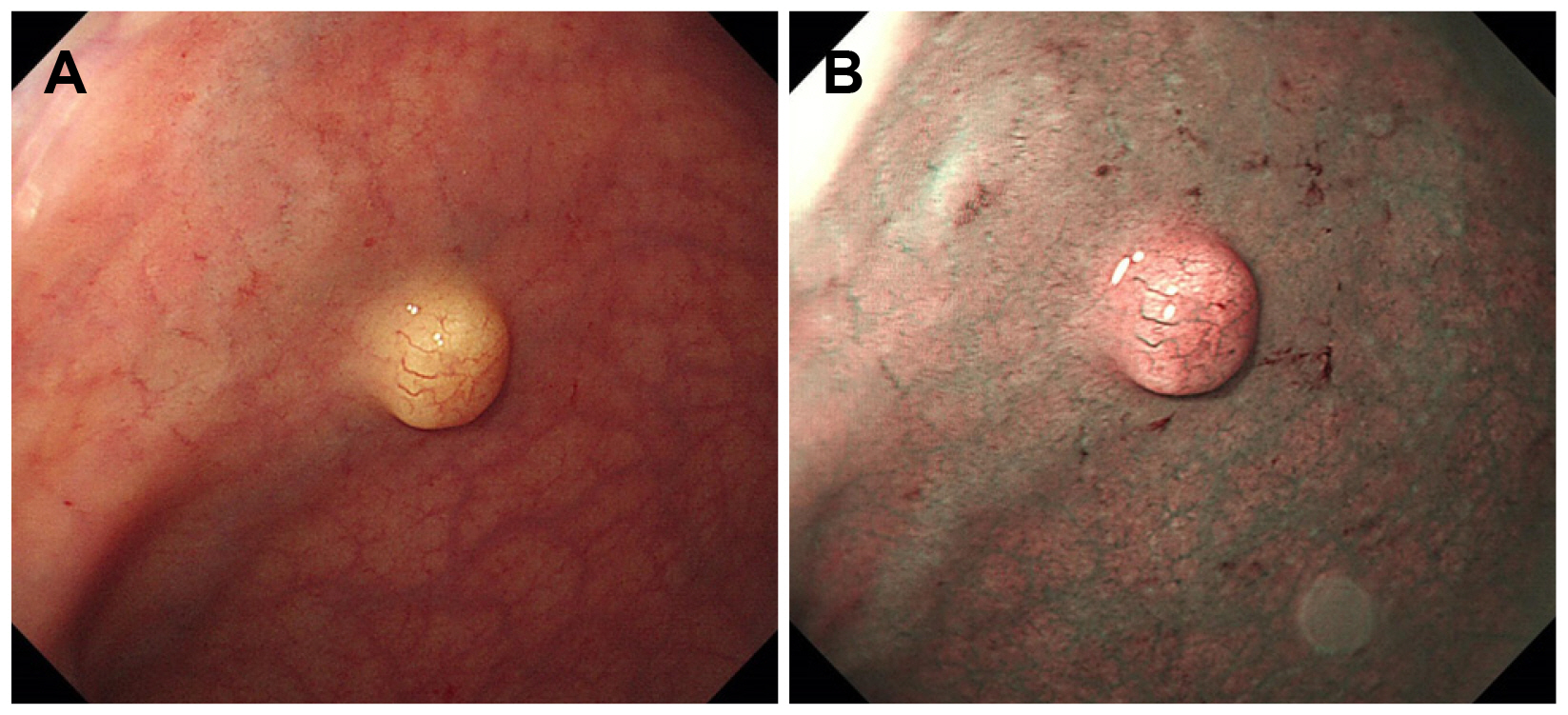
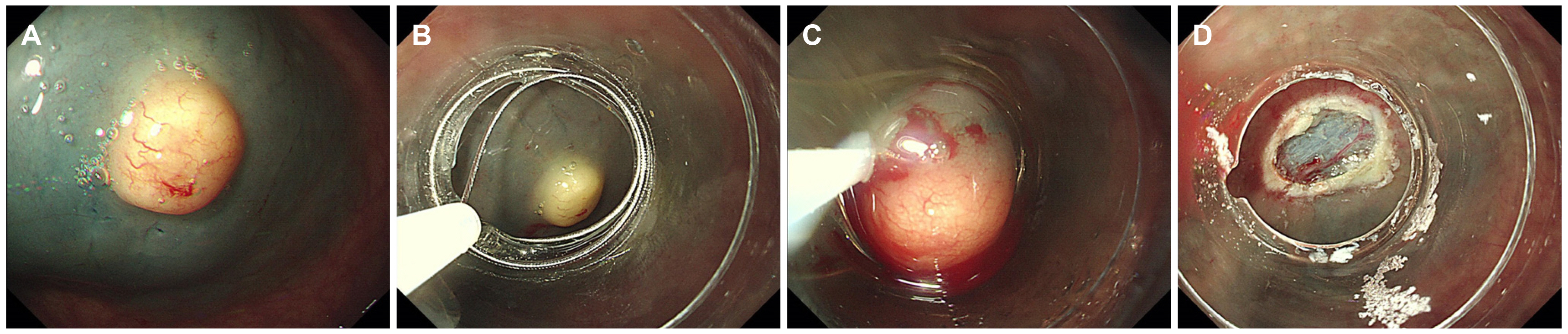
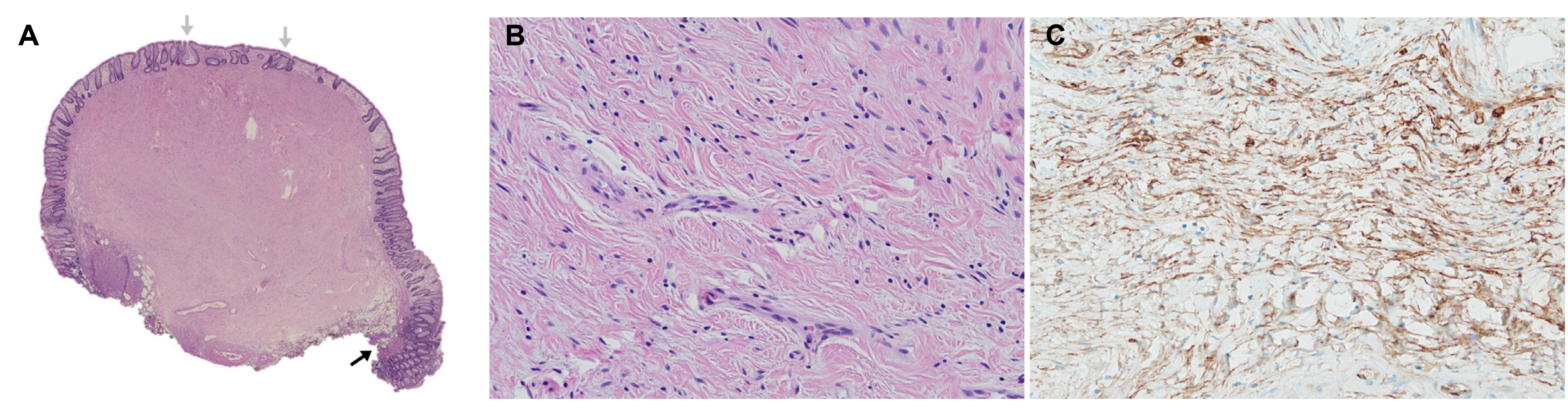
- Colorectal perineuriomas are benign mucosal-based mesenchymal tumors composed of perineurial cells and show serrated or hyperplastic crypts in epithelium on histopathological evaluation. Most perineuriomas are usually presented as sessile polyps and often as subepithelial tumors. In this case, colonoscopy revealed a rectal subepithelial tumor (measuring approximately 7 mm) with yellowish-colored normal mucosa. A rectal neuroendocrine tumor was suspected, and cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection was performed. Histopathological examination of the resected specimen revealed bland spindle cells showing immunopositivity for CD34. The patient was finally diagnosed with rectal perineurioma
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eslami-Varzaneh F, Washington K, Robert ME, Kashgarian M, Goldblum JR, Jain D. 2004; Benign fibroblastic polyps of the colon: a histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study. Am J Surg Pathol. 28:374–378. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-200403000-00010. PMID: 15104300.2. van Wyk AC, van Zyl H, Rigby J. 2018; Colonic perineurioma (benign fibroblastic polyp): case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. 13:16. DOI: 10.1186/s13000-018-0694-z. PMID: 29463272. PMCID: PMC5819702.
Article3. Fujino Y, Muguruma N, Kitamura S, et al. 2014; Perineurioma in the sigmoid colon diagnosed and treated by endoscopic resection. Clin J Gastroenterol. 7:392–396. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-014-0519-x. PMID: 26184017.
Article4. Groisman GM, Polak-Charcon S. 2008; Fibroblastic polyp of the colon and colonic perineurioma: 2 names for a single entity? Am J Surg Pathol. 32:1088–1094. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318160df3f. PMID: 18520438.
