Role of CRTC2 in Metabolic Homeostasis: Key Regulator of Whole-Body Energy Metabolism?
- Affiliations
-
- 0Division of Life Sciences, College of Life Sciences & Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2513010
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0200
Abstract
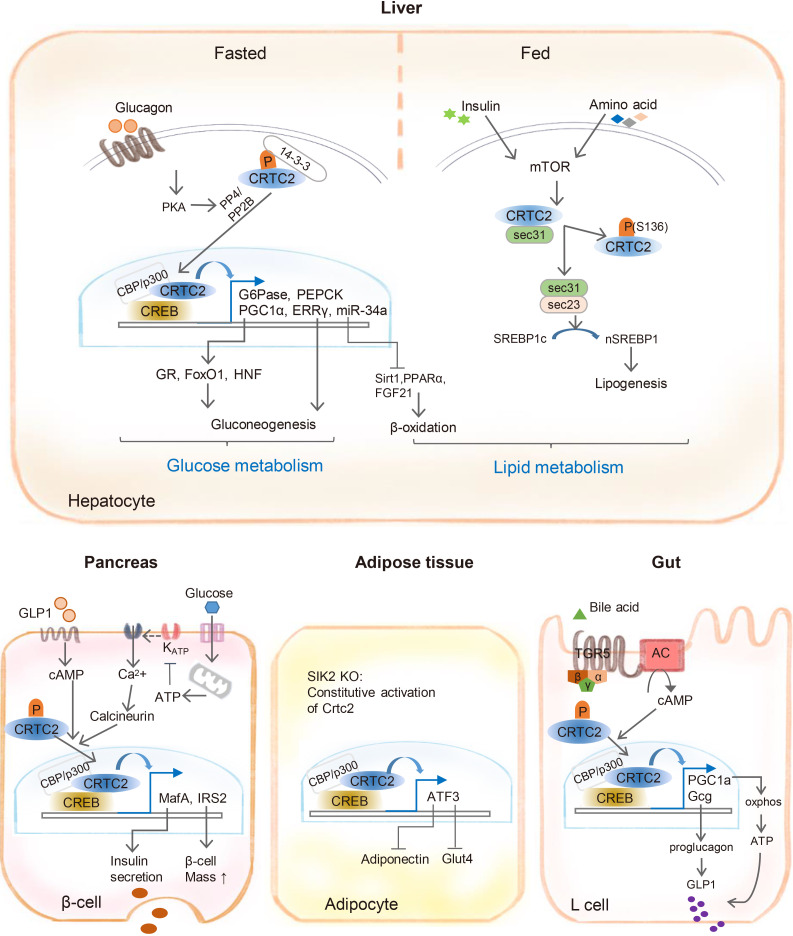
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling is critical for regulating metabolic homeostasis in mammals. In particular, transcriptional regulation by cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and its coactivator, CREB-regulated transcription coactivator (CRTC), is essential for controlling the expression of critical enzymes in the metabolic process, leading to more chronic changes in metabolic flux. Among the CRTC isoforms, CRTC2 is predominantly expressed in peripheral tissues and has been shown to be associated with various metabolic pathways in tissue-specific manners. While initial reports showed the physiological role of CRTC2 in regulating gluconeogenesis in the liver, recent studies have further delineated the role of this transcriptional coactivator in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism in various tissues, including the liver, pancreatic islets, endocrine tissues of the small intestines, and adipose tissues. In this review, we discuss recent studies that have utilized knockout mouse models to delineate the role of CRTC2 in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sako Y, Grill VE. A 48-hour lipid infusion in the rat time-dependently inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion and B cell oxidation through a process likely coupled to fatty acid oxidation. Endocrinology. 1990; 127:1580–1589. PMID: 1698143.
Article2. Gerich JE. Lilly lecture 1988. Glucose counterregulation and its impact on diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1988; 37:1608–1617. PMID: 3056759.
Article3. Cheng X, Ji Z, Tsalkova T, Mei F. Epac and PKA: a tale of two intracellular cAMP receptors. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008; 40:651–662. PMID: 18604457.
Article4. Han HS, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, Koo SH. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp Mol Med. 2016; 48:e218. PMID: 26964834.
Article5. Nielsen TS, Jessen N, Jorgensen JO, Moller N, Lund S. Dissecting adipose tissue lipolysis: molecular regulation and implications for metabolic disease. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014; 52:R199–R222. PMID: 24577718.
Article6. Klingenspor M. Cold-induced recruitment of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Exp Physiol. 2003; 88:141–148. PMID: 12525862.
Article7. Altarejos JY, Montminy M. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011; 12:141–151. PMID: 21346730.
Article8. Oh KJ, Han HS, Kim MJ, Koo SH. CREB and FoxO1: two transcription factors for the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. BMB Rep. 2013; 46:567–574. PMID: 24238363.
Article9. Conkright MD, Canettieri G, Screaton R, Guzman E, Miraglia L, Hogenesch JB, Montminy M. TORCs: transducers of regulated CREB activity. Mol Cell. 2003; 12:413–423. PMID: 14536081.10. Screaton RA, Conkright MD, Katoh Y, Best JL, Canettieri G, Jeffries S, Guzman E, Niessen S, Yates JR 3rd, Takemori H, Okamoto M, Montminy M. The CREB coactivator TORC2 functions as a calcium- and cAMP-sensitive coincidence detector. Cell. 2004; 119:61–74. PMID: 15454081.
Article11. Tonon G, Modi S, Wu L, Kubo A, Coxon AB, Komiya T, O'Neil K, Stover K, El-Naggar A, Griffin JD, Kirsch IR, Kaye FJ. t(11;19)(q21;p13) translocation in mucoepidermoid carcinoma creates a novel fusion product that disrupts a Notch signaling pathway. Nat Genet. 2003; 33:208–213. PMID: 12539049.
Article12. Luo Q, Viste K, Urday-Zaa JC, Senthil Kumar G, Tsai WW, Talai A, Mayo KE, Montminy M, Radhakrishnan I. Mechanism of CREB recognition and coactivation by the CREB-regulated transcriptional coactivator CRTC2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:20865–20870. PMID: 23213254.
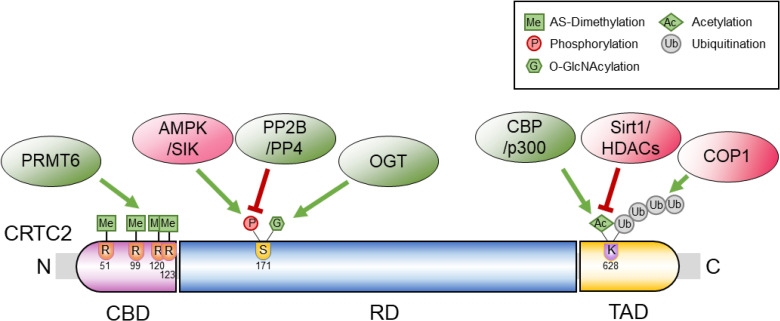
Article13. Han HS, Jung CY, Yoon YS, Choi S, Choi D, Kang G, Park KG, Kim ST, Koo SH. Arginine methylation of CRTC2 is critical in the transcriptional control of hepatic glucose metabolism. Sci Signal. 2014; 7:ra19. PMID: 24570487.
Article14. Koo SH, Flechner L, Qi L, Zhang X, Screaton RA, Jeffries S, Hedrick S, Xu W, Boussouar F, Brindle P, Takemori H, Montminy M. The CREB coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting glucose metabolism. Nature. 2005; 437:1109–1111. PMID: 16148943.
Article15. Wang Y, Li G, Goode J, Paz JC, Ouyang K, Screaton R, Fischer WH, Chen J, Tabas I, Montminy M. Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes. Nature. 2012; 485:128–132. PMID: 22495310.
Article16. Yoon YS, Lee MW, Ryu D, Kim JH, Ma H, Seo WY, Kim YN, Kim SS, Lee CH, Hunter T, Choi CS, Montminy MR, Koo SH. Suppressor of MEK null (SMEK)/protein phosphatase 4 catalytic subunit (PP4C) is a key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:17704–17709. PMID: 20876121.
Article17. Dentin R, Hedrick S, Xie J, Yates J 3rd, Montminy M. Hepatic glucose sensing via the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Science. 2008; 319:1402–1405. PMID: 18323454.
Article18. Liu Y, Dentin R, Chen D, Hedrick S, Ravnskjaer K, Schenk S, Milne J, Meyers DJ, Cole P, Yates J 3rd, Olefsky J, Guarente L, Montminy M. A fasting inducible switch modulates gluconeogenesis via activator/coactivator exchange. Nature. 2008; 456:269–273. PMID: 18849969.
Article19. Ravnskjaer K, Hogan MF, Lackey D, Tora L, Dent SY, Olefsky J, Montminy M. Glucagon regulates gluconeogenesis through KAT2B- and WDR5-mediated epigenetic effects. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:4318–4328. PMID: 24051374.
Article20. Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocr Rev. 2003; 24:78–90. PMID: 12588810.21. Kim DK, Ryu D, Koh M, Lee MW, Lim D, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Cho WJ, Lee CH, Park SB, Koo SH, Choi HS. Orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ) is key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:21628–21639. PMID: 22549789.
Article22. Saberi M, Bjelica D, Schenk S, Imamura T, Bandyopadhyay G, Li P, Jadhar V, Vargeese C, Wang W, Bowman K, Zhang Y, Polisky B, Olefsky JM. Novel liver-specific TORC2 siRNA corrects hyperglycemia in rodent models of type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 297:E1137–E1146. PMID: 19706791.
Article23. Le Lay J, Tuteja G, White P, Dhir R, Ahima R, Kaestner KH. CRTC2 (TORC2) contributes to the transcriptional response to fasting in the liver but is not required for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009; 10:55–62. PMID: 19583954.
Article24. Wang Y, Inoue H, Ravnskjaer K, Viste K, Miller N, Liu Y, Hedrick S, Vera L, Montminy M. Targeted disruption of the CREB coactivator Crtc2 increases insulin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:3087–3092. PMID: 20133702.
Article25. Han HS, Choi BH, Kim JS, Kang G, Koo SH. Hepatic Crtc2 controls whole body energy metabolism via a miR-34a-Fgf21 axis. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:1878. PMID: 29192248.
Article26. Han J, Li E, Chen L, Zhang Y, Wei F, Liu J, Deng H, Wang Y. The CREB coactivator CRTC2 controls hepatic lipid metabolism by regulating SREBP1. Nature. 2015; 524:243–246. PMID: 26147081.
Article27. Li Y, Song Y, Zhao M, Guo Y, Yu C, Chen W, Shao S, Xu C, Zhou X, Zhao L, Zhang Z, Bo T, Xia Y, Proud CG, Wang X, Wang L, Zhao J, Gao L. A novel role for CRTC2 in hepatic cholesterol synthesis through SREBP-2. Hepatology. 2017; 66:481–497. PMID: 28395113.
Article28. Eberhard CE, Fu A, Reeks C, Screaton RA. CRTC2 is required for β-cell function and proliferation. Endocrinology. 2013; 154:2308–2317. PMID: 23677932.
Article29. Blanchet E, Van de Velde S, Matsumura S, Hao E, LeLay J, Kaestner K, Montminy M. Feedback inhibition of CREB signaling promotes beta cell dysfunction in insulin resistance. Cell Rep. 2015; 10:1149–1157. PMID: 25704817.
Article30. Drucker DJ. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006; 3:153–165. PMID: 16517403.
Article31. Drucker DJ. The role of gut hormones in glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:24–32. PMID: 17200703.
Article32. Hirasawa A, Tsumaya K, Awaji T, Katsuma S, Adachi T, Yamada M, Sugimoto Y, Miyazaki S, Tsujimoto G. Free fatty acids regulate gut incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through GPR120. Nat Med. 2005; 11:90–94. PMID: 15619630.
Article33. Katsuma S, Hirasawa A, Tsujimoto G. Bile acids promote glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through TGR5 in a murine enteroendocrine cell line STC-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 329:386–390. PMID: 15721318.
Article34. Thomas C, Gioiello A, Noriega L, Strehle A, Oury J, Rizzo G, Macchiarulo A, Yamamoto H, Mataki C, Pruzanski M, Pellicciari R, Auwerx J, Schoonjans K. TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009; 10:167–177. PMID: 19723493.
Article35. Lee JH, Wen X, Cho H, Koo SH. CREB/CRTC2 controls GLP-1-dependent regulation of glucose homeostasis. FASEB J. 2018; 32:1566–1578. PMID: 29118086.
Article36. Muraoka M, Fukushima A, Viengchareun S, Lombes M, Kishi F, Miyauchi A, Kanematsu M, Doi J, Kajimura J, Nakai R, Uebi T, Okamoto M, Takemori H. Involvement of SIK2/TORC2 signaling cascade in the regulation of insulin-induced PGC-1alpha and UCP-1 gene expression in brown adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 296:E1430–E1439. PMID: 19351809.37. Qi L, Saberi M, Zmuda E, Wang Y, Altarejos J, Zhang X, Dentin R, Hedrick S, Bandyopadhyay G, Hai T, Olefsky J, Montminy M. Adipocyte CREB promotes insulin resistance in obesity. Cell Metab. 2009; 9:277–286. PMID: 19254572.
Article38. Park J, Yoon YS, Han HS, Kim YH, Ogawa Y, Park KG, Lee CH, Kim ST, Koo SH. SIK2 is critical in the regulation of lipid homeostasis and adipogenesis in vivo. Diabetes. 2014; 63:3659–3673. PMID: 24898145.
Article39. Wang Y, Vera L, Fischer WH, Montminy M. The CREB coactivator CRTC2 links hepatic ER stress and fasting gluconeogenesis. Nature. 2009; 460:534–537. PMID: 19543265.
Article40. Lee MW, Chanda D, Yang J, Oh H, Kim SS, Yoon YS, Hong S, Park KG, Lee IK, Choi CS, Hanson RW, Choi HS, Koo SH. Regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis by an ER-bound transcription factor, CREBH. Cell Metab. 2010; 11:331–339. PMID: 20374965.
Article41. Altarejos JY, Goebel N, Conkright MD, Inoue H, Xie J, Arias CM, Sawchenko PE, Montminy M. The Creb1 coactivator Crtc1 is required for energy balance and fertility. Nat Med. 2008; 14:1112–1117. PMID: 18758446.
Article42. Saura CA, Cardinaux JR. Emerging roles of CREB-regulated transcription coactivators in brain physiology and pathology. Trends Neurosci. 2017; 40:720–733. PMID: 29097017.
Article43. Song Y, Altarejos J, Goodarzi MO, Inoue H, Guo X, Berdeaux R, Kim JH, Goode J, Igata M, Paz JC, Hogan MF, Singh PK, Goebel N, Vera L, Miller N, Cui J, Jones MR, Chen YD, Taylor KD, Hsueh WA, Rotter JI, Montminy M. CHARGE Consortium. CRTC3 links catecholamine signalling to energy balance. Nature. 2010; 468:933–939. PMID: 21164481.
Article44. Yoon YS, Tsai WW, Van de Velde S, Chen Z, Lee KF, Morgan DA, Rahmouni K, Matsumura S, Wiater E, Song Y, Montminy M. cAMP-inducible coactivator CRTC3 attenuates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115:E5289–E5297. PMID: 29784793.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Brain Regulation of Energy Metabolism
- Bone and Energy Metabolism
- Thermogenic Brown Fat in Humans: Implications in Energy Homeostasis, Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
- Emerging role of the brain in the homeostatic regulation of energy and glucose metabolism
- Brown Fat as a Regulator of Systemic Metabolism beyond Thermogenesis