Can Habitual Exercise Help Reduce Serum Concentrations of Lipophilic Chemical Mixtures? Association between Physical Activity and Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Department of Biomedical Science, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Division of Epidemiology and Community Health, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA.
- KMID: 2513037
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0158
Abstract
Background Low-dose persistent organic pollutants (POPs), especially organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), have emerged as a new risk factor of many chronic diseases. As serum concentrations of POPs in humans are mainly determined by both their release from adipose tissue to circulation and their elimination from circulation, management of these internal pathways may be important in controlling the serum concentrations of POPs. As habitual physical activity can increase the elimination of POPs from circulation, we evaluated whether chronic physical activity is related to low serum POP concentrations.
Methods A cross-sectional study of 1,850 healthy adults (age ≥20 years) without cardio-metabolic diseases who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999 to 2004 was conducted. Information on moderate or vigorous leisure-time physical activity was obtained based on questionnaires. Serum concentrations of OCPs and polychlorinated biphenyls were investigated as typical POPs.
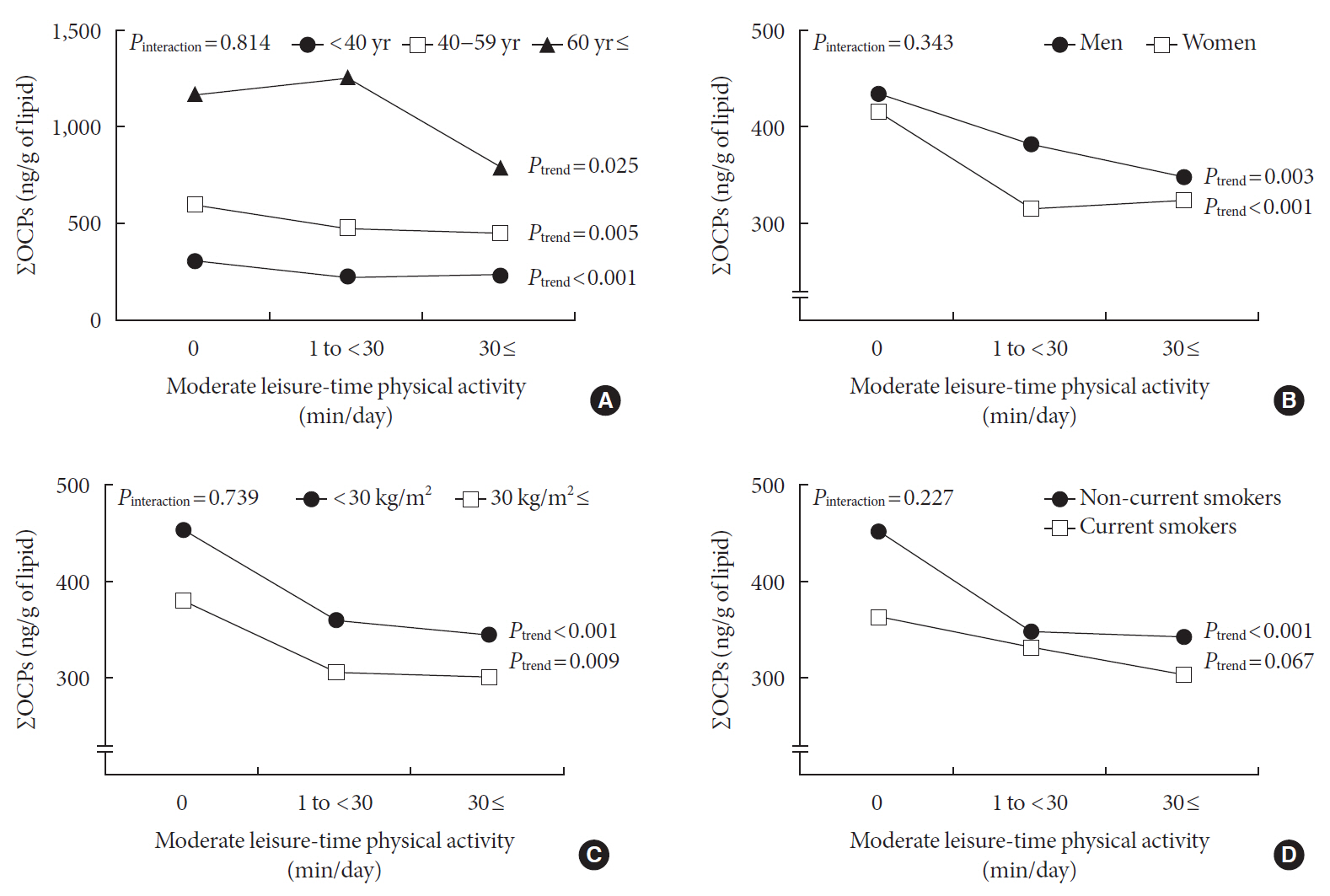
Results Serum concentrations of OCPs among physically active subjects were significantly lower than those among physically inactive subjects (312.8 ng/g lipid vs. 538.0 ng/g lipid,
P <0.001). This difference was maintained after adjustment for potential confounders. When analyses were restricted to physically active subjects, there were small decreases in the serum concentrations of OCPs with increasing duration of physical activity, showing a curvilinear relationship over the whole range of physical activity (P quadratic <0.001). In analyses stratified by age, sex, body mass index, and smoking status, a strong inverse association was similarly observed among all subgroups.Conclusion Physical activity may assist in decreasing serum concentrations of lipophilic chemical mixtures such as OCPs.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Can Environmental Pollutants Be a Factor Linking Obesity and COVID-19?
Duk-Hee Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(43):e305. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e305.
Reference
-
1. Lee DH, Porta M, Jacobs DR Jr, Vandenberg LN. Chlorinated persistent organic pollutants, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2014; 35:557–601.
Article2. Ruzzin J, Lee DH, Carpenter DO, Jacobs DR Jr. Reconsidering metabolic diseases: the impacts of persistent organic pollutants. Atherosclerosis. 2012; 224:1–3.
Article3. Lee DH, Jacobs DR Jr, Park HY, Carpenter DO. A role of low dose chemical mixtures in adipose tissue in carcinogenesis. Environ Int. 2017; 108:170–175.
Article4. Lee DH, Porta M, Lind L, Lind PM, Jacobs DR Jr. Neurotoxic chemicals in adipose tissue: a role in puzzling findings on obesity and dementia. Neurology. 2018; 90:176–182.5. Lee YM, Jacobs DR Jr, Lee DH. Persistent organic pollutants and type 2 diabetes: a critical review of review articles. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018; 9:712.
Article6. Needham LL, Burse VW, Head SL, Korver MP, McClure PC, Andrews JS Jr, Rowley DL, Sung J, Kahn SE. Adipose tissue/serum partitioning of chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides in humans. Chemosphere. 1990; 20:975–980.
Article7. Lee DH, Jacobs DR Jr. New approaches to cope with possible harms of low-dose environmental chemicals. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2019; 73:193–197.
Article8. Lee YM, Kim KS, Jacobs DR Jr, Lee DH. Persistent organic pollutants in adipose tissue should be considered in obesity research. Obes Rev. 2017; 18:129–139.
Article9. Birnbaum LS. The role of structure in the disposition of halogenated aromatic xenobiotics. Environ Health Perspect. 1985; 61:11–20.
Article10. Macdonald TL. Chemical mechanisms of halocarbon metabolism. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1983; 11:85–120.
Article11. Balkau B, Mhamdi L, Oppert JM, Nolan J, Golay A, Porcellati F, Laakso M, Ferrannini E. EGIR-RISC Study Group. Physical activity and insulin sensitivity: the RISC study. Diabetes. 2008; 57:2613–2618.
Article12. Mayer-Davis EJ, D'Agostino R Jr, Karter AJ, Haffner SM, Rewers MJ, Saad M, Bergman RN. Intensity and amount of physical activity in relation to insulin sensitivity: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. JAMA. 1998; 279:669–674.13. Yiamouyiannis CA, Sanders RA, Watkins JB 3rd, Martin BJ. Chronic physical activity: hepatic hypertrophy and increased total biotransformation enzyme activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992; 44:121–127.
Article14. Watkins JB 3rd, Crawford ST, Sanders RA. Chronic voluntary exercise may alter hepatobiliary clearance of endogenous and exogenous chemicals in rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 1994; 22:537–543.15. Genuis SJ, Beesoon S, Birkholz D. Biomonitoring and elimination of perfluorinated compounds and polychlorinated biphenyls through perspiration: blood, urine, and sweat study. ISRN Toxicol. 2013; 2013:483832.
Article16. Genuis SJ, Lane K, Birkholz D. Human elimination of organochlorine pesticides: blood, urine, and sweat study. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:1624643.
Article17. Pelletier C, Despres JP, Tremblay A. Plasma organochlorine concentrations in endurance athletes and obese individuals. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002; 34:1971–1975.
Article18. Imbeault P, Chevrier J, Dewailly E, Ayotte P, Despres JP, Mauriege P, Tremblay A. Increase in plasma pollutant levels in response to weight loss is associated with the reduction of fasting insulin levels in men but not in women. Metabolism. 2002; 51:482–486.