Article5. Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. 2005; Intestinal perineuriomas: clinicopathologic definition of a new anatomic subset in a series of 10 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:859–865. DOI: 10.1097/01.pas.0000154130.87219.2c. PMID: 15958849.6. Agaimy A, Stoehr R, Vieth M, Hartmann A. 2010; Benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineuriomas are true mixed epithelial-stromal polyps (hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma) with frequent BRAF mutations. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:1663–1671. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f4a458. PMID: 20962618.
Article7. Groisman GM, Hershkovitz D, Vieth M, Sabo E. 2013; Colonic perineuriomas with and without crypt serration: a comparative study. Am J Surg Pathol. 37:745–751. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318277a1a9. PMID: 23588369.8. McCarthy AJ, Karamchandani DM, Chetty R. 2018; Neural and neurogenic tumours of the gastroenteropancreaticobiliary tract. J Clin Pathol. 71:565–578. DOI: 10.1136/jclinpath-2017-204895. PMID: 29419412.
Article9. Kolli S, Gujjula S, Ona MA. 2019; Colonic perineurioma's malignant proximity to serrated colonic polyps. Cureus. 11:e4815. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.4815. PMID: 31404377. PMCID: PMC6682396.
Article10. Jama GM, Evans M, Fazal MW, Singh-Ranger D. 2018; Perineurioma of the sigmoid colon. BMJ Case Rep. 2018:bcr2018227170. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-227170. PMID: 30262546. PMCID: PMC6169695.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Treatment Outcome of Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors Removed by Ligation-assisted Endoscopic Submucosal Resection
- Endoscopic treatment for rectal neuroendocrine tumor: which method is better?
- Tips and Tricks for Better Endoscopic Treatment of Colorectal Tumors: Usefulness of Cap and Band in Colorectal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Recurrence after endoscopic resection of small rectal neuroendocrine tumors: a retrospective cohort study
- Three Cases of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Rectal Carcinoid Tumor by Band Ligation and the Snare Resection Technique