Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2021 Feb;14(1):137-144. 10.21053/ceo.2020.01585.
Initial Experience With Robotic Modified Radical Neck Dissection Using the da Vinci Xi System Through the Bilateral Axillo-Breast Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Inha University Hospital, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Research Institute for Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University and Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2512892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2020.01585
Abstract
Objectives
. The bilateral axillo-breast approach (BABA) to robotic thyroidectomy has been extended to modified radical neck dissection (MRND). This study assessed outcomes in patients who underwent robotic MRND through BABA using the da Vinci Xi system.
Methods
. The medical records of 40 patients who underwent total thyroidectomy, bilateral central neck dissection, and MRND from September 2018 to March 2020 were reviewed retrospectively, including 12 who underwent robotic surgery and 28 who underwent open surgery. All operations were performed by a single endocrine surgeon.
Results
. The operation time was significantly longer in the robotic group than in the open group (277.08±32.64 vs. 191.43± 60.43 minutes, respectively, P<0.01), but the number of retrieved lymph nodes did not differ significantly (32.58± 9.31 vs. 34.54±10.90, respectively, P=0.569). The incidence of transient hypoparathyroidism was significantly lower in the robotic group (16.7% [2/12] vs. 53.6% [15/28], P=0.041). The mean hospital stay was shorter (3.92±0.90 vs. 4.71±1.63 days) and the pain score on the first postoperative day was lower (2.92±0.29 vs. 3.18±0.67) in the robotic group. Six of the 12 patients (50%) in the robotic group had stimulated thyroglobulin levels <1.0 ng/mL.
Conclusion
. Robotic MRND through BABA has several advantages, including excellent cosmetic outcomes and a lower incidence of transient hypoparathyroidism than is the case for open MRND. Robotic MRND through BABA may be a promising surgical approach compared with conventional open MRND.
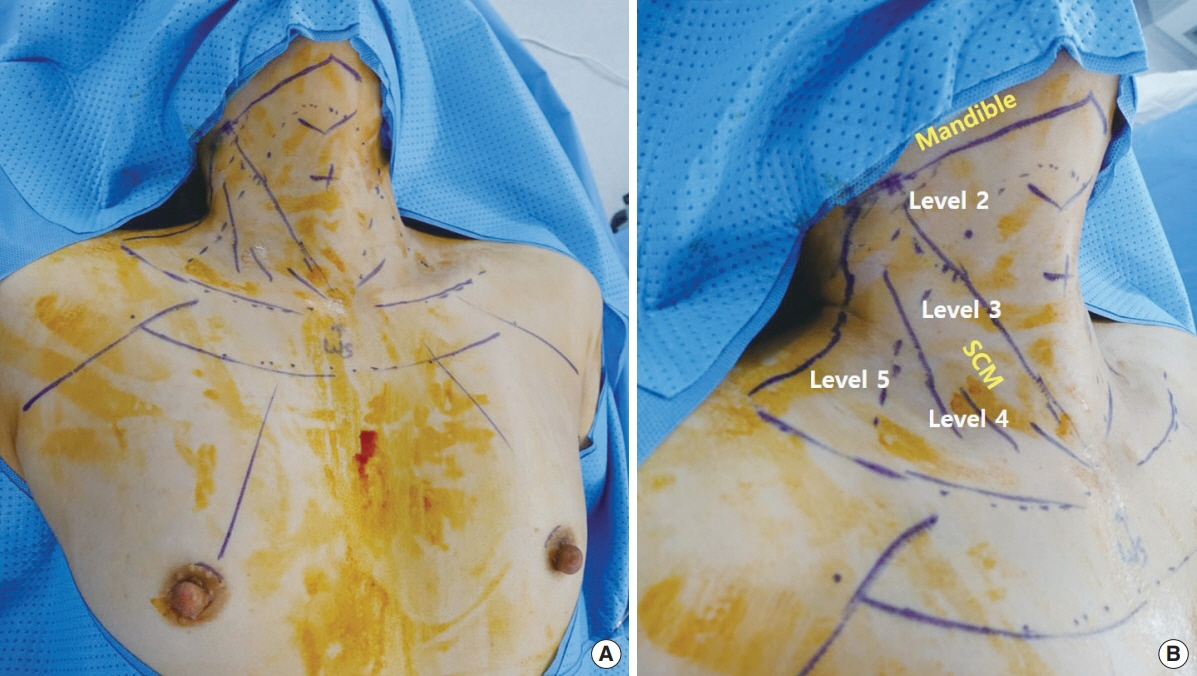
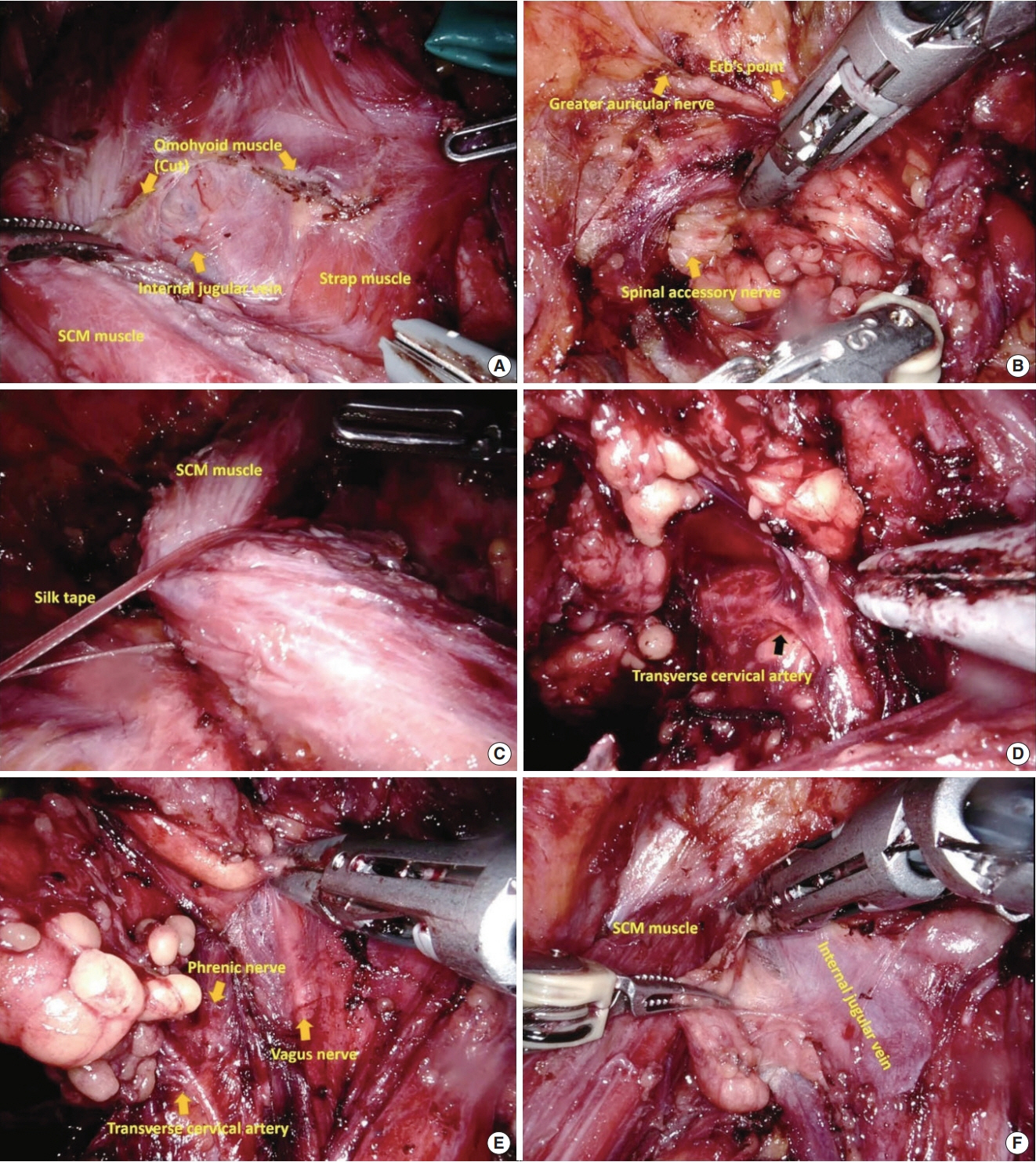
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Robotic Modified Radical Neck Dissection Through the Bilateral Axillary Breast Approach
Yong Tae Hong, Seung Hoon Woo
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;14(1):13-14. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2021.00213.
Reference
-
1. Lee KE, Kim E, Koo do H, Choi JY, Kim KH, Youn YK. Robotic thyroidectomy by bilateral axillo-breast approach: review of 1,026 cases and surgical completeness. Surg Endosc. 2013; Aug. 27(8):2955–62.