Article19. Jansen A, Lyche JL, Polder A, Aaseth J, Skaug MA. Increased blood levels of persistent organic pollutants (POP) in obese individuals after weight loss: a review. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2017; 20:22–37.20. Curtin LR, Mohadjer LK, Dohrmann SM, Montaquila JM, Kruszan-Moran D, Mirel LB, Carroll MD, Hirsch R, Schober S, Johnson CL. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: sample design, 1999-2006. Vital Health Stat 2. 2012; (155):1–39.21. Centers for Disease Control Prevention/National Center for Health Statistics. Laboratory procedure manual, PCBs and persistent pesticides (lab protocol for NHANES 1999-2000 data). cited 2020 Feb 21. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_03_04/l28_c_met_%20PCBs_and_Persistent_Pesticides.pdf.22. Centers for Disease Control Prevention. How to create new variables to describe leisure-time physical activity. cited 2020 Feb 21. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/tutorials/PhysicalActivity/Preparing/PAQ/Task4_Step2c.htm.23. Phillips DL, Pirkle JL, Burse VW, Bernert JT Jr, Henderson LO, Needham LL. Chlorinated hydrocarbon levels in human serum: effects of fasting and feeding. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1989; 18:495–500.
Article24. Korn EL, Graubard BI. Epidemiologic studies utilizing surveys: accounting for the sampling design. Am J Public Health. 1991; 81:1166–1173.
Article25. Graubard BI, Korn EL. Analyzing health surveys for cancer-related objectives. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999; 91:1005–1016.
Article26. Lee DH, Lee IK, Song K, Steffes M, Toscano W, Baker BA, Jacobs DR Jr. A strong dose-response relation between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and diabetes: results from the National Health and Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:1638–1644.
Article27. Lee DH, Lind L, Jacobs DR Jr, Salihovic S, van Bavel B, Lind PM. Associations of persistent organic pollutants with abdominal obesity in the elderly: the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS) study. Environ Int. 2012; 40:170–178.
Article28. Kim HW, Kim JH, Lee DW, Cho SH, Jung JH, Kim KS, Lee DH. Different associations of albuminuria with total and cardiovascular mortality by concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in the elderly. Environ Res. 2017; 155:175–181.
Article29. Kim SA, Kim KS, Lee YM, Jacobs DR, Lee DH. Associations of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls with total, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality in elders with differing fat mass. Environ Res. 2015; 138:1–7.
Article30. Lee YM, Ha CM, Kim SA, Thoudam T, Yoon YR, Kim DJ, Kim HC, Moon HB, Park S, Lee IK, Lee DH. Low-dose persistent organic pollutants impair insulin secretory function of pancreatic β-cells: human and in vitro evidence. Diabetes. 2017; 66:2669–2680.
Article31. McLachlan AJ, Pont LG. Drug metabolism in older people: a key consideration in achieving optimal outcomes with medicines. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012; 67:175–180.32. Washburn RA, Jette AM, Janney CA. Using age-neutral physical activity questionnaires in research with the elderly. J Aging Health. 1990; 2:341–356.
Article33. Takagi D, Nishida Y, Fujita D. Age-associated changes in the level of physical activity in elderly adults. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015; 27:3685–3687.
Article34. Saponaro C, Gaggini M, Carli F, Gastaldelli A. The subtle balance between lipolysis and lipogenesis: a critical point in metabolic homeostasis. Nutrients. 2015; 7:9453–9474.
Article35. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2008 Physical activity guidelines for Americans: be active, healthy, and happy! cited 2020 Feb 21. Available from: https://health.gov/our-work/physical-activity/previous-guidelines/2008-physical-activity-guidelines.36. Despres JP, Bouchard C, Savard R, Tremblay A, Marcotte M, Theriault G. Level of physical fitness and adipocyte lipolysis in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984; 56:1157–1161.
Article37. Helmerhorst HJ, Brage S, Warren J, Besson H, Ekelund U. A systematic review of reliability and objective criterion-related validity of physical activity questionnaires. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2012; 9:103.
Article38. Skender S, Ose J, Chang-Claude J, Paskow M, Bruhmann B, Siegel EM, Steindorf K, Ulrich CM. Accelerometry and physical activity questionnaires: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2016; 16:515.
Article39. Pedisic Z, Bauman A. Accelerometer-based measures in physical activity surveillance: current practices and issues. Br J Sports Med. 2015; 49:219–223.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Persistent Organic Pollutants and Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction: Focusing on Type 2 Diabetes
- Environmental Pollutant and Cardiovascular Disease
- Mitochondrial Toxins and Healthy Lifestyle Meet at the Crossroad of Hormesis
- Associations between Cigarette Smoking and Total Mortality Differ Depending on Serum Concentrations of Persistent Organic Pollutants among the Elderly
- Interaction Between Persistent Organic Pollutants and C-reactive Protein in Estimating Insulin Resistance Among Non-diabetic Adults