Article2. Song J, Yan T, Qiu W, Fan Y, Yang Z. Clinical analysis of risk factors for cervical lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective study of 3686 patients. Cancer Manag Res. 2020; Apr. 12:2523–30.3. Haugen BR. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: what is new and what has changed. Cancer. 2017; Feb. 123(3):372–81.
Article4. Lee KE, Choi JY, Youn YK. Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic thyroidectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2011; Aug. 21(4):230–6.
Article5. Lee KE, Koo do H, Kim SJ, Lee J, Park KS, Oh SK, et al. Outcomes of 109 patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma who underwent robotic total thyroidectomy with central node dissection via the bilateral axillo-breast approach. Surgery. 2010; Dec. 148(6):1207–13.
Article6. Byeon HK, Holsinger FC, Tufano RP, Chung HJ, Kim WS, Koh YW, et al. Robotic total thyroidectomy with modified radical neck dissection via unilateral retroauricular approach. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; Nov. 21(12):3872–5.
Article7. Choi JY, Kang KH. Robotic modified radical neck dissection with bilateral axillo-breast approach. Gland Surg. 2017; Jun. 6(3):243–9.
Article8. Kim K, Kang SW, Chung WY. Robotic-assisted modified radical neck dissection: transaxillary, bilateral axill-breast approach (BABA), Facelift. Curr Surg Rep. 2019; 7:20.
Article9. Kim MJ, Lee J, Lee SG, Choi JB, Kim TH, Ban EJ, et al. Transaxillary robotic modified radical neck dissection: a 5-year assessment of operative and oncologic outcomes. Surg Endosc. 2017; Apr. 31(4):1599–606.
Article10. Lee J, Kwon IS, Bae EH, Chung WY. Comparative analysis of oncological outcomes and quality of life after robotic versus conventional open thyroidectomy with modified radical neck dissection in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma and lateral neck node metastases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; Jul. 98(7):2701–8.
Article11. Paek SH, Lee HA, Kwon H, Kang KH, Park SJ. Comparison of robotassisted modified radical neck dissection using a bilateral axillary breast approach with a conventional open procedure after propensity score matching. Surg Endosc. 2020; Feb. 34(2):622–7.
Article12. Yu HW, Chai YJ, Kim SJ, Choi JY, Lee KE. Robotic-assisted modified radical neck dissection using a bilateral axillo-breast approach (robotic BABA MRND) for papillary thyroid carcinoma with lateral lymph node metastasis. Surg Endosc. 2018; May. 32(5):2322–7.
Article13. Yoon HJ, Ahn JH, Kim JH, Yi JW, Hur MH. Initial experience of BABA robotic thyroidectomy using the da Vinci Xi system in Incheon, Korea. J Endocr Surg. 2019; Sep. 19(3):59–67.
Article14. Juarez MC, Ishii L, Nellis JC, Bater K, Huynh PP, Fung N, et al. Objectively measuring social attention of thyroid neck scars and transoral surgery using eye tracking. Laryngoscope. 2019; Dec. 129(12):2789–94.
Article15. Tan Y, Guo B, Deng X, Ding Z, Wu B, Niu Y, et al. Transoral endoscopic selective lateral neck dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma: a pilot study. Surg Endosc. 2020; 34:5274–82.
Article16. Seup Kim B, Kang KH, Park SJ. Robotic modified radical neck dissection by bilateral axillary breast approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma with lateral neck metastasis. Head Neck. 2015; Jan. 37(1):37–45.
Article17. Yang SC, Ahn JH, Kim JH, Yi JW, Hur MH, Lee KY. Comparison of the vessel sealer Extend® with harmonic ACE® in robotic bilateral axillary-breast approach thyroid surgery. Gland Surg. 2020; Apr. 9(2):164–71.
Article18. Hong YT, Ahn JH, Kim JH, Yi JW, Hong KH. Bi-institutional experience of transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy: challenges and outcomes. Head Neck. 2020; Aug. 42(8):2115–22.
Article19. Duren M, Siperstein AE, Shen W, Duh QY, Morita E, Clark OH. Value of stimulated serum thyroglobulin levels for detecting persistent or recurrent differentiated thyroid cancer in high- and low-risk patients. Surgery. 1999; Jul. 126(1):13–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic total thyroidectomy without isthmectomy: a case report
- Robotic Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection: Description of A Technique
- Initial Experience of BABA Robotic Thyroidectomy Using the Da Vinci Xi System in Incheon, Korea
- The short video lecture for robotic bilateral axillo-breast approach to lateral neck lymph node dissection
- The da Vinci Xi System in Robotic Gastric Cancer Surgery: A Comparison with the S